Quizbank/How things work/Sample exam 1
< Quizbank < How things workHTW T1 sample
If you are reading this as a Wikiversity page, proper pagebreaks should result if printed using your browser's print option. On Chrome, Explorer, and Firefox, this option is available in the upper right hand corner of your screen. But, pagebreaks do not render properly if you use "Printable version" on Wikiversity's Print/export option on the left-hand sidebar.
- This document contains either a study guide OR pairs of exams taken from the same exam bank
- If two exams have the same s-number, then v1 and v2 have the same questions, presented in different (random) order.
- Exams with different s-numbers have different questions and may not have the same difficulty.
- Click items in the table of contents and appropriate page should be reached. This feature should allow you to print only those pages that you need.
- At the end of this document
- Attribution for the quizzes identifies where the questions were obtained
- Study guide links reading materials and/or relevant equations.
HTW T1 sample-v1s1
1. An important principle that allows fiber optics to work is
- ___ a) the Doppler shift
- ___ b) total internal reflection
- ___ c) the invariance of the speed of light
- ___ d) partial internal absorption
- ___ e) total external refraction
2. A tuning fork with a frequency of 440 Hz is played simultaneously with a tuning fork of 442 Hz. How many beats are heard in 10 seconds?
- ___ a) 40
- ___ b) 60
- ___ c) 50
- ___ d) 20
- ___ e) 30
3. What are the units of Plank's constant?
- ___ a) all of the above
- ___ b) mass x velocity x distance
- ___ c) energy x time
- ___ d) none of the above
- ___ e) momentum x distance
4. The law of reflection applies to
- ___ a) telescopes but not microscopes
- ___ b) curved surfaces
- ___ c) flat surfaces
- ___ d) only light in a vacuum
- ___ e) both flat and curved surfaces
5. What are examples of energy?
- ___ a)
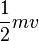
- ___ b) heat
- ___ c) all of the above
- ___ d) momentum
6. 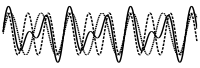 Two signals (dashed) add to a solid
Two signals (dashed) add to a solid
- ___ a) fifth
- ___ b) dissonance
- ___ c) octave
7. Mr. Smith is driving at a speed of 7 m/s, when he slows down to a speed of 5 m/s, when he hits a wall at this speed, after travelling for 2 seconds. How far did he travel?
- ___ a) 9.0 meters
- ___ b) 12.0 meters
- ___ c) 10.0 meters
- ___ d) 11.0 meters
- ___ e) 8.0 meters
8. A car is traveling east and slowing down. The acceleration is
- ___ a) zero
- ___ b) to the east
- ___ c) to the west
9.  Two signals (dashed) add to a solid
Two signals (dashed) add to a solid
- ___ a) dissonance
- ___ b) octave
- ___ c) fifth
10. When a table cloth is quickly pulled out from under dishes, they hardly move. This is because
- ___ a) objects don't begin to accelerate until after the force has been applied
- ___ b) the cloth is more slippery when it is pulled quickly
- ___ c) the cloth is accelerating for such a brief time that there is little motion
11. Excepting cases where where quantum jumps in energy are induced in another object (i.e., using only the uncertainty principle), which would NOT put a classical particle into the quantum regime?
- ___ a) low mass
- ___ b) confinement to a small space
- ___ c) low speed
- ___ d) high speed
12. Mr. Smith is driving at a speed of 4 m/s, when he slows down to a speed of 1 m/s, when he hits a wall at this speed, after travelling for 4 seconds. How far did he travel?
- ___ a) 10.0 meters
- ___ b) 7.0 meters
- ___ c) 11.0 meters
- ___ d) 9.0 meters
- ___ e) 8.0 meters
13. ![]() Mr. Smith is gazing at something as shown in the figure to the left. Suppose he does not refocus, but attempts to stare at the star shown in the figures below. Which diagram depicts how the rays from the star would travel if he does not refocus?
Mr. Smith is gazing at something as shown in the figure to the left. Suppose he does not refocus, but attempts to stare at the star shown in the figures below. Which diagram depicts how the rays from the star would travel if he does not refocus?
- ___ a)
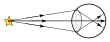
- ___ b)

- ___ c)

14. If you toss a coin into the air, the acceleration while it as its highest point is
- ___ a) up
- ___ b) down
- ___ c) zero
15.
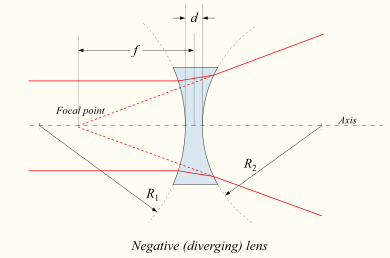
Shown is a corrective lens by a person who needs glasses. This ray diagram illustrates
- ___ a) how a farsighted person might see a distant object
- ___ b) how a nearsighted person might see an object that is too close for comfort
- ___ c) how a farsighted person might see an object that is too close for comfort
- ___ d) how a nearsighted person might see a distant object
16. A car is traveling in a perfect circle at constant speed. If the car is headed north while turning west, the acceleration is
- ___ a) north
- ___ b) west
- ___ c) south
- ___ d) zero
- ___ e) east
17. A dense rope is connected to a rope with less density (i.e. fewer kilograms per meter). If the rope is stretched and a wave is sent along high density rope,
- ___ a) the low density rope supports a wave with a higher frequency
- ___ b) the low density rope supports a wave with a lower frequency
- ___ c) the low density rope supports a wave with a lower speed
- ___ d) the low density rope supports a wave with a higher speed
18. A car is traveling east and speeding up. The acceleration is
- ___ a) zero
- ___ b) to the west
- ___ c) to the east
19. The focal point is where
- ___ a) rays meet whenever they pass through a lens
- ___ b) rays meet whenever they are forming an image
- ___ c) rays meet if they were parallel to the optical axis before striking a lens
- ___ d) rays meet if they are parallel to each other
- ___ e) the center of the lens
20. Mr. Smith is driving at a speed of 7 m/s, when he slows down to a speed of 5 m/s, when he hits a wall at this speed, after travelling for 4 seconds. How far did he travel?
- ___ a) 27.0 meters
- ___ b) 24.0 meters
- ___ c) 25.0 meters
- ___ d) 23.0 meters
- ___ e) 26.0 meters
21. A car is headed due north and decreasing its speed. It is also turning right because it is also traveling in a perfect circle. The acceleration vector points
- ___ a) south
- ___ b) southeast
- ___ c) northeast
- ___ d) north
- ___ e) northwest
22. What are examples of energy?
- ___ a) mgh where m is mass, g is gravity, and h is height
- ___ b) heat
- ___ c) all of the above
- ___ d)
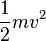
23. Mr. Smith is driving at a speed of 5 m/s, when he slows down to a speed of 4 m/s, when he hits a wall at this speed, after travelling for 2 seconds. How far did he travel?
- ___ a) 11.0 meters
- ___ b) 9.0 meters
- ___ c) 8.0 meters
- ___ d) 12.0 meters
- ___ e) 10.0 meters
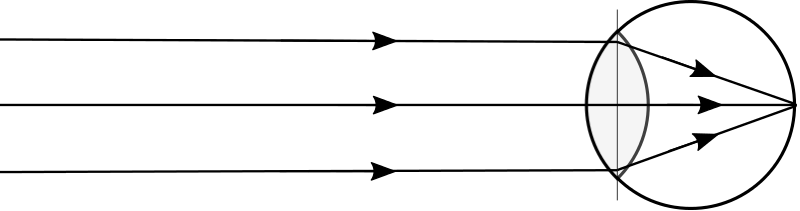
24. ![]() If this represents the eye looking at an object, where is this object?
If this represents the eye looking at an object, where is this object?
- ___ a) directly in front of the eye (almost touching)
- ___ b) Two (of the other answers) are true
- ___ c) very far away
- ___ d) One focal length in front of the eye
- ___ e) at infinity
25. When a wave is reflected off a stationary barrier, the reflected wave
- ___ a) has higher frequency than the incident wave
- ___ b) has lower amplitude than the incident wave
- ___ c) both of these are true
26. If a source of sound is moving towards you, the pitch becomes
- ___ a) higher
- ___ b) lower
- ___ c) unchanged
27. What happens to the wavelength on a wave on a stretched string if the wave passes from lightweight (low density) region of the rope to a heavy (high density) rope?
- ___ a) the wavelength stays the same
- ___ b) the wavelength gets shorter
- ___ c) the wavelength gets longer
28. A car is headed due north and increasing its speed. It is also turning left because it is also traveling in a perfect circle. The velocity vector points
- ___ a) southeast
- ___ b) northwest
- ___ c) northeast
- ___ d) north
- ___ e) northeast
29. If you toss a coin into the air, the velocity on the way up is
- ___ a) zero
- ___ b) up
- ___ c) down
30. Mr. Smith starts from rest and accelerates to 4 m/s in 3 seconds. How far did he travel?
- ___ a) 7.0 meters
- ___ b) 5.0 meters
- ___ c) 3.0 meters
- ___ d) 4.0 meters
- ___ e) 6.0 meters
Key to HTW T1 sample-v1s1
1. An important principle that allows fiber optics to work is
- - a) the Doppler shift
- + b) total internal reflection
- - c) the invariance of the speed of light
- - d) partial internal absorption
- - e) total external refraction
2. A tuning fork with a frequency of 440 Hz is played simultaneously with a tuning fork of 442 Hz. How many beats are heard in 10 seconds?
- - a) 40
- - b) 60
- - c) 50
- + d) 20
- - e) 30
3. What are the units of Plank's constant?
- + a) all of the above
- - b) mass x velocity x distance
- - c) energy x time
- - d) none of the above
- - e) momentum x distance
4. The law of reflection applies to
- - a) telescopes but not microscopes
- - b) curved surfaces
- - c) flat surfaces
- - d) only light in a vacuum
- + e) both flat and curved surfaces
5. What are examples of energy?
- - a)
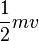
- - a)
- - b) heat
- + c) all of the above
- - d) momentum
6.  Two signals (dashed) add to a solid
Two signals (dashed) add to a solid
- + a) fifth
- - b) dissonance
- - c) octave
7. Mr. Smith is driving at a speed of 7 m/s, when he slows down to a speed of 5 m/s, when he hits a wall at this speed, after travelling for 2 seconds. How far did he travel?
- - a) 9.0 meters
- + b) 12.0 meters
- - c) 10.0 meters
- - d) 11.0 meters
- - e) 8.0 meters
8. A car is traveling east and slowing down. The acceleration is
- - a) zero
- - b) to the east
- + c) to the west
9.  Two signals (dashed) add to a solid
Two signals (dashed) add to a solid
- - a) dissonance
- + b) octave
- - c) fifth
10. When a table cloth is quickly pulled out from under dishes, they hardly move. This is because
- - a) objects don't begin to accelerate until after the force has been applied
- - b) the cloth is more slippery when it is pulled quickly
- + c) the cloth is accelerating for such a brief time that there is little motion
11. Excepting cases where where quantum jumps in energy are induced in another object (i.e., using only the uncertainty principle), which would NOT put a classical particle into the quantum regime?
- - a) low mass
- - b) confinement to a small space
- - c) low speed
- + d) high speed
12. Mr. Smith is driving at a speed of 4 m/s, when he slows down to a speed of 1 m/s, when he hits a wall at this speed, after travelling for 4 seconds. How far did he travel?
- + a) 10.0 meters
- - b) 7.0 meters
- - c) 11.0 meters
- - d) 9.0 meters
- - e) 8.0 meters
13. ![]() Mr. Smith is gazing at something as shown in the figure to the left. Suppose he does not refocus, but attempts to stare at the star shown in the figures below. Which diagram depicts how the rays from the star would travel if he does not refocus?
Mr. Smith is gazing at something as shown in the figure to the left. Suppose he does not refocus, but attempts to stare at the star shown in the figures below. Which diagram depicts how the rays from the star would travel if he does not refocus?
- - a)
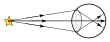
- - a)
- - b)

- - b)
- + c)

- + c)
14. If you toss a coin into the air, the acceleration while it as its highest point is
- - a) up
- + b) down
- - c) zero
15.

Shown is a corrective lens by a person who needs glasses. This ray diagram illustrates
- - a) how a farsighted person might see a distant object
- - b) how a nearsighted person might see an object that is too close for comfort
- - c) how a farsighted person might see an object that is too close for comfort
- + d) how a nearsighted person might see a distant object
16. A car is traveling in a perfect circle at constant speed. If the car is headed north while turning west, the acceleration is
- - a) north
- + b) west
- - c) south
- - d) zero
- - e) east
17. A dense rope is connected to a rope with less density (i.e. fewer kilograms per meter). If the rope is stretched and a wave is sent along high density rope,
- - a) the low density rope supports a wave with a higher frequency
- - b) the low density rope supports a wave with a lower frequency
- - c) the low density rope supports a wave with a lower speed
- + d) the low density rope supports a wave with a higher speed
18. A car is traveling east and speeding up. The acceleration is
- - a) zero
- - b) to the west
- + c) to the east
19. The focal point is where
- - a) rays meet whenever they pass through a lens
- - b) rays meet whenever they are forming an image
- + c) rays meet if they were parallel to the optical axis before striking a lens
- - d) rays meet if they are parallel to each other
- - e) the center of the lens
20. Mr. Smith is driving at a speed of 7 m/s, when he slows down to a speed of 5 m/s, when he hits a wall at this speed, after travelling for 4 seconds. How far did he travel?
- - a) 27.0 meters
- + b) 24.0 meters
- - c) 25.0 meters
- - d) 23.0 meters
- - e) 26.0 meters
21. A car is headed due north and decreasing its speed. It is also turning right because it is also traveling in a perfect circle. The acceleration vector points
- - a) south
- + b) southeast
- - c) northeast
- - d) north
- - e) northwest
22. What are examples of energy?
- - a) mgh where m is mass, g is gravity, and h is height
- - b) heat
- + c) all of the above
- - d)
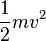
- - d)
23. Mr. Smith is driving at a speed of 5 m/s, when he slows down to a speed of 4 m/s, when he hits a wall at this speed, after travelling for 2 seconds. How far did he travel?
- - a) 11.0 meters
- + b) 9.0 meters
- - c) 8.0 meters
- - d) 12.0 meters
- - e) 10.0 meters
24. ![]() If this represents the eye looking at an object, where is this object?
If this represents the eye looking at an object, where is this object?
- - a) directly in front of the eye (almost touching)
- + b) Two (of the other answers) are true
- - c) very far away
- - d) One focal length in front of the eye
- - e) at infinity
25. When a wave is reflected off a stationary barrier, the reflected wave
- - a) has higher frequency than the incident wave
- + b) has lower amplitude than the incident wave
- - c) both of these are true
26. If a source of sound is moving towards you, the pitch becomes
- + a) higher
- - b) lower
- - c) unchanged
27. What happens to the wavelength on a wave on a stretched string if the wave passes from lightweight (low density) region of the rope to a heavy (high density) rope?
- - a) the wavelength stays the same
- - b) the wavelength gets shorter
- + c) the wavelength gets longer
28. A car is headed due north and increasing its speed. It is also turning left because it is also traveling in a perfect circle. The velocity vector points
- - a) southeast
- - b) northwest
- - c) northeast
- + d) north
- - e) northeast
29. If you toss a coin into the air, the velocity on the way up is
- - a) zero
- + b) up
- - c) down
30. Mr. Smith starts from rest and accelerates to 4 m/s in 3 seconds. How far did he travel?
- - a) 7.0 meters
- - b) 5.0 meters
- - c) 3.0 meters
- - d) 4.0 meters
- + e) 6.0 meters
HTW T1 sample-v2s1
1. If a source of sound is moving towards you, the pitch becomes
- ___ a) higher
- ___ b) lower
- ___ c) unchanged
2. If you toss a coin into the air, the velocity on the way up is
- ___ a) down
- ___ b) up
- ___ c) zero
3. Mr. Smith starts from rest and accelerates to 4 m/s in 3 seconds. How far did he travel?
- ___ a) 4.0 meters
- ___ b) 5.0 meters
- ___ c) 6.0 meters
- ___ d) 7.0 meters
- ___ e) 3.0 meters
4. A car is traveling east and slowing down. The acceleration is
- ___ a) to the west
- ___ b) zero
- ___ c) to the east
5. What are the units of Plank's constant?
- ___ a) all of the above
- ___ b) momentum x distance
- ___ c) none of the above
- ___ d) mass x velocity x distance
- ___ e) energy x time
6. Mr. Smith is driving at a speed of 7 m/s, when he slows down to a speed of 5 m/s, when he hits a wall at this speed, after travelling for 4 seconds. How far did he travel?
- ___ a) 23.0 meters
- ___ b) 27.0 meters
- ___ c) 26.0 meters
- ___ d) 24.0 meters
- ___ e) 25.0 meters
7. The focal point is where
- ___ a) rays meet if they are parallel to each other
- ___ b) rays meet if they were parallel to the optical axis before striking a lens
- ___ c) rays meet whenever they are forming an image
- ___ d) the center of the lens
- ___ e) rays meet whenever they pass through a lens
8. A car is traveling east and speeding up. The acceleration is
- ___ a) to the west
- ___ b) to the east
- ___ c) zero
9. A car is headed due north and increasing its speed. It is also turning left because it is also traveling in a perfect circle. The velocity vector points
- ___ a) northeast
- ___ b) southeast
- ___ c) northwest
- ___ d) northeast
- ___ e) north
10. A tuning fork with a frequency of 440 Hz is played simultaneously with a tuning fork of 442 Hz. How many beats are heard in 10 seconds?
- ___ a) 40
- ___ b) 50
- ___ c) 20
- ___ d) 30
- ___ e) 60
11. When a wave is reflected off a stationary barrier, the reflected wave
- ___ a) both of these are true
- ___ b) has higher frequency than the incident wave
- ___ c) has lower amplitude than the incident wave
12. ![]() If this represents the eye looking at an object, where is this object?
If this represents the eye looking at an object, where is this object?
- ___ a) at infinity
- ___ b) One focal length in front of the eye
- ___ c) Two (of the other answers) are true
- ___ d) directly in front of the eye (almost touching)
- ___ e) very far away
13. Excepting cases where where quantum jumps in energy are induced in another object (i.e., using only the uncertainty principle), which would NOT put a classical particle into the quantum regime?
- ___ a) low speed
- ___ b) low mass
- ___ c) confinement to a small space
- ___ d) high speed
14.  Two signals (dashed) add to a solid
Two signals (dashed) add to a solid
- ___ a) fifth
- ___ b) octave
- ___ c) dissonance
15.

Shown is a corrective lens by a person who needs glasses. This ray diagram illustrates
- ___ a) how a farsighted person might see an object that is too close for comfort
- ___ b) how a nearsighted person might see an object that is too close for comfort
- ___ c) how a nearsighted person might see a distant object
- ___ d) how a farsighted person might see a distant object
16. A dense rope is connected to a rope with less density (i.e. fewer kilograms per meter). If the rope is stretched and a wave is sent along high density rope,
- ___ a) the low density rope supports a wave with a higher frequency
- ___ b) the low density rope supports a wave with a lower speed
- ___ c) the low density rope supports a wave with a higher speed
- ___ d) the low density rope supports a wave with a lower frequency
17. Mr. Smith is driving at a speed of 5 m/s, when he slows down to a speed of 4 m/s, when he hits a wall at this speed, after travelling for 2 seconds. How far did he travel?
- ___ a) 12.0 meters
- ___ b) 10.0 meters
- ___ c) 8.0 meters
- ___ d) 11.0 meters
- ___ e) 9.0 meters
18.  Two signals (dashed) add to a solid
Two signals (dashed) add to a solid
- ___ a) octave
- ___ b) fifth
- ___ c) dissonance
19. What are examples of energy?
- ___ a)
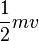
- ___ b) heat
- ___ c) momentum
- ___ d) all of the above
20. What happens to the wavelength on a wave on a stretched string if the wave passes from lightweight (low density) region of the rope to a heavy (high density) rope?
- ___ a) the wavelength gets shorter
- ___ b) the wavelength stays the same
- ___ c) the wavelength gets longer
21. If you toss a coin into the air, the acceleration while it as its highest point is
- ___ a) down
- ___ b) zero
- ___ c) up
22. A car is headed due north and decreasing its speed. It is also turning right because it is also traveling in a perfect circle. The acceleration vector points
- ___ a) southeast
- ___ b) northeast
- ___ c) north
- ___ d) northwest
- ___ e) south
23. Mr. Smith is driving at a speed of 7 m/s, when he slows down to a speed of 5 m/s, when he hits a wall at this speed, after travelling for 2 seconds. How far did he travel?
- ___ a) 8.0 meters
- ___ b) 10.0 meters
- ___ c) 9.0 meters
- ___ d) 11.0 meters
- ___ e) 12.0 meters
24. When a table cloth is quickly pulled out from under dishes, they hardly move. This is because
- ___ a) objects don't begin to accelerate until after the force has been applied
- ___ b) the cloth is more slippery when it is pulled quickly
- ___ c) the cloth is accelerating for such a brief time that there is little motion
25. Mr. Smith is driving at a speed of 4 m/s, when he slows down to a speed of 1 m/s, when he hits a wall at this speed, after travelling for 4 seconds. How far did he travel?
- ___ a) 11.0 meters
- ___ b) 10.0 meters
- ___ c) 9.0 meters
- ___ d) 8.0 meters
- ___ e) 7.0 meters
26. The law of reflection applies to
- ___ a) both flat and curved surfaces
- ___ b) telescopes but not microscopes
- ___ c) curved surfaces
- ___ d) only light in a vacuum
- ___ e) flat surfaces
27. A car is traveling in a perfect circle at constant speed. If the car is headed north while turning west, the acceleration is
- ___ a) east
- ___ b) west
- ___ c) north
- ___ d) south
- ___ e) zero
28. ![]() Mr. Smith is gazing at something as shown in the figure to the left. Suppose he does not refocus, but attempts to stare at the star shown in the figures below. Which diagram depicts how the rays from the star would travel if he does not refocus?
Mr. Smith is gazing at something as shown in the figure to the left. Suppose he does not refocus, but attempts to stare at the star shown in the figures below. Which diagram depicts how the rays from the star would travel if he does not refocus?
- ___ a)
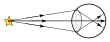
- ___ b)

- ___ c)

29. An important principle that allows fiber optics to work is
- ___ a) total external refraction
- ___ b) total internal reflection
- ___ c) the Doppler shift
- ___ d) the invariance of the speed of light
- ___ e) partial internal absorption
30. What are examples of energy?
- ___ a) mgh where m is mass, g is gravity, and h is height
- ___ b) all of the above
- ___ c)
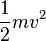
- ___ d) heat
Key to HTW T1 sample-v2s1
1. If a source of sound is moving towards you, the pitch becomes
- + a) higher
- - b) lower
- - c) unchanged
2. If you toss a coin into the air, the velocity on the way up is
- - a) down
- + b) up
- - c) zero
3. Mr. Smith starts from rest and accelerates to 4 m/s in 3 seconds. How far did he travel?
- - a) 4.0 meters
- - b) 5.0 meters
- + c) 6.0 meters
- - d) 7.0 meters
- - e) 3.0 meters
4. A car is traveling east and slowing down. The acceleration is
- + a) to the west
- - b) zero
- - c) to the east
5. What are the units of Plank's constant?
- + a) all of the above
- - b) momentum x distance
- - c) none of the above
- - d) mass x velocity x distance
- - e) energy x time
6. Mr. Smith is driving at a speed of 7 m/s, when he slows down to a speed of 5 m/s, when he hits a wall at this speed, after travelling for 4 seconds. How far did he travel?
- - a) 23.0 meters
- - b) 27.0 meters
- - c) 26.0 meters
- + d) 24.0 meters
- - e) 25.0 meters
7. The focal point is where
- - a) rays meet if they are parallel to each other
- + b) rays meet if they were parallel to the optical axis before striking a lens
- - c) rays meet whenever they are forming an image
- - d) the center of the lens
- - e) rays meet whenever they pass through a lens
8. A car is traveling east and speeding up. The acceleration is
- - a) to the west
- + b) to the east
- - c) zero
9. A car is headed due north and increasing its speed. It is also turning left because it is also traveling in a perfect circle. The velocity vector points
- - a) northeast
- - b) southeast
- - c) northwest
- - d) northeast
- + e) north
10. A tuning fork with a frequency of 440 Hz is played simultaneously with a tuning fork of 442 Hz. How many beats are heard in 10 seconds?
- - a) 40
- - b) 50
- + c) 20
- - d) 30
- - e) 60
11. When a wave is reflected off a stationary barrier, the reflected wave
- - a) both of these are true
- - b) has higher frequency than the incident wave
- + c) has lower amplitude than the incident wave
12. ![]() If this represents the eye looking at an object, where is this object?
If this represents the eye looking at an object, where is this object?
- - a) at infinity
- - b) One focal length in front of the eye
- + c) Two (of the other answers) are true
- - d) directly in front of the eye (almost touching)
- - e) very far away
13. Excepting cases where where quantum jumps in energy are induced in another object (i.e., using only the uncertainty principle), which would NOT put a classical particle into the quantum regime?
- - a) low speed
- - b) low mass
- - c) confinement to a small space
- + d) high speed
14.  Two signals (dashed) add to a solid
Two signals (dashed) add to a solid
- - a) fifth
- + b) octave
- - c) dissonance
15.

Shown is a corrective lens by a person who needs glasses. This ray diagram illustrates
- - a) how a farsighted person might see an object that is too close for comfort
- - b) how a nearsighted person might see an object that is too close for comfort
- + c) how a nearsighted person might see a distant object
- - d) how a farsighted person might see a distant object
16. A dense rope is connected to a rope with less density (i.e. fewer kilograms per meter). If the rope is stretched and a wave is sent along high density rope,
- - a) the low density rope supports a wave with a higher frequency
- - b) the low density rope supports a wave with a lower speed
- + c) the low density rope supports a wave with a higher speed
- - d) the low density rope supports a wave with a lower frequency
17. Mr. Smith is driving at a speed of 5 m/s, when he slows down to a speed of 4 m/s, when he hits a wall at this speed, after travelling for 2 seconds. How far did he travel?
- - a) 12.0 meters
- - b) 10.0 meters
- - c) 8.0 meters
- - d) 11.0 meters
- + e) 9.0 meters
18.  Two signals (dashed) add to a solid
Two signals (dashed) add to a solid
- - a) octave
- + b) fifth
- - c) dissonance
19. What are examples of energy?
- - a)
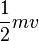
- - a)
- - b) heat
- - c) momentum
- + d) all of the above
20. What happens to the wavelength on a wave on a stretched string if the wave passes from lightweight (low density) region of the rope to a heavy (high density) rope?
- - a) the wavelength gets shorter
- - b) the wavelength stays the same
- + c) the wavelength gets longer
21. If you toss a coin into the air, the acceleration while it as its highest point is
- + a) down
- - b) zero
- - c) up
22. A car is headed due north and decreasing its speed. It is also turning right because it is also traveling in a perfect circle. The acceleration vector points
- + a) southeast
- - b) northeast
- - c) north
- - d) northwest
- - e) south
23. Mr. Smith is driving at a speed of 7 m/s, when he slows down to a speed of 5 m/s, when he hits a wall at this speed, after travelling for 2 seconds. How far did he travel?
- - a) 8.0 meters
- - b) 10.0 meters
- - c) 9.0 meters
- - d) 11.0 meters
- + e) 12.0 meters
24. When a table cloth is quickly pulled out from under dishes, they hardly move. This is because
- - a) objects don't begin to accelerate until after the force has been applied
- - b) the cloth is more slippery when it is pulled quickly
- + c) the cloth is accelerating for such a brief time that there is little motion
25. Mr. Smith is driving at a speed of 4 m/s, when he slows down to a speed of 1 m/s, when he hits a wall at this speed, after travelling for 4 seconds. How far did he travel?
- - a) 11.0 meters
- + b) 10.0 meters
- - c) 9.0 meters
- - d) 8.0 meters
- - e) 7.0 meters
26. The law of reflection applies to
- + a) both flat and curved surfaces
- - b) telescopes but not microscopes
- - c) curved surfaces
- - d) only light in a vacuum
- - e) flat surfaces
27. A car is traveling in a perfect circle at constant speed. If the car is headed north while turning west, the acceleration is
- - a) east
- + b) west
- - c) north
- - d) south
- - e) zero
28. ![]() Mr. Smith is gazing at something as shown in the figure to the left. Suppose he does not refocus, but attempts to stare at the star shown in the figures below. Which diagram depicts how the rays from the star would travel if he does not refocus?
Mr. Smith is gazing at something as shown in the figure to the left. Suppose he does not refocus, but attempts to stare at the star shown in the figures below. Which diagram depicts how the rays from the star would travel if he does not refocus?
- - a)
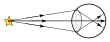
- - a)
- - b)

- - b)
- + c)

- + c)
29. An important principle that allows fiber optics to work is
- - a) total external refraction
- + b) total internal reflection
- - c) the Doppler shift
- - d) the invariance of the speed of light
- - e) partial internal absorption
30. What are examples of energy?
- - a) mgh where m is mass, g is gravity, and h is height
- + b) all of the above
- - c)
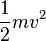
- - c)
- - d) heat
HTW T1 sample-v1s2
1. If you toss a coin into the air, the acceleration on the way down is
- ___ a) down
- ___ b) up
- ___ c) zero
2. Why don't we hear beats when two different notes on a piano are played at the same time?
- ___ a) The note is over by the time the first beat is heard
- ___ b) Reverberation usually stifles the beats
- ___ c) Echo usually stifles the beats
- ___ d) The beats happen so many times per second you can't hear them.
3. If you toss a coin into the air, the velocity on the way down is
- ___ a) zero
- ___ b) up
- ___ c) down
4. A car is headed due north and increasing its speed. It is also turning right because it is also traveling in a perfect circle. The velocity vector points
- ___ a) southwest
- ___ b) northwest
- ___ c) north
- ___ d) northeast
- ___ e) south
5. Mr. Smith starts at rest and accelerates to a speed of 2 m/s, in 6 seconds. He then travels at this speed for an additional 3 seconds. Then he decelerates uniformly, taking 4 seconds to come to rest. How far did he travel?
- ___ a) 13.0 meters
- ___ b) 16.0 meters
- ___ c) 15.0 meters
- ___ d) 17.0 meters
- ___ e) 14.0 meters
6. The focal point is where
- ___ a) rays meet if they are parallel to each other
- ___ b) rays meet whenever they are forming an image
- ___ c) rays meet if they were parallel to the optical axis before striking a lens
- ___ d) the center of the lens
- ___ e) rays meet whenever they pass through a lens
7. A tuning fork with a frequency of 440 Hz is played simultaneously with a tuning fork of 442 Hz. How many beats are heard in 10 seconds?
- ___ a) 60
- ___ b) 40
- ___ c) 30
- ___ d) 20
- ___ e) 50
8. A car is traveling east and speeding up. The acceleration is
- ___ a) to the east
- ___ b) zero
- ___ c) to the west
9. A car is headed due north and increasing its speed. It is also turning right because it is also traveling in a perfect circle. The acceleration vector points
- ___ a) north
- ___ b) northeast
- ___ c) southwest
- ___ d) northwest
- ___ e) south
10. What are examples of energy?
- ___ a) momentum
- ___ b) all of the above
- ___ c)
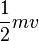
- ___ d) heat
11. ![]() Mr. Smith is gazing at something as shown in the figure to the left. Suppose he does not refocus, but attempts to stare at the star shown in the figures below. Which diagram depicts how the rays from the star would travel if he does not refocus?
Mr. Smith is gazing at something as shown in the figure to the left. Suppose he does not refocus, but attempts to stare at the star shown in the figures below. Which diagram depicts how the rays from the star would travel if he does not refocus?
- ___ a)
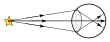
- ___ b)

- ___ c)

12. When light passes from air to glass
- ___ a) it bends away from the normal
- ___ b) the frequency increases
- ___ c) it does not bend
- ___ d) it bends towards the normal
- ___ e) the frequency decreases
13. In optics, normal means
- ___ a) parallel to the surface
- ___ b) to the right of the optical axis
- ___ c) to the left of the optical axis
- ___ d) perpendicular to the surface
14. The first paper that introduced quantum mechanics was the study of
- ___ a) light
- ___ b) energy
- ___ c) electrons
- ___ d) protons
15. Which lens has the shorter focal length?
- ___ a)
- ___ b)

- ___ c) They have the same focal lengh.
16. ![]() These two pulses will collide and produce
These two pulses will collide and produce
- ___ a) negative interference
- ___ b) positive interference
- ___ c) positive diffraction
- ___ d) negative diffraction
17. A car is traveling east and slowing down. The acceleration is
- ___ a) to the east
- ___ b) to the west
- ___ c) zero
18. What are examples of energy?
- ___ a) heat
- ___ b) mgh where m is mass, g is gravity, and h is height
- ___ c)
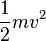
- ___ d) all of the above
19. Mr. Smith starts from rest and accelerates to 4 m/s in 5 seconds. How far did he travel?
- ___ a) 10.0 meters
- ___ b) 8.0 meters
- ___ c) 11.0 meters
- ___ d) 7.0 meters
- ___ e) 9.0 meters
20. What are the units of Plank's constant?
- ___ a) momentum x distance x mass
- ___ b) energy x time
- ___ c) none of the above
- ___ d) mass x velocity
- ___ e) all of the above
21. A dense rope is connected to a rope with less density (i.e. fewer kilograms per meter). If the rope is stretched and a wave is sent along high density rope,
- ___ a) the low density rope supports a wave with a higher frequency
- ___ b) the low density rope supports a wave with a higher speed
- ___ c) the low density rope supports a wave with a lower speed
- ___ d) the low density rope supports a wave with a lower frequency
22. A car is headed due north and increasing its speed. It is also turning left because it is also traveling in a perfect circle. The velocity vector points
- ___ a) north
- ___ b) southeast
- ___ c) northwest
- ___ d) northeast
- ___ e) northeast
23. Mr. Smith starts from rest and accelerates to 2 m/s in 3 seconds. How far did he travel?
- ___ a) 7.0 meters
- ___ b) 4.0 meters
- ___ c) 3.0 meters
- ___ d) 5.0 meters
- ___ e) 6.0 meters
24. Mr. Smith starts at rest and accelerates to a speed of 2 m/s, in 6 seconds. He then travels at this speed for an additional 3 seconds. Then he decelerates uniformly, taking 4 seconds to come to rest. How far did he travel?
- ___ a) 20.0 meters
- ___ b) 17.0 meters
- ___ c) 16.0 meters
- ___ d) 18.0 meters
- ___ e) 19.0 meters
25. Why do rough walls give a concert hall a “fuller” sound, compared to smooth walls?
- ___ a) The difference in path lengths creates more reverberation.
- ___ b) The difference in path lengths creates more echo.
- ___ c) Rough walls make for a louder sound.
26. Mr. Smith starts at rest and accelerates to a speed of 4 m/s, in 2 seconds. He then travels at this speed for an additional 3 seconds. Then he decelerates uniformly, taking 2 seconds to come to rest. How far did he travel?
- ___ a) 21.0 meters
- ___ b) 22.0 meters
- ___ c) 19.0 meters
- ___ d) 23.0 meters
- ___ e) 20.0 meters
27. ![]() These two pulses will collide and produce
These two pulses will collide and produce
- ___ a) positive interference
- ___ b) negative interference
- ___ c) positive diffraction
- ___ d) negative diffraction
28. As the Moon circles Earth, the acceleration of the Moon is
- ___ a) in the same direction as the Moon's velocity
- ___ b) away from Earth
- ___ c) opposite the direction of the Moon's velocity
- ___ d) towards Earth
- ___ e) zero
29. If a source of sound is moving towards you, the pitch becomes
- ___ a) unchanged
- ___ b) lower
- ___ c) higher
30.

Shown is a corrective lens by a person who needs glasses. This ray diagram illustrates
- ___ a) how a farsighted person might see an object that is too close for comfort
- ___ b) how a nearsighted person might see a distant object
- ___ c) how a nearsighted person might see an object that is too close for comfort
- ___ d) how a farsighted person might see a distant object
Key to HTW T1 sample-v1s2
1. If you toss a coin into the air, the acceleration on the way down is
- + a) down
- - b) up
- - c) zero
2. Why don't we hear beats when two different notes on a piano are played at the same time?
- - a) The note is over by the time the first beat is heard
- - b) Reverberation usually stifles the beats
- - c) Echo usually stifles the beats
- + d) The beats happen so many times per second you can't hear them.
3. If you toss a coin into the air, the velocity on the way down is
- - a) zero
- - b) up
- + c) down
4. A car is headed due north and increasing its speed. It is also turning right because it is also traveling in a perfect circle. The velocity vector points
- - a) southwest
- - b) northwest
- + c) north
- - d) northeast
- - e) south
5. Mr. Smith starts at rest and accelerates to a speed of 2 m/s, in 6 seconds. He then travels at this speed for an additional 3 seconds. Then he decelerates uniformly, taking 4 seconds to come to rest. How far did he travel?
- - a) 13.0 meters
- + b) 16.0 meters
- - c) 15.0 meters
- - d) 17.0 meters
- - e) 14.0 meters
6. The focal point is where
- - a) rays meet if they are parallel to each other
- - b) rays meet whenever they are forming an image
- + c) rays meet if they were parallel to the optical axis before striking a lens
- - d) the center of the lens
- - e) rays meet whenever they pass through a lens
7. A tuning fork with a frequency of 440 Hz is played simultaneously with a tuning fork of 442 Hz. How many beats are heard in 10 seconds?
- - a) 60
- - b) 40
- - c) 30
- + d) 20
- - e) 50
8. A car is traveling east and speeding up. The acceleration is
- + a) to the east
- - b) zero
- - c) to the west
9. A car is headed due north and increasing its speed. It is also turning right because it is also traveling in a perfect circle. The acceleration vector points
- - a) north
- + b) northeast
- - c) southwest
- - d) northwest
- - e) south
10. What are examples of energy?
- - a) momentum
- + b) all of the above
- - c)
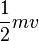
- - c)
- - d) heat
11. ![]() Mr. Smith is gazing at something as shown in the figure to the left. Suppose he does not refocus, but attempts to stare at the star shown in the figures below. Which diagram depicts how the rays from the star would travel if he does not refocus?
Mr. Smith is gazing at something as shown in the figure to the left. Suppose he does not refocus, but attempts to stare at the star shown in the figures below. Which diagram depicts how the rays from the star would travel if he does not refocus?
- - a)
- - a)
- + b)

- + b)
- - c)

- - c)
12. When light passes from air to glass
- - a) it bends away from the normal
- - b) the frequency increases
- - c) it does not bend
- + d) it bends towards the normal
- - e) the frequency decreases
13. In optics, normal means
- - a) parallel to the surface
- - b) to the right of the optical axis
- - c) to the left of the optical axis
- + d) perpendicular to the surface
14. The first paper that introduced quantum mechanics was the study of
- + a) light
- - b) energy
- - c) electrons
- - d) protons
15. Which lens has the shorter focal length?
- - a)

- - a)
- + b)

- + b)
- - c) They have the same focal lengh.
16. ![]() These two pulses will collide and produce
These two pulses will collide and produce
- + a) negative interference
- - b) positive interference
- - c) positive diffraction
- - d) negative diffraction
17. A car is traveling east and slowing down. The acceleration is
- - a) to the east
- + b) to the west
- - c) zero
18. What are examples of energy?
- - a) heat
- - b) mgh where m is mass, g is gravity, and h is height
- - c)
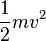
- - c)
- + d) all of the above
19. Mr. Smith starts from rest and accelerates to 4 m/s in 5 seconds. How far did he travel?
- + a) 10.0 meters
- - b) 8.0 meters
- - c) 11.0 meters
- - d) 7.0 meters
- - e) 9.0 meters
20. What are the units of Plank's constant?
- - a) momentum x distance x mass
- - b) energy x time
- - c) none of the above
- - d) mass x velocity
- + e) all of the above
21. A dense rope is connected to a rope with less density (i.e. fewer kilograms per meter). If the rope is stretched and a wave is sent along high density rope,
- - a) the low density rope supports a wave with a higher frequency
- + b) the low density rope supports a wave with a higher speed
- - c) the low density rope supports a wave with a lower speed
- - d) the low density rope supports a wave with a lower frequency
22. A car is headed due north and increasing its speed. It is also turning left because it is also traveling in a perfect circle. The velocity vector points
- + a) north
- - b) southeast
- - c) northwest
- - d) northeast
- - e) northeast
23. Mr. Smith starts from rest and accelerates to 2 m/s in 3 seconds. How far did he travel?
- - a) 7.0 meters
- - b) 4.0 meters
- + c) 3.0 meters
- - d) 5.0 meters
- - e) 6.0 meters
24. Mr. Smith starts at rest and accelerates to a speed of 2 m/s, in 6 seconds. He then travels at this speed for an additional 3 seconds. Then he decelerates uniformly, taking 4 seconds to come to rest. How far did he travel?
- - a) 20.0 meters
- - b) 17.0 meters
- + c) 16.0 meters
- - d) 18.0 meters
- - e) 19.0 meters
25. Why do rough walls give a concert hall a “fuller” sound, compared to smooth walls?
- + a) The difference in path lengths creates more reverberation.
- - b) The difference in path lengths creates more echo.
- - c) Rough walls make for a louder sound.
26. Mr. Smith starts at rest and accelerates to a speed of 4 m/s, in 2 seconds. He then travels at this speed for an additional 3 seconds. Then he decelerates uniformly, taking 2 seconds to come to rest. How far did he travel?
- - a) 21.0 meters
- - b) 22.0 meters
- - c) 19.0 meters
- - d) 23.0 meters
- + e) 20.0 meters
27. ![]() These two pulses will collide and produce
These two pulses will collide and produce
- + a) positive interference
- - b) negative interference
- - c) positive diffraction
- - d) negative diffraction
28. As the Moon circles Earth, the acceleration of the Moon is
- - a) in the same direction as the Moon's velocity
- - b) away from Earth
- - c) opposite the direction of the Moon's velocity
- + d) towards Earth
- - e) zero
29. If a source of sound is moving towards you, the pitch becomes
- - a) unchanged
- - b) lower
- + c) higher
30.

Shown is a corrective lens by a person who needs glasses. This ray diagram illustrates
- - a) how a farsighted person might see an object that is too close for comfort
- + b) how a nearsighted person might see a distant object
- - c) how a nearsighted person might see an object that is too close for comfort
- - d) how a farsighted person might see a distant object
HTW T1 sample-v2s2
1. What are the units of Plank's constant?
- ___ a) all of the above
- ___ b) momentum x distance x mass
- ___ c) energy x time
- ___ d) none of the above
- ___ e) mass x velocity
2. Which lens has the shorter focal length?
- ___ a) They have the same focal lengh.
- ___ b)

- ___ c)

3. If you toss a coin into the air, the velocity on the way down is
- ___ a) zero
- ___ b) up
- ___ c) down
4. A tuning fork with a frequency of 440 Hz is played simultaneously with a tuning fork of 442 Hz. How many beats are heard in 10 seconds?
- ___ a) 40
- ___ b) 60
- ___ c) 20
- ___ d) 30
- ___ e) 50
5. If a source of sound is moving towards you, the pitch becomes
- ___ a) lower
- ___ b) unchanged
- ___ c) higher
6. In optics, normal means
- ___ a) to the left of the optical axis
- ___ b) to the right of the optical axis
- ___ c) perpendicular to the surface
- ___ d) parallel to the surface
7. Mr. Smith starts from rest and accelerates to 4 m/s in 5 seconds. How far did he travel?
- ___ a) 8.0 meters
- ___ b) 10.0 meters
- ___ c) 9.0 meters
- ___ d) 11.0 meters
- ___ e) 7.0 meters
8. Why do rough walls give a concert hall a “fuller” sound, compared to smooth walls?
- ___ a) The difference in path lengths creates more reverberation.
- ___ b) Rough walls make for a louder sound.
- ___ c) The difference in path lengths creates more echo.
9. When light passes from air to glass
- ___ a) the frequency increases
- ___ b) it bends towards the normal
- ___ c) it does not bend
- ___ d) it bends away from the normal
- ___ e) the frequency decreases
10. ![]() These two pulses will collide and produce
These two pulses will collide and produce
- ___ a) negative diffraction
- ___ b) positive diffraction
- ___ c) negative interference
- ___ d) positive interference
11. A car is traveling east and speeding up. The acceleration is
- ___ a) to the west
- ___ b) zero
- ___ c) to the east
12. The focal point is where
- ___ a) rays meet if they are parallel to each other
- ___ b) rays meet whenever they pass through a lens
- ___ c) the center of the lens
- ___ d) rays meet if they were parallel to the optical axis before striking a lens
- ___ e) rays meet whenever they are forming an image
13. The first paper that introduced quantum mechanics was the study of
- ___ a) electrons
- ___ b) light
- ___ c) energy
- ___ d) protons
14. If you toss a coin into the air, the acceleration on the way down is
- ___ a) up
- ___ b) zero
- ___ c) down
15. A dense rope is connected to a rope with less density (i.e. fewer kilograms per meter). If the rope is stretched and a wave is sent along high density rope,
- ___ a) the low density rope supports a wave with a lower frequency
- ___ b) the low density rope supports a wave with a higher frequency
- ___ c) the low density rope supports a wave with a lower speed
- ___ d) the low density rope supports a wave with a higher speed
16. A car is traveling east and slowing down. The acceleration is
- ___ a) zero
- ___ b) to the east
- ___ c) to the west
17. A car is headed due north and increasing its speed. It is also turning right because it is also traveling in a perfect circle. The acceleration vector points
- ___ a) north
- ___ b) south
- ___ c) southwest
- ___ d) northwest
- ___ e) northeast
18. A car is headed due north and increasing its speed. It is also turning right because it is also traveling in a perfect circle. The velocity vector points
- ___ a) south
- ___ b) north
- ___ c) southwest
- ___ d) northwest
- ___ e) northeast
19. Mr. Smith starts at rest and accelerates to a speed of 2 m/s, in 6 seconds. He then travels at this speed for an additional 3 seconds. Then he decelerates uniformly, taking 4 seconds to come to rest. How far did he travel?
- ___ a) 15.0 meters
- ___ b) 16.0 meters
- ___ c) 17.0 meters
- ___ d) 14.0 meters
- ___ e) 13.0 meters
20. What are examples of energy?
- ___ a) mgh where m is mass, g is gravity, and h is height
- ___ b) heat
- ___ c)
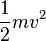
- ___ d) all of the above
21. What are examples of energy?
- ___ a) heat
- ___ b) all of the above
- ___ c)
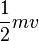
- ___ d) momentum
22. Mr. Smith starts from rest and accelerates to 2 m/s in 3 seconds. How far did he travel?
- ___ a) 4.0 meters
- ___ b) 3.0 meters
- ___ c) 6.0 meters
- ___ d) 7.0 meters
- ___ e) 5.0 meters
23. Mr. Smith starts at rest and accelerates to a speed of 4 m/s, in 2 seconds. He then travels at this speed for an additional 3 seconds. Then he decelerates uniformly, taking 2 seconds to come to rest. How far did he travel?
- ___ a) 22.0 meters
- ___ b) 20.0 meters
- ___ c) 21.0 meters
- ___ d) 23.0 meters
- ___ e) 19.0 meters
24.

Shown is a corrective lens by a person who needs glasses. This ray diagram illustrates
- ___ a) how a nearsighted person might see a distant object
- ___ b) how a farsighted person might see an object that is too close for comfort
- ___ c) how a farsighted person might see a distant object
- ___ d) how a nearsighted person might see an object that is too close for comfort
25. ![]() Mr. Smith is gazing at something as shown in the figure to the left. Suppose he does not refocus, but attempts to stare at the star shown in the figures below. Which diagram depicts how the rays from the star would travel if he does not refocus?
Mr. Smith is gazing at something as shown in the figure to the left. Suppose he does not refocus, but attempts to stare at the star shown in the figures below. Which diagram depicts how the rays from the star would travel if he does not refocus?
- ___ a)
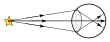
- ___ b)

- ___ c)

26. As the Moon circles Earth, the acceleration of the Moon is
- ___ a) zero
- ___ b) in the same direction as the Moon's velocity
- ___ c) opposite the direction of the Moon's velocity
- ___ d) towards Earth
- ___ e) away from Earth
27. Why don't we hear beats when two different notes on a piano are played at the same time?
- ___ a) The beats happen so many times per second you can't hear them.
- ___ b) Reverberation usually stifles the beats
- ___ c) The note is over by the time the first beat is heard
- ___ d) Echo usually stifles the beats
28. Mr. Smith starts at rest and accelerates to a speed of 2 m/s, in 6 seconds. He then travels at this speed for an additional 3 seconds. Then he decelerates uniformly, taking 4 seconds to come to rest. How far did he travel?
- ___ a) 16.0 meters
- ___ b) 17.0 meters
- ___ c) 20.0 meters
- ___ d) 18.0 meters
- ___ e) 19.0 meters
29. A car is headed due north and increasing its speed. It is also turning left because it is also traveling in a perfect circle. The velocity vector points
- ___ a) northeast
- ___ b) northwest
- ___ c) southeast
- ___ d) northeast
- ___ e) north
30. ![]() These two pulses will collide and produce
These two pulses will collide and produce
- ___ a) negative diffraction
- ___ b) positive diffraction
- ___ c) positive interference
- ___ d) negative interference
Key to HTW T1 sample-v2s2
1. What are the units of Plank's constant?
- + a) all of the above
- - b) momentum x distance x mass
- - c) energy x time
- - d) none of the above
- - e) mass x velocity
2. Which lens has the shorter focal length?
- - a) They have the same focal lengh.
- - b)

- - b)
- + c)

- + c)
3. If you toss a coin into the air, the velocity on the way down is
- - a) zero
- - b) up
- + c) down
4. A tuning fork with a frequency of 440 Hz is played simultaneously with a tuning fork of 442 Hz. How many beats are heard in 10 seconds?
- - a) 40
- - b) 60
- + c) 20
- - d) 30
- - e) 50
5. If a source of sound is moving towards you, the pitch becomes
- - a) lower
- - b) unchanged
- + c) higher
6. In optics, normal means
- - a) to the left of the optical axis
- - b) to the right of the optical axis
- + c) perpendicular to the surface
- - d) parallel to the surface
7. Mr. Smith starts from rest and accelerates to 4 m/s in 5 seconds. How far did he travel?
- - a) 8.0 meters
- + b) 10.0 meters
- - c) 9.0 meters
- - d) 11.0 meters
- - e) 7.0 meters
8. Why do rough walls give a concert hall a “fuller” sound, compared to smooth walls?
- + a) The difference in path lengths creates more reverberation.
- - b) Rough walls make for a louder sound.
- - c) The difference in path lengths creates more echo.
9. When light passes from air to glass
- - a) the frequency increases
- + b) it bends towards the normal
- - c) it does not bend
- - d) it bends away from the normal
- - e) the frequency decreases
10. ![]() These two pulses will collide and produce
These two pulses will collide and produce
- - a) negative diffraction
- - b) positive diffraction
- + c) negative interference
- - d) positive interference
11. A car is traveling east and speeding up. The acceleration is
- - a) to the west
- - b) zero
- + c) to the east
12. The focal point is where
- - a) rays meet if they are parallel to each other
- - b) rays meet whenever they pass through a lens
- - c) the center of the lens
- + d) rays meet if they were parallel to the optical axis before striking a lens
- - e) rays meet whenever they are forming an image
13. The first paper that introduced quantum mechanics was the study of
- - a) electrons
- + b) light
- - c) energy
- - d) protons
14. If you toss a coin into the air, the acceleration on the way down is
- - a) up
- - b) zero
- + c) down
15. A dense rope is connected to a rope with less density (i.e. fewer kilograms per meter). If the rope is stretched and a wave is sent along high density rope,
- - a) the low density rope supports a wave with a lower frequency
- - b) the low density rope supports a wave with a higher frequency
- - c) the low density rope supports a wave with a lower speed
- + d) the low density rope supports a wave with a higher speed
16. A car is traveling east and slowing down. The acceleration is
- - a) zero
- - b) to the east
- + c) to the west
17. A car is headed due north and increasing its speed. It is also turning right because it is also traveling in a perfect circle. The acceleration vector points
- - a) north
- - b) south
- - c) southwest
- - d) northwest
- + e) northeast
18. A car is headed due north and increasing its speed. It is also turning right because it is also traveling in a perfect circle. The velocity vector points
- - a) south
- + b) north
- - c) southwest
- - d) northwest
- - e) northeast
19. Mr. Smith starts at rest and accelerates to a speed of 2 m/s, in 6 seconds. He then travels at this speed for an additional 3 seconds. Then he decelerates uniformly, taking 4 seconds to come to rest. How far did he travel?
- - a) 15.0 meters
- + b) 16.0 meters
- - c) 17.0 meters
- - d) 14.0 meters
- - e) 13.0 meters
20. What are examples of energy?
- - a) mgh where m is mass, g is gravity, and h is height
- - b) heat
- - c)
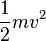
- - c)
- + d) all of the above
21. What are examples of energy?
- - a) heat
- + b) all of the above
- - c)
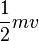
- - c)
- - d) momentum
22. Mr. Smith starts from rest and accelerates to 2 m/s in 3 seconds. How far did he travel?
- - a) 4.0 meters
- + b) 3.0 meters
- - c) 6.0 meters
- - d) 7.0 meters
- - e) 5.0 meters
23. Mr. Smith starts at rest and accelerates to a speed of 4 m/s, in 2 seconds. He then travels at this speed for an additional 3 seconds. Then he decelerates uniformly, taking 2 seconds to come to rest. How far did he travel?
- - a) 22.0 meters
- + b) 20.0 meters
- - c) 21.0 meters
- - d) 23.0 meters
- - e) 19.0 meters
24.

Shown is a corrective lens by a person who needs glasses. This ray diagram illustrates
- + a) how a nearsighted person might see a distant object
- - b) how a farsighted person might see an object that is too close for comfort
- - c) how a farsighted person might see a distant object
- - d) how a nearsighted person might see an object that is too close for comfort
25. ![]() Mr. Smith is gazing at something as shown in the figure to the left. Suppose he does not refocus, but attempts to stare at the star shown in the figures below. Which diagram depicts how the rays from the star would travel if he does not refocus?
Mr. Smith is gazing at something as shown in the figure to the left. Suppose he does not refocus, but attempts to stare at the star shown in the figures below. Which diagram depicts how the rays from the star would travel if he does not refocus?
- - a)
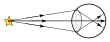
- - a)
- - b)

- - b)
- + c)

- + c)
26. As the Moon circles Earth, the acceleration of the Moon is
- - a) zero
- - b) in the same direction as the Moon's velocity
- - c) opposite the direction of the Moon's velocity
- + d) towards Earth
- - e) away from Earth
27. Why don't we hear beats when two different notes on a piano are played at the same time?
- + a) The beats happen so many times per second you can't hear them.
- - b) Reverberation usually stifles the beats
- - c) The note is over by the time the first beat is heard
- - d) Echo usually stifles the beats
28. Mr. Smith starts at rest and accelerates to a speed of 2 m/s, in 6 seconds. He then travels at this speed for an additional 3 seconds. Then he decelerates uniformly, taking 4 seconds to come to rest. How far did he travel?
- + a) 16.0 meters
- - b) 17.0 meters
- - c) 20.0 meters
- - d) 18.0 meters
- - e) 19.0 meters
29. A car is headed due north and increasing its speed. It is also turning left because it is also traveling in a perfect circle. The velocity vector points
- - a) northeast
- - b) northwest
- - c) southeast
- - d) northeast
- + e) north
30. ![]() These two pulses will collide and produce
These two pulses will collide and produce
- - a) negative diffraction
- - b) positive diffraction
- + c) positive interference
- - d) negative interference
- Attribution (for quiz questions) under CC-by-SA license
- http://en.wikiversity.org/w/index.php?title=Physics_equations/25-Geometric_Optics/Q:image&oldid=1395836
- http://en.wikiversity.org/wiki/How_things_work_college_course/Waves_(Physics_Classroom)
- http://en.wikiversity.org/w/index.php?title=How_things_work_college_course/Quantum_mechanics_timeline/Quiz&oldid=1396075
- http://en.wikiversity.org/w/index.php?title=How_things_work_college_course/Motion_simple_arithmetic&oldid=1395847
- http://en.wikiversity.org/w/index.php?title=How_things_work_college_course/Conceptual_physics_wikiquizzes/Velocity_and_acceleration&oldid=137851
- http://en.wikiversity.org/w/index.php?title=Physics_equations/25-Geometric_Optics/Q:vision&oldid=1378615
- Study guide
- http://en.wikiversity.org/w/index.php?title=Light_and_optics&oldid=1326970
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Optics - http://www.physicsclassroom.com/class/waves
- http://en.wikiversity.org/w/index.php?title=How_things_work_college_course/Quantum_mechanics_timeline&oldid=1383060
- http://en.wikiversity.org/w/index.php?title=Physics_equations/Sheet/All_chapters&oldid=1283423
- http://en.wikibooks.org/w/index.php?title=Physics_Study_Guide&oldid=2516212
- http://en.wikiversity.org/wiki/Physics_equations/Sheet/All_chapters
http://en.wikiversity.org/wiki/Light_and_optics