Volcanoes/Campi Flegrei
< Volcanoes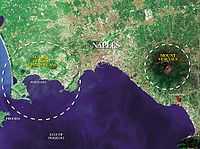
"Campi Flegrei [is] an active four-mile-wide sunken volcano."[1]
"The Campi Flegrei caldera is a supervolcano [as outlined in the image on the right]. Although there’s no picture-postcard volcanic cone, hidden beneath the seemingly placid landscape lies a volcano of immense power. While a new eruption here would be more likely to result in the creation of another Vesuvius-like cone, the worst-case scenario could see it obliterating much of life in Europe."[1]
Eruptions

"The last time the ground gave way like this, 39,000 years ago when the caldera was formed, it created the cliffs that the postcard town of Sorrento stands on now – volcanic deposits over 300 ft deep. If the same kind of eruption happened today, this part of Italy could cease to exist, and the ash clouds would blot out the Sun and lower the Earth’s temperature. Life in the UK as we know it would end. We would lose our livestock, crops and three-quarters of our plant species, plunging us into a new dark age of rioting, starvation and perpetual winter."[1]
Volcanic activity

"Right now we may well be in another period of uplift. If it occurs as before, we might expect another 60 years’ worth of unrest, and possible earthquakes and eruptions, with two or three more episodes and uplift to occur in the next ten years. We have to presume we have a few more decades of unrest, and if this is going to be the case, then we have to get more data about the volcano now."[2]
Volcanism
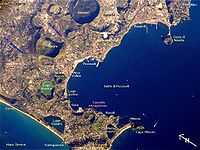




Def. any remnants "of the natural phenomena and processes associated with the action of volcanos, geysers and fumaroles"[3], especially any remnants of past volcanic activity, are called volcanism.
The image on the right from space of Campi Flegrei shows multiple volcanic cones and crater lakes from the past volcanism.
The second image down on the right is a trachytic dome formed from a lava flow from Solfatara.
The third image down on the right is the massive tuff of Monte Gauro.
Monte di Procida in the fourth image down on the right is a volcanic remnant of Campi Flegrei.
Collina dei Camaldoli, the fifth image down on the right, apparently originated about 35,000 b2k as a result of violent eruptions across Campi Flegrei.
The sixth image down on the right shows Monte Nuovo, a relatively recent cinder cone in the caldera of Campi Flegrei.
The image on the left shows relative relief around Campi Flegrei. This emphasizes that most or all of the relief is due to remnants of volcanic activity. Some of these features are shown in the images on the right.
Research
Hypothesis:
- The most recent supervolcano eruption of Campi Flegrei left a dust layer in the Greenland ice cores.
Control groups

The findings demonstrate a statistically systematic change from the status quo or the control group.
“In the design of experiments, treatments [or special properties or characteristics] are applied to [or observed in] experimental units in the treatment group(s).[4] In comparative experiments, members of the complementary group, the control group, receive either no treatment or a standard treatment.[5]"[6]
Proof of concept
Def. a “short and/or incomplete realization of a certain method or idea to demonstrate its feasibility"[7] is called a proof of concept.
Def. evidence that demonstrates that a concept is possible is called proof of concept.
The proof-of-concept structure consists of
- background,
- procedures,
- findings, and
- interpretation.[8]
See also
References
- 1 2 3 Phil Robinson (3 January 2011). "Vesuvius's big daddy: The supervolcano that threatens all life in Europe". UK: DailyMail. Retrieved 2015-03-20.
- ↑ Chris Kilburn (3 January 2011). "Vesuvius's big daddy: The supervolcano that threatens all life in Europe". UK: DailyMail. Retrieved 2015-03-20.
- ↑ SemperBlotto (5 July 2007). "volcanism, In: Wiktionary". San Francisco, California: Wikimedia Foundation, Inc. Retrieved 2015-03-20.
- ↑ Klaus Hinkelmann, Oscar Kempthorne (2008). Design and Analysis of Experiments, Volume I: Introduction to Experimental Design (2nd ed.). Wiley. ISBN 978-0-471-72756-9. http://books.google.com/?id=T3wWj2kVYZgC&printsec=frontcover.
- ↑ R. A. Bailey (2008). Design of comparative experiments. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-68357-9. http://www.cambridge.org/uk/catalogue/catalogue.asp?isbn=9780521683579.
- ↑ "Treatment and control groups, In: Wikipedia". San Francisco, California: Wikimedia Foundation, Inc. May 18, 2012. Retrieved 2012-05-31.
- ↑ "proof of concept, In: Wiktionary". San Francisco, California: Wikimedia Foundation, Inc. November 10, 2012. Retrieved 2013-01-13.
- ↑ Ginger Lehrman and Ian B Hogue, Sarah Palmer, Cheryl Jennings, Celsa A Spina, Ann Wiegand, Alan L Landay, Robert W Coombs, Douglas D Richman, John W Mellors, John M Coffin, Ronald J Bosch, David M Margolis (August 13, 2005). "Depletion of latent HIV-1 infection in vivo: a proof-of-concept study". Lancet 366 (9485): 549-55. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(05)67098-5. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1894952/. Retrieved 2012-05-09.
External links
![]() This is a research project at http://en.wikiversity.org
This is a research project at http://en.wikiversity.org
| |
Development status: this resource is experimental in nature. |
| |
Educational level: this is a research resource. |
| |
Resource type: this resource is an article. |
| |
Resource type: this resource contains a lecture or lecture notes. |
| |
Subject classification: this is a Geology resource. |