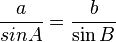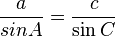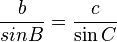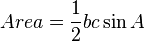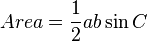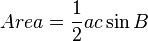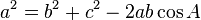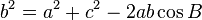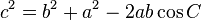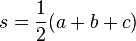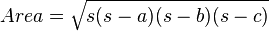Trigonometry/Plane
< TrigonometryPlane trigonometry involves solving the mathematics of triangles. The law of sines and cosines are fundamental to this.
Law of sines
Area of a triangle
Law of cosines
- This law uses the Pythagorean theorem, but this includes non-right angles.
Heron's area formula
- s is the semi-perimeter
References
This article is issued from Wikiversity - version of the Wednesday, January 02, 2013. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.