Zeroth order logic
☞ This page belongs to resource collections on Logic and Inquiry.
Zeroth order logic is an informal term that is sometimes used to indicate the common principles underlying the algebra of sets, boolean algebra, boolean functions, logical connectives, monadic predicate calculus, propositional calculus, and sentential logic. The term serves to mark a level of abstraction in which the more inessential differences among these subjects can be subsumed under the appropriate isomorphisms.
Propositional forms on two variables
By way of initial orientation, Table 1 lists equivalent expressions for the sixteen functions of concrete type 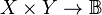 and abstract type
and abstract type 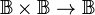 in a number of different languages for zeroth order logic.
in a number of different languages for zeroth order logic.
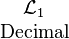 |
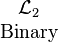 |
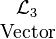 |
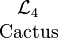 |
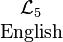 |
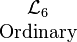 |
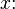 |
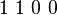 |
||||
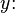 |
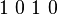 |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
These six languages for the sixteen boolean functions are conveniently described in the following order:
- Language
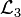 describes each boolean function
describes each boolean function 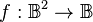 by means of the sequence of four boolean values,
by means of the sequence of four boolean values, 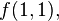
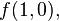
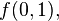
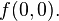 Such a sequence, perhaps in another order, and perhaps with the logical values
Such a sequence, perhaps in another order, and perhaps with the logical values 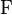 and
and 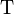 instead of the boolean values
instead of the boolean values 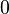 and
and 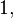 respectively, would normally be displayed as a column in a truth table.
respectively, would normally be displayed as a column in a truth table.
- Language
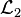 lists the sixteen functions in the form
lists the sixteen functions in the form 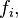 where the index
where the index 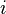 is a bit string formed from the sequence of boolean values in
is a bit string formed from the sequence of boolean values in 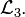
- Language
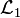 notates the boolean functions
notates the boolean functions 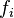 with an index
with an index 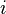 that is the decimal equivalent of the binary numeral index in
that is the decimal equivalent of the binary numeral index in 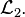
- Language
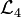 expresses the sixteen functions in terms of logical conjunction, indicated by concatenating function names or proposition expressions in the manner of products, plus the family of minimal negation operators, the first few of which are given in the following variant notations:
expresses the sixteen functions in terms of logical conjunction, indicated by concatenating function names or proposition expressions in the manner of products, plus the family of minimal negation operators, the first few of which are given in the following variant notations:
|
|
It may be noted that 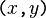 is the same function as
is the same function as 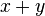 and
and 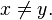 The inclusive disjunctions indicated for
The inclusive disjunctions indicated for 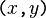 and for
and for 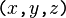 may be replaced with exclusive disjunctions without affecting the meaning, since the terms disjoined are already disjoint. However, the function
may be replaced with exclusive disjunctions without affecting the meaning, since the terms disjoined are already disjoint. However, the function 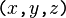 is not the same thing as the function
is not the same thing as the function 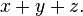
- Language
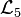 lists ordinary language expressions for the sixteen functions. Many other paraphrases are possible, but these afford a sample of the simplest equivalents.
lists ordinary language expressions for the sixteen functions. Many other paraphrases are possible, but these afford a sample of the simplest equivalents.
- Language
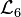 expresses the sixteen functions in one of several notations that are commonly used in formal logic.
expresses the sixteen functions in one of several notations that are commonly used in formal logic.
Translations
Syllabus
Focal nodes
Peer nodes
- Zeroth Order Logic @ InterSciWiki
- Zeroth Order Logic @ Subject Wikis
- Zeroth Order Logic @ Wikiversity
- Zeroth Order Logic @ Wikiversity Beta
Logical operators
Related topics
Relational concepts
Information, Inquiry
Related articles
Document history
Portions of the above article were adapted from the following sources under the GNU Free Documentation License, under other applicable licenses, or by permission of the copyright holders.
- Zeroth Order Logic, InterSciWiki
- Zeroth Order Logic, PlanetMath
- Zeroth Order Logic, Wikinfo
- Zeroth Order Logic, Wikiversity
- Zeroth Order Logic, Wikiversity Beta
- Zeroth Order Logic, Wikipedia
- Zeroth Order Logic, Altheim.com
![\begin{matrix}
f_{0}
\\[4pt]
f_{1}
\\[4pt]
f_{2}
\\[4pt]
f_{3}
\\[4pt]
f_{4}
\\[4pt]
f_{5}
\\[4pt]
f_{6}
\\[4pt]
f_{7}
\end{matrix}\!](../I/m/624ea2ac13886e2da77a24ada483d994.png)
![\begin{matrix}
f_{0000}
\\[4pt]
f_{0001}
\\[4pt]
f_{0010}
\\[4pt]
f_{0011}
\\[4pt]
f_{0100}
\\[4pt]
f_{0101}
\\[4pt]
f_{0110}
\\[4pt]
f_{0111}
\end{matrix}\!](../I/m/3953b3e8a416321e1dc61d6d49b0a17b.png)
![\begin{matrix}
0~0~0~0
\\[4pt]
0~0~0~1
\\[4pt]
0~0~1~0
\\[4pt]
0~0~1~1
\\[4pt]
0~1~0~0
\\[4pt]
0~1~0~1
\\[4pt]
0~1~1~0
\\[4pt]
0~1~1~1
\end{matrix}\!](../I/m/d22a7431740f52bf85ecf6e893b267b5.png)
![\begin{matrix}
\texttt{(~)}
\\[4pt]
\texttt{(} x \texttt{)(} y \texttt{)}
\\[4pt]
\texttt{(} x \texttt{)} ~ y ~
\\[4pt]
\texttt{(} x \texttt{)}
\\[4pt]
~ x ~ \texttt{(} y \texttt{)}
\\[4pt]
\texttt{(} y \texttt{)}
\\[4pt]
\texttt{(} x \texttt{,} ~ y \texttt{)}
\\[4pt]
\texttt{(} x ~ y \texttt{)}
\end{matrix}\!](../I/m/93a1599513e2ed21278037fc64873746.png)
![\begin{matrix}
\text{false}
\\[4pt]
\text{neither}~ x ~\text{nor}~ y
\\[4pt]
y ~\text{without}~ x
\\[4pt]
\text{not}~ x
\\[4pt]
x ~\text{without}~ y
\\[4pt]
\text{not}~ y
\\[4pt]
x ~\text{not equal to}~ y
\\[4pt]
\text{not both}~ x ~\text{and}~ y
\end{matrix}\!](../I/m/12649e5a8d41b68398417feea27b9f4a.png)
![\begin{matrix}
0
\\[4pt]
\lnot x \land \lnot y
\\[4pt]
\lnot x \land y
\\[4pt]
\lnot x
\\[4pt]
x \land \lnot y
\\[4pt]
\lnot y
\\[4pt]
x \ne y
\\[4pt]
\lnot x \lor \lnot y
\end{matrix}\!](../I/m/8c69849fc65e742de12998cac9861bfd.png)
![\begin{matrix}
f_{8}
\\[4pt]
f_{9}
\\[4pt]
f_{10}
\\[4pt]
f_{11}
\\[4pt]
f_{12}
\\[4pt]
f_{13}
\\[4pt]
f_{14}
\\[4pt]
f_{15}
\end{matrix}\!](../I/m/be8858fb8c82f45c971113bd3f93a968.png)
![\begin{matrix}
f_{1000}
\\[4pt]
f_{1001}
\\[4pt]
f_{1010}
\\[4pt]
f_{1011}
\\[4pt]
f_{1100}
\\[4pt]
f_{1101}
\\[4pt]
f_{1110}
\\[4pt]
f_{1111}
\end{matrix}\!](../I/m/780e21455717ec355a5ba82da4d5c0d6.png)
![\begin{matrix}
1~0~0~0
\\[4pt]
1~0~0~1
\\[4pt]
1~0~1~0
\\[4pt]
1~0~1~1
\\[4pt]
1~1~0~0
\\[4pt]
1~1~0~1
\\[4pt]
1~1~1~0
\\[4pt]
1~1~1~1
\end{matrix}\!](../I/m/e6e101f9e99243fc484b898f1ed54e6d.png)
![\begin{matrix}
x ~ y
\\[4pt]
\texttt{((} x \texttt{,} ~ y \texttt{))}
\\[4pt]
y
\\[4pt]
\texttt{(} x ~ \texttt{(} y \texttt{))}
\\[4pt]
x
\\[4pt]
\texttt{((} x \texttt{)} ~ y \texttt{)}
\\[4pt]
\texttt{((} x \texttt{)(} y \texttt{))}
\\[4pt]
\texttt{((~))}
\end{matrix}\!](../I/m/01f64acf13dc4871fc3cb4ca0dd5be9d.png)
![\begin{matrix}
x ~\text{and}~ y
\\[4pt]
x ~\text{equal to}~ y
\\[4pt]
y
\\[4pt]
\text{not}~ x ~\text{without}~ y
\\[4pt]
x
\\[4pt]
\text{not}~ y ~\text{without}~ x
\\[4pt]
x ~\text{or}~ y
\\[4pt]
\text{true}
\end{matrix}\!](../I/m/0af3d9ce1a1199da8e66c805e8b4900a.png)
![\begin{matrix}
x \land y
\\[4pt]
x = y
\\[4pt]
y
\\[4pt]
x \Rightarrow y
\\[4pt]
x
\\[4pt]
x \Leftarrow y
\\[4pt]
x \lor y
\\[4pt]
1
\end{matrix}\!](../I/m/12b67838b1a228bdf3890f94f0e2c184.png)
![\begin{matrix}
\texttt{()}
& = & 0
& = & \mathrm{false}
\\[6pt]
\texttt{(} x \texttt{)}
& = & \tilde{x}
& = & x^\prime
\\[6pt]
\texttt{(} x \texttt{,} y \texttt{)}
& = & \tilde{x}y \lor x\tilde{y}
& = & x^\prime y \lor x y^\prime
\\[6pt]
\texttt{(} x \texttt{,} y \texttt{,} z \texttt{)}
& = & \tilde{x}yz \lor x\tilde{y}z \lor xy\tilde{z}
& = & x^\prime y z \lor x y^\prime z \lor x y z^\prime
\end{matrix}\!](../I/m/d5ef4cfc1aa9b0bc30f4bf0f3e4939fd.png)