The periodic table/Argon
< The periodic table

| |
Subject classification: this is a chemistry resource . |
| |
Completion status: this resource is ~60% complete. |
| |
Educational level: this is a research resource. |
| |
Resource type: this resource is an article. |
Argon is a Noble Gas, abbreviated "Ar" and discovered in 1894.
Discovery
Argon (αργόν, neuter singular form of αργός, Greek name for "inactive", in reference to chemical inactivity of Argon) was discovered by a Scottish chemist, Sir William Ramsay, and English chemist, Lord Rayleigh in 1894, in the University College London in England. Argon was isolated by examination of nitrogen, oxygen, carbon dioxide, and water from sampled air, that was clean. Until 1957, Argon was abbreviated to "A".
Quick Facts
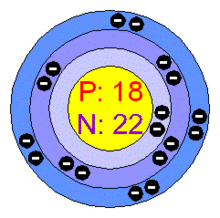
Name: Argon Atom Symbol: Ar Mass: 40 Classification: Group 0 (Noble Gases) |
Protons: 18 Electrons: 18 Neutrons: 22 Color: colorless Discovered in: 1894 Number of Energy Levels: 1 (2 electrons), 2 (8 electrons), 3 (8 electrons) |
Crystal Structure: Cubic Melting Point: -189.3 °C Boiling Point: -186.0 °C Crystal Structure: Cubic Density: 1.784 g/cm3 Electron Configuration: [Ne] 3s23p1 Common Uses: Electric Light Bulbs, Fluorescent Lights |
Uses
- The colorless, odorless gas makes .94 of the air you breath in.
- Nonreactive metal, has no impact on living organisms (like humans).
- Argon is used, typically, in incandescent light bulbs, because this noble gas [ehm... a little hint] will not react to the filament, even at high temperatures!
- Argon is used in some double-panned glass windows, because Argon is used as an insulator between the two windows, because it's a poor conductor of heat.
- Argon is sometimes used to inflate dry suits for the wonderful game of scuba diving!
- Argon is found in ice sheets, and helps (to scientists) to figure out the temperature over a given number of time.
- Argon gas may be used for military use, as it harms those that are exposed to the gas
Atomic Data
Atomic radius: 1.88 Å Covalent radius: 1.01 Å Electronegativity: Unknown Electron affinity: Unstable |
Ionisation energies First: 1520.571 Second: 2665.857 Third: 3930.81 Fourth: 5770.79 Fifth: 7238.33 Sixth: 8781.034 Seventh: 11995.347 Eighth: 13841.79 |