Quizbank/College Physics/II T1
< Quizbank < College PhysicsTrigPhysT1_151021
If you are reading this as a Wikiversity page, proper pagebreaks should result if printed using your browser's print option. On Chrome, Explorer, and Firefox, this option is available in the upper right hand corner of your screen. But, pagebreaks do not render properly if you use "Printable version" on Wikiversity's Print/export option on the left-hand sidebar.
- This document contains either a study guide OR pairs of exams taken from the same exam bank
- If two exams have the same s-number, then v1 and v2 have the same questions, presented in different (random) order.
- Exams with different s-numbers have different questions and may not have the same difficulty.
- Click items in the table of contents and appropriate page should be reached. This feature should allow you to print only those pages that you need.
- At the end of this document
- Attribution for the quizzes identifies where the questions were obtained
- Study guide links reading materials and/or relevant equations.
TrigPhysT1_151021-v1s1
1. What is the speed of a transverse wave on a string if the string is 0.45 m long, clamped at both ends, and harmonic number 4 has a frequency of 996 Hz?
- ___a) 1.53 x 102 unit
- ___b) 1.85 x 102 unit
- ___c) 2.24 x 102 unit
- ___d) 2.72 x 102 unit
- ___e) 3.29 x 102 unit
2. ![]() Two signals (dashed) add to a solid
Two signals (dashed) add to a solid
- ___ a) dissonance
- ___ b) octave
- ___ c) fifth
3. A 0.047 kg mass is on a spring that causes the frequency of oscillation to be 26 cycles per second. The maximum velocity is 90.5 m/s. What is the maximum force on the mass?
- ___a) 1.5 x 102 N
- ___b) 3.2 x 102 N
- ___c) 6.9 x 102 N
- ___d) 1.5 x 103 N
- ___e) 3.2 x 103 N
4. A spring with spring constant 1.7 kN/m undergoes simple harmonic motion with a frequency of 3.9 kHz. The maximum force is 8.6 N. What is the total energy?
- ___a) 2.18 x 10-4 J
- ___b) 6.88 x 10-4 J
- ___c) 2.18 x 10-3 J
- ___d) 6.88 x 10-3 J
- ___e) 2.18 x 10-2 J
5. 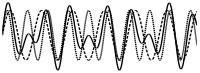 Two signals (dashed) add to a solid
Two signals (dashed) add to a solid
- ___ a) dissonance
- ___ b) fifth
- ___ c) octave
6. What happens to the wavelength on a wave on a stretched string if the wave passes from lightweight (low density) region of the rope to a heavy (high density) rope?
- ___ a) the wavelength gets shorter
- ___ b) the wavelength gets longer
- ___ c) the wavelength stays the same
7. ![]() These two pulses will collide and produce
These two pulses will collide and produce
- ___ a) positive interference
- ___ b) negative diffraction
- ___ c) negative interference
- ___ d) positive diffraction
8. A tuning fork with a frequency of 440 Hz is played simultaneously with a tuning fork of 442 Hz. How many beats are heard in 10 seconds?
- ___ a) 30
- ___ b) 20
- ___ c) 50
- ___ d) 60
- ___ e) 40
9. When a wave is reflected off a stationary barrier, the reflected wave
- ___ a) has lower amplitude than the incident wave
- ___ b) both of these are true
- ___ c) has higher frequency than the incident wave
10. While standing 0.58 km from a cliff, you measure the echo time to be 3.38 seconds. What is the temperature?
- ___a) 1.53 x 101Celsius
- ___b) 1.76 x 101Celsius
- ___c) 2.03 x 101Celsius
- ___d) 2.35 x 101Celsius
- ___e) 2.71 x 101Celsius
11. ![]() These two pulses will collide and produce
These two pulses will collide and produce
- ___ a) positive diffraction
- ___ b) negative interference
- ___ c) negative diffraction
- ___ d) positive interference
12. Why don't we hear beats when two different notes on a piano are played at the same time?
- ___ a) Reverberation usually stifles the beats
- ___ b) Echo usually stifles the beats
- ___ c) The note is over by the time the first beat is heard
- ___ d) The beats happen so many times per second you can't hear them.
13. Why do rough walls give a concert hall a “fuller” sound, compared to smooth walls?
- ___ a) The difference in path lengths creates more reverberation.
- ___ b) The difference in path lengths creates more echo.
- ___ c) Rough walls make for a louder sound.
14. A spring of spring constant 8.7 kN/m causes a mass to move with a period of 5.2 ms. The maximum displacement is 7.1 mm. What is the maximum kinetic energy?
- ___a) 2.19 x 10-1 J
- ___b) 6.93 x 10-1 J
- ___c) 2.19 x 100 J
- ___d) 6.93 x 100 J
- ___e) 2.19 x 101 J
15. Comparing a typical church to a professional baseball stadium, the church is likely to have
- ___ a) both reverberation and echo
- ___ b) neither reverberation nor echo
- ___ c) echo instead of reverberation
- ___ d) reverberation instead of echo
Key to TrigPhysT1_151021-v1s1
1. What is the speed of a transverse wave on a string if the string is 0.45 m long, clamped at both ends, and harmonic number 4 has a frequency of 996 Hz?
- -a) 1.53 x 102 unit
- -b) 1.85 x 102 unit
- +c) 2.24 x 102 unit
- -d) 2.72 x 102 unit
- -e) 3.29 x 102 unit
2. ![]() Two signals (dashed) add to a solid
Two signals (dashed) add to a solid
- - a) dissonance
- - b) octave
- + c) fifth
3. A 0.047 kg mass is on a spring that causes the frequency of oscillation to be 26 cycles per second. The maximum velocity is 90.5 m/s. What is the maximum force on the mass?
- -a) 1.5 x 102 N
- -b) 3.2 x 102 N
- +c) 6.9 x 102 N
- -d) 1.5 x 103 N
- -e) 3.2 x 103 N
4. A spring with spring constant 1.7 kN/m undergoes simple harmonic motion with a frequency of 3.9 kHz. The maximum force is 8.6 N. What is the total energy?
- -a) 2.18 x 10-4 J
- -b) 6.88 x 10-4 J
- -c) 2.18 x 10-3 J
- -d) 6.88 x 10-3 J
- +e) 2.18 x 10-2 J
5.  Two signals (dashed) add to a solid
Two signals (dashed) add to a solid
- + a) dissonance
- - b) fifth
- - c) octave
6. What happens to the wavelength on a wave on a stretched string if the wave passes from lightweight (low density) region of the rope to a heavy (high density) rope?
- - a) the wavelength gets shorter
- + b) the wavelength gets longer
- - c) the wavelength stays the same
7. ![]() These two pulses will collide and produce
These two pulses will collide and produce
- + a) positive interference
- - b) negative diffraction
- - c) negative interference
- - d) positive diffraction
8. A tuning fork with a frequency of 440 Hz is played simultaneously with a tuning fork of 442 Hz. How many beats are heard in 10 seconds?
- - a) 30
- + b) 20
- - c) 50
- - d) 60
- - e) 40
9. When a wave is reflected off a stationary barrier, the reflected wave
- + a) has lower amplitude than the incident wave
- - b) both of these are true
- - c) has higher frequency than the incident wave
10. While standing 0.58 km from a cliff, you measure the echo time to be 3.38 seconds. What is the temperature?
- -a) 1.53 x 101Celsius
- -b) 1.76 x 101Celsius
- +c) 2.03 x 101Celsius
- -d) 2.35 x 101Celsius
- -e) 2.71 x 101Celsius
11. ![]() These two pulses will collide and produce
These two pulses will collide and produce
- - a) positive diffraction
- - b) negative interference
- - c) negative diffraction
- + d) positive interference
12. Why don't we hear beats when two different notes on a piano are played at the same time?
- - a) Reverberation usually stifles the beats
- - b) Echo usually stifles the beats
- - c) The note is over by the time the first beat is heard
- + d) The beats happen so many times per second you can't hear them.
13. Why do rough walls give a concert hall a “fuller” sound, compared to smooth walls?
- + a) The difference in path lengths creates more reverberation.
- - b) The difference in path lengths creates more echo.
- - c) Rough walls make for a louder sound.
14. A spring of spring constant 8.7 kN/m causes a mass to move with a period of 5.2 ms. The maximum displacement is 7.1 mm. What is the maximum kinetic energy?
- +a) 2.19 x 10-1 J
- -b) 6.93 x 10-1 J
- -c) 2.19 x 100 J
- -d) 6.93 x 100 J
- -e) 2.19 x 101 J
15. Comparing a typical church to a professional baseball stadium, the church is likely to have
- - a) both reverberation and echo
- - b) neither reverberation nor echo
- - c) echo instead of reverberation
- + d) reverberation instead of echo
TrigPhysT1_151021-v2s1
1. While standing 0.94 km from a cliff, you measure the echo time to be 5.522 seconds. What is the temperature?
- ___a) 1.57 x 101Celsius
- ___b) 1.81 x 101Celsius
- ___c) 2.09 x 101Celsius
- ___d) 2.41 x 101Celsius
- ___e) 2.79 x 101Celsius
2. A tuning fork with a frequency of 440 Hz is played simultaneously with a tuning fork of 442 Hz. How many beats are heard in 10 seconds?
- ___ a) 30
- ___ b) 60
- ___ c) 50
- ___ d) 40
- ___ e) 20
3. Comparing a typical church to a professional baseball stadium, the church is likely to have
- ___ a) echo instead of reverberation
- ___ b) reverberation instead of echo
- ___ c) neither reverberation nor echo
- ___ d) both reverberation and echo
4. Why don't we hear beats when two different notes on a piano are played at the same time?
- ___ a) Echo usually stifles the beats
- ___ b) Reverberation usually stifles the beats
- ___ c) The beats happen so many times per second you can't hear them.
- ___ d) The note is over by the time the first beat is heard
5. A spring with spring constant 2.7 kN/m undergoes simple harmonic motion with a frequency of 3.1 kHz. The maximum force is 6.3 N. What is the total energy?
- ___a) 2.32 x 10-3 J
- ___b) 7.35 x 10-3 J
- ___c) 2.32 x 10-2 J
- ___d) 7.35 x 10-2 J
- ___e) 2.32 x 10-1 J
6. ![]() These two pulses will collide and produce
These two pulses will collide and produce
- ___ a) negative diffraction
- ___ b) negative interference
- ___ c) positive diffraction
- ___ d) positive interference
7. What happens to the wavelength on a wave on a stretched string if the wave passes from lightweight (low density) region of the rope to a heavy (high density) rope?
- ___ a) the wavelength stays the same
- ___ b) the wavelength gets longer
- ___ c) the wavelength gets shorter
8. A 0.062 kg mass is on a spring that causes the frequency of oscillation to be 65 cycles per second. The maximum velocity is 70.2 m/s. What is the maximum force on the mass?
- ___a) 1.8 x 103 N
- ___b) 3.8 x 103 N
- ___c) 8.3 x 103 N
- ___d) 1.8 x 104 N
- ___e) 3.8 x 104 N
9.  Two signals (dashed) add to a solid
Two signals (dashed) add to a solid
- ___ a) fifth
- ___ b) dissonance
- ___ c) octave
10. A spring of spring constant 8.7 kN/m causes a mass to move with a period of 5.2 ms. The maximum displacement is 7.1 mm. What is the maximum kinetic energy?
- ___a) 2.19 x 10-1 J
- ___b) 6.93 x 10-1 J
- ___c) 2.19 x 100 J
- ___d) 6.93 x 100 J
- ___e) 2.19 x 101 J
11. ![]() Two signals (dashed) add to a solid
Two signals (dashed) add to a solid
- ___ a) fifth
- ___ b) dissonance
- ___ c) octave
12. When a wave is reflected off a stationary barrier, the reflected wave
- ___ a) both of these are true
- ___ b) has higher frequency than the incident wave
- ___ c) has lower amplitude than the incident wave
13. Why do rough walls give a concert hall a “fuller” sound, compared to smooth walls?
- ___ a) Rough walls make for a louder sound.
- ___ b) The difference in path lengths creates more reverberation.
- ___ c) The difference in path lengths creates more echo.
14. What is the speed of a transverse wave on a string if the string is 1.19 m long, clamped at both ends, and harmonic number 6 has a frequency of 834 Hz?
- ___a) 2.25 x 102 unit
- ___b) 2.73 x 102 unit
- ___c) 3.31 x 102 unit
- ___d) 4.01 x 102 unit
- ___e) 4.86 x 102 unit
15. ![]() These two pulses will collide and produce
These two pulses will collide and produce
- ___ a) positive diffraction
- ___ b) positive interference
- ___ c) negative diffraction
- ___ d) negative interference
Key to TrigPhysT1_151021-v2s1
1. While standing 0.94 km from a cliff, you measure the echo time to be 5.522 seconds. What is the temperature?
- +a) 1.57 x 101Celsius
- -b) 1.81 x 101Celsius
- -c) 2.09 x 101Celsius
- -d) 2.41 x 101Celsius
- -e) 2.79 x 101Celsius
2. A tuning fork with a frequency of 440 Hz is played simultaneously with a tuning fork of 442 Hz. How many beats are heard in 10 seconds?
- - a) 30
- - b) 60
- - c) 50
- - d) 40
- + e) 20
3. Comparing a typical church to a professional baseball stadium, the church is likely to have
- - a) echo instead of reverberation
- + b) reverberation instead of echo
- - c) neither reverberation nor echo
- - d) both reverberation and echo
4. Why don't we hear beats when two different notes on a piano are played at the same time?
- - a) Echo usually stifles the beats
- - b) Reverberation usually stifles the beats
- + c) The beats happen so many times per second you can't hear them.
- - d) The note is over by the time the first beat is heard
5. A spring with spring constant 2.7 kN/m undergoes simple harmonic motion with a frequency of 3.1 kHz. The maximum force is 6.3 N. What is the total energy?
- -a) 2.32 x 10-3 J
- +b) 7.35 x 10-3 J
- -c) 2.32 x 10-2 J
- -d) 7.35 x 10-2 J
- -e) 2.32 x 10-1 J
6. ![]() These two pulses will collide and produce
These two pulses will collide and produce
- - a) negative diffraction
- - b) negative interference
- - c) positive diffraction
- + d) positive interference
7. What happens to the wavelength on a wave on a stretched string if the wave passes from lightweight (low density) region of the rope to a heavy (high density) rope?
- - a) the wavelength stays the same
- + b) the wavelength gets longer
- - c) the wavelength gets shorter
8. A 0.062 kg mass is on a spring that causes the frequency of oscillation to be 65 cycles per second. The maximum velocity is 70.2 m/s. What is the maximum force on the mass?
- +a) 1.8 x 103 N
- -b) 3.8 x 103 N
- -c) 8.3 x 103 N
- -d) 1.8 x 104 N
- -e) 3.8 x 104 N
9.  Two signals (dashed) add to a solid
Two signals (dashed) add to a solid
- - a) fifth
- + b) dissonance
- - c) octave
10. A spring of spring constant 8.7 kN/m causes a mass to move with a period of 5.2 ms. The maximum displacement is 7.1 mm. What is the maximum kinetic energy?
- +a) 2.19 x 10-1 J
- -b) 6.93 x 10-1 J
- -c) 2.19 x 100 J
- -d) 6.93 x 100 J
- -e) 2.19 x 101 J
11. ![]() Two signals (dashed) add to a solid
Two signals (dashed) add to a solid
- + a) fifth
- - b) dissonance
- - c) octave
12. When a wave is reflected off a stationary barrier, the reflected wave
- - a) both of these are true
- - b) has higher frequency than the incident wave
- + c) has lower amplitude than the incident wave
13. Why do rough walls give a concert hall a “fuller” sound, compared to smooth walls?
- - a) Rough walls make for a louder sound.
- + b) The difference in path lengths creates more reverberation.
- - c) The difference in path lengths creates more echo.
14. What is the speed of a transverse wave on a string if the string is 1.19 m long, clamped at both ends, and harmonic number 6 has a frequency of 834 Hz?
- -a) 2.25 x 102 unit
- -b) 2.73 x 102 unit
- +c) 3.31 x 102 unit
- -d) 4.01 x 102 unit
- -e) 4.86 x 102 unit
15. ![]() These two pulses will collide and produce
These two pulses will collide and produce
- - a) positive diffraction
- + b) positive interference
- - c) negative diffraction
- - d) negative interference
TrigPhysT1_151021-v1s2
1. A spring of spring constant 2.9 kN/m causes a mass to move with a period of 5.2 ms. The maximum displacement is 3.8 mm. What is the maximum kinetic energy?
- ___a) 2.09 x 10-3 J
- ___b) 6.62 x 10-3 J
- ___c) 2.09 x 10-2 J
- ___d) 6.62 x 10-2 J
- ___e) 2.09 x 10-1 J
2. When a wave is reflected off a stationary barrier, the reflected wave
- ___ a) both of these are true
- ___ b) has lower amplitude than the incident wave
- ___ c) has higher frequency than the incident wave
3.  Two signals (dashed) add to a solid
Two signals (dashed) add to a solid
- ___ a) fifth
- ___ b) octave
- ___ c) dissonance
4. Why do rough walls give a concert hall a “fuller” sound, compared to smooth walls?
- ___ a) The difference in path lengths creates more reverberation.
- ___ b) Rough walls make for a louder sound.
- ___ c) The difference in path lengths creates more echo.
5. What happens to the wavelength on a wave on a stretched string if the wave passes from lightweight (low density) region of the rope to a heavy (high density) rope?
- ___ a) the wavelength gets shorter
- ___ b) the wavelength stays the same
- ___ c) the wavelength gets longer
6. A spring with spring constant 9.6 kN/m is attached to a 9.1 gram mass. The maximum acelleration is 1.6 m/s2. What is the maximum displacement?
- ___a) 4.8 x 10-7 m
- ___b) 1.52 x 10-6 m
- ___c) 4.8 x 10-6 m
- ___d) 1.52 x 10-5 m
- ___e) 4.8 x 10-5 m
7. While standing 0.76 km from a cliff, you measure the echo time to be 4.339 seconds. What is the temperature?
- ___a) 2.83 x 101Celsius
- ___b) 3.26 x 101Celsius
- ___c) 3.77 x 101Celsius
- ___d) 4.35 x 101Celsius
- ___e) 5.03 x 101Celsius
8. A dense rope is connected to a rope with less density (i.e. fewer kilograms per meter). If the rope is stretched and a wave is sent along high density rope,
- ___ a) the low density rope supports a wave with a higher speed
- ___ b) the low density rope supports a wave with a lower frequency
- ___ c) the low density rope supports a wave with a higher frequency
- ___ d) the low density rope supports a wave with a lower speed
9. The temperature is -3 degrees Celsius, and you are standing 0.66 km from a cliff. What is the echo time?
- ___a) 2.949 x 100 seconds
- ___b) 3.184 x 100 seconds
- ___c) 3.438 x 100 seconds
- ___d) 3.713 x 100 seconds
- ___e) 4.009 x 100 seconds
10. ![]() These two pulses will collide and produce
These two pulses will collide and produce
- ___ a) negative diffraction
- ___ b) positive diffraction
- ___ c) negative interference
- ___ d) positive interference
11. If you start moving towards a source of sound, the pitch becomes
- ___ a) unchanged
- ___ b) higher
- ___ c) lower
12. A spring with spring constant 2.8 kN/m undergoes simple harmonic motion with a frequency of 8.5 kHz. The maximum force is 8.2 N. What is the total energy?
- ___a) 1.2 x 10-2 J
- ___b) 3.8 x 10-2 J
- ___c) 1.2 x 10-1 J
- ___d) 3.8 x 10-1 J
- ___e) 1.2 x 100 J
13. People don't usually perceive an echo when
- ___ a) it takes more than a tenth of a second after the original sound to arrive
- ___ b) it arrives at a higher pitch
- ___ c) it arrives at exactly the same pitch
- ___ d) it arrives less than a tenth of a second after the original sound
- ___ e) it arrives at a lower pitch
14. ![]() Two signals (dashed) add to a solid
Two signals (dashed) add to a solid
- ___ a) octave
- ___ b) dissonance
- ___ c) fifth
15. Comparing a typical church to a professional baseball stadium, the church is likely to have
- ___ a) neither reverberation nor echo
- ___ b) both reverberation and echo
- ___ c) reverberation instead of echo
- ___ d) echo instead of reverberation
Key to TrigPhysT1_151021-v1s2
1. A spring of spring constant 2.9 kN/m causes a mass to move with a period of 5.2 ms. The maximum displacement is 3.8 mm. What is the maximum kinetic energy?
- -a) 2.09 x 10-3 J
- -b) 6.62 x 10-3 J
- +c) 2.09 x 10-2 J
- -d) 6.62 x 10-2 J
- -e) 2.09 x 10-1 J
2. When a wave is reflected off a stationary barrier, the reflected wave
- - a) both of these are true
- + b) has lower amplitude than the incident wave
- - c) has higher frequency than the incident wave
3.  Two signals (dashed) add to a solid
Two signals (dashed) add to a solid
- - a) fifth
- - b) octave
- + c) dissonance
4. Why do rough walls give a concert hall a “fuller” sound, compared to smooth walls?
- + a) The difference in path lengths creates more reverberation.
- - b) Rough walls make for a louder sound.
- - c) The difference in path lengths creates more echo.
5. What happens to the wavelength on a wave on a stretched string if the wave passes from lightweight (low density) region of the rope to a heavy (high density) rope?
- - a) the wavelength gets shorter
- - b) the wavelength stays the same
- + c) the wavelength gets longer
6. A spring with spring constant 9.6 kN/m is attached to a 9.1 gram mass. The maximum acelleration is 1.6 m/s2. What is the maximum displacement?
- -a) 4.8 x 10-7 m
- +b) 1.52 x 10-6 m
- -c) 4.8 x 10-6 m
- -d) 1.52 x 10-5 m
- -e) 4.8 x 10-5 m
7. While standing 0.76 km from a cliff, you measure the echo time to be 4.339 seconds. What is the temperature?
- -a) 2.83 x 101Celsius
- +b) 3.26 x 101Celsius
- -c) 3.77 x 101Celsius
- -d) 4.35 x 101Celsius
- -e) 5.03 x 101Celsius
8. A dense rope is connected to a rope with less density (i.e. fewer kilograms per meter). If the rope is stretched and a wave is sent along high density rope,
- + a) the low density rope supports a wave with a higher speed
- - b) the low density rope supports a wave with a lower frequency
- - c) the low density rope supports a wave with a higher frequency
- - d) the low density rope supports a wave with a lower speed
9. The temperature is -3 degrees Celsius, and you are standing 0.66 km from a cliff. What is the echo time?
- -a) 2.949 x 100 seconds
- -b) 3.184 x 100 seconds
- -c) 3.438 x 100 seconds
- -d) 3.713 x 100 seconds
- +e) 4.009 x 100 seconds
10. ![]() These two pulses will collide and produce
These two pulses will collide and produce
- - a) negative diffraction
- - b) positive diffraction
- - c) negative interference
- + d) positive interference
11. If you start moving towards a source of sound, the pitch becomes
- - a) unchanged
- + b) higher
- - c) lower
12. A spring with spring constant 2.8 kN/m undergoes simple harmonic motion with a frequency of 8.5 kHz. The maximum force is 8.2 N. What is the total energy?
- +a) 1.2 x 10-2 J
- -b) 3.8 x 10-2 J
- -c) 1.2 x 10-1 J
- -d) 3.8 x 10-1 J
- -e) 1.2 x 100 J
13. People don't usually perceive an echo when
- - a) it takes more than a tenth of a second after the original sound to arrive
- - b) it arrives at a higher pitch
- - c) it arrives at exactly the same pitch
- + d) it arrives less than a tenth of a second after the original sound
- - e) it arrives at a lower pitch
14. ![]() Two signals (dashed) add to a solid
Two signals (dashed) add to a solid
- - a) octave
- - b) dissonance
- + c) fifth
15. Comparing a typical church to a professional baseball stadium, the church is likely to have
- - a) neither reverberation nor echo
- - b) both reverberation and echo
- + c) reverberation instead of echo
- - d) echo instead of reverberation
TrigPhysT1_151021-v2s2
1. Comparing a typical church to a professional baseball stadium, the church is likely to have
- ___ a) echo instead of reverberation
- ___ b) neither reverberation nor echo
- ___ c) both reverberation and echo
- ___ d) reverberation instead of echo
2. When a wave is reflected off a stationary barrier, the reflected wave
- ___ a) has lower amplitude than the incident wave
- ___ b) both of these are true
- ___ c) has higher frequency than the incident wave
3. A dense rope is connected to a rope with less density (i.e. fewer kilograms per meter). If the rope is stretched and a wave is sent along high density rope,
- ___ a) the low density rope supports a wave with a higher speed
- ___ b) the low density rope supports a wave with a higher frequency
- ___ c) the low density rope supports a wave with a lower speed
- ___ d) the low density rope supports a wave with a lower frequency
4. A spring with spring constant 1.1 kN/m undergoes simple harmonic motion with a frequency of 8.4 kHz. The maximum force is 3.8 N. What is the total energy?
- ___a) 6.56 x 10-4 J
- ___b) 2.08 x 10-3 J
- ___c) 6.56 x 10-3 J
- ___d) 2.08 x 10-2 J
- ___e) 6.56 x 10-2 J
5. People don't usually perceive an echo when
- ___ a) it arrives less than a tenth of a second after the original sound
- ___ b) it takes more than a tenth of a second after the original sound to arrive
- ___ c) it arrives at exactly the same pitch
- ___ d) it arrives at a higher pitch
- ___ e) it arrives at a lower pitch
6. A spring of spring constant 2.9 kN/m causes a mass to move with a period of 5.2 ms. The maximum displacement is 3.8 mm. What is the maximum kinetic energy?
- ___a) 2.09 x 10-3 J
- ___b) 6.62 x 10-3 J
- ___c) 2.09 x 10-2 J
- ___d) 6.62 x 10-2 J
- ___e) 2.09 x 10-1 J
7. ![]() These two pulses will collide and produce
These two pulses will collide and produce
- ___ a) negative diffraction
- ___ b) positive interference
- ___ c) positive diffraction
- ___ d) negative interference
8. ![]() Two signals (dashed) add to a solid
Two signals (dashed) add to a solid
- ___ a) dissonance
- ___ b) fifth
- ___ c) octave
9. While standing 0.58 km from a cliff, you measure the echo time to be 3.38 seconds. What is the temperature?
- ___a) 1.53 x 101Celsius
- ___b) 1.76 x 101Celsius
- ___c) 2.03 x 101Celsius
- ___d) 2.35 x 101Celsius
- ___e) 2.71 x 101Celsius
10.  Two signals (dashed) add to a solid
Two signals (dashed) add to a solid
- ___ a) fifth
- ___ b) octave
- ___ c) dissonance
11. A spring with spring constant 2.5 kN/m is attached to a 7.7 gram mass. The maximum acelleration is 1.2 m/s2. What is the maximum displacement?
- ___a) 3.7 x 10-8 m
- ___b) 1.17 x 10-7 m
- ___c) 3.7 x 10-7 m
- ___d) 1.17 x 10-6 m
- ___e) 3.7 x 10-6 m
12. Why do rough walls give a concert hall a “fuller” sound, compared to smooth walls?
- ___ a) Rough walls make for a louder sound.
- ___ b) The difference in path lengths creates more reverberation.
- ___ c) The difference in path lengths creates more echo.
13. The temperature is -2.1 degrees Celsius, and you are standing 0.83 km from a cliff. What is the echo time?
- ___a) 5.033 x 100 seconds
- ___b) 5.435 x 100 seconds
- ___c) 5.868 x 100 seconds
- ___d) 6.336 x 100 seconds
- ___e) 6.842 x 100 seconds
14. What happens to the wavelength on a wave on a stretched string if the wave passes from lightweight (low density) region of the rope to a heavy (high density) rope?
- ___ a) the wavelength gets shorter
- ___ b) the wavelength stays the same
- ___ c) the wavelength gets longer
15. If you start moving towards a source of sound, the pitch becomes
- ___ a) lower
- ___ b) unchanged
- ___ c) higher
Key to TrigPhysT1_151021-v2s2
1. Comparing a typical church to a professional baseball stadium, the church is likely to have
- - a) echo instead of reverberation
- - b) neither reverberation nor echo
- - c) both reverberation and echo
- + d) reverberation instead of echo
2. When a wave is reflected off a stationary barrier, the reflected wave
- + a) has lower amplitude than the incident wave
- - b) both of these are true
- - c) has higher frequency than the incident wave
3. A dense rope is connected to a rope with less density (i.e. fewer kilograms per meter). If the rope is stretched and a wave is sent along high density rope,
- + a) the low density rope supports a wave with a higher speed
- - b) the low density rope supports a wave with a higher frequency
- - c) the low density rope supports a wave with a lower speed
- - d) the low density rope supports a wave with a lower frequency
4. A spring with spring constant 1.1 kN/m undergoes simple harmonic motion with a frequency of 8.4 kHz. The maximum force is 3.8 N. What is the total energy?
- -a) 6.56 x 10-4 J
- -b) 2.08 x 10-3 J
- +c) 6.56 x 10-3 J
- -d) 2.08 x 10-2 J
- -e) 6.56 x 10-2 J
5. People don't usually perceive an echo when
- + a) it arrives less than a tenth of a second after the original sound
- - b) it takes more than a tenth of a second after the original sound to arrive
- - c) it arrives at exactly the same pitch
- - d) it arrives at a higher pitch
- - e) it arrives at a lower pitch
6. A spring of spring constant 2.9 kN/m causes a mass to move with a period of 5.2 ms. The maximum displacement is 3.8 mm. What is the maximum kinetic energy?
- -a) 2.09 x 10-3 J
- -b) 6.62 x 10-3 J
- +c) 2.09 x 10-2 J
- -d) 6.62 x 10-2 J
- -e) 2.09 x 10-1 J
7. ![]() These two pulses will collide and produce
These two pulses will collide and produce
- - a) negative diffraction
- + b) positive interference
- - c) positive diffraction
- - d) negative interference
8. ![]() Two signals (dashed) add to a solid
Two signals (dashed) add to a solid
- - a) dissonance
- + b) fifth
- - c) octave
9. While standing 0.58 km from a cliff, you measure the echo time to be 3.38 seconds. What is the temperature?
- -a) 1.53 x 101Celsius
- -b) 1.76 x 101Celsius
- +c) 2.03 x 101Celsius
- -d) 2.35 x 101Celsius
- -e) 2.71 x 101Celsius
10.  Two signals (dashed) add to a solid
Two signals (dashed) add to a solid
- - a) fifth
- - b) octave
- + c) dissonance
11. A spring with spring constant 2.5 kN/m is attached to a 7.7 gram mass. The maximum acelleration is 1.2 m/s2. What is the maximum displacement?
- -a) 3.7 x 10-8 m
- -b) 1.17 x 10-7 m
- -c) 3.7 x 10-7 m
- -d) 1.17 x 10-6 m
- +e) 3.7 x 10-6 m
12. Why do rough walls give a concert hall a “fuller” sound, compared to smooth walls?
- - a) Rough walls make for a louder sound.
- + b) The difference in path lengths creates more reverberation.
- - c) The difference in path lengths creates more echo.
13. The temperature is -2.1 degrees Celsius, and you are standing 0.83 km from a cliff. What is the echo time?
- +a) 5.033 x 100 seconds
- -b) 5.435 x 100 seconds
- -c) 5.868 x 100 seconds
- -d) 6.336 x 100 seconds
- -e) 6.842 x 100 seconds
14. What happens to the wavelength on a wave on a stretched string if the wave passes from lightweight (low density) region of the rope to a heavy (high density) rope?
- - a) the wavelength gets shorter
- - b) the wavelength stays the same
- + c) the wavelength gets longer
15. If you start moving towards a source of sound, the pitch becomes
- - a) lower
- - b) unchanged
- + c) higher
TrigPhysT1_151021-v1s3
1. ![]() These two pulses will collide and produce
These two pulses will collide and produce
- ___ a) negative diffraction
- ___ b) negative interference
- ___ c) positive diffraction
- ___ d) positive interference
2. ![]() These two pulses will collide and produce
These two pulses will collide and produce
- ___ a) positive diffraction
- ___ b) positive interference
- ___ c) negative interference
- ___ d) negative diffraction
3. If you start moving towards a source of sound, the pitch becomes
- ___ a) lower
- ___ b) higher
- ___ c) unchanged
4. A spring with spring constant 9.6 kN/m is attached to a 9.1 gram mass. The maximum acelleration is 1.6 m/s2. What is the maximum displacement?
- ___a) 4.8 x 10-7 m
- ___b) 1.52 x 10-6 m
- ___c) 4.8 x 10-6 m
- ___d) 1.52 x 10-5 m
- ___e) 4.8 x 10-5 m
5. A dense rope is connected to a rope with less density (i.e. fewer kilograms per meter). If the rope is stretched and a wave is sent along high density rope,
- ___ a) the low density rope supports a wave with a higher frequency
- ___ b) the low density rope supports a wave with a lower frequency
- ___ c) the low density rope supports a wave with a higher speed
- ___ d) the low density rope supports a wave with a lower speed
6. What happens to the wavelength on a wave on a stretched string if the wave passes from lightweight (low density) region of the rope to a heavy (high density) rope?
- ___ a) the wavelength gets longer
- ___ b) the wavelength gets shorter
- ___ c) the wavelength stays the same
7. ![]() Two signals (dashed) add to a solid
Two signals (dashed) add to a solid
- ___ a) dissonance
- ___ b) fifth
- ___ c) octave
8. While standing 0.66 km from a cliff, you measure the echo time to be 3.768 seconds. What is the temperature?
- ___a) 3.26 x 101Celsius
- ___b) 3.77 x 101Celsius
- ___c) 4.35 x 101Celsius
- ___d) 5.03 x 101Celsius
- ___e) 5.81 x 101Celsius
9. A spring with spring constant 7.7 kN/m undergoes simple harmonic motion with a frequency of 4.4 kHz. The maximum force is 9.4 N. What is the total energy?
- ___a) 5.74 x 10-5 J
- ___b) 1.81 x 10-4 J
- ___c) 5.74 x 10-4 J
- ___d) 1.81 x 10-3 J
- ___e) 5.74 x 10-3 J
10. A spring of spring constant 2.1 kN/m causes a mass to move with a period of 1.4 ms. The maximum displacement is 6.6 mm. What is the maximum kinetic energy?
- ___a) 1.45 x 10-3 J
- ___b) 4.57 x 10-3 J
- ___c) 1.45 x 10-2 J
- ___d) 4.57 x 10-2 J
- ___e) 1.45 x 10-1 J
11. A tuning fork with a frequency of 440 Hz is played simultaneously with a tuning fork of 442 Hz. How many beats are heard in 10 seconds?
- ___ a) 30
- ___ b) 20
- ___ c) 40
- ___ d) 50
- ___ e) 60
12. When a wave is reflected off a stationary barrier, the reflected wave
- ___ a) has higher frequency than the incident wave
- ___ b) has lower amplitude than the incident wave
- ___ c) both of these are true
13. ![]() These two pulses will collide and produce
These two pulses will collide and produce
- ___ a) negative diffraction
- ___ b) positive interference
- ___ c) positive diffraction
- ___ d) negative interference
14. What is the speed of a transverse wave on a string if the string is 0.58 m long, clamped at both ends, and harmonic number 4 has a frequency of 543 Hz?
- ___a) 8.86 x 101 unit
- ___b) 1.07 x 102 unit
- ___c) 1.3 x 102 unit
- ___d) 1.57 x 102 unit
- ___e) 1.91 x 102 unit
15. If a source of sound is moving towards you, the pitch becomes
- ___ a) higher
- ___ b) unchanged
- ___ c) lower
Key to TrigPhysT1_151021-v1s3
1. ![]() These two pulses will collide and produce
These two pulses will collide and produce
- - a) negative diffraction
- - b) negative interference
- - c) positive diffraction
- + d) positive interference
2. ![]() These two pulses will collide and produce
These two pulses will collide and produce
- - a) positive diffraction
- - b) positive interference
- + c) negative interference
- - d) negative diffraction
3. If you start moving towards a source of sound, the pitch becomes
- - a) lower
- + b) higher
- - c) unchanged
4. A spring with spring constant 9.6 kN/m is attached to a 9.1 gram mass. The maximum acelleration is 1.6 m/s2. What is the maximum displacement?
- -a) 4.8 x 10-7 m
- +b) 1.52 x 10-6 m
- -c) 4.8 x 10-6 m
- -d) 1.52 x 10-5 m
- -e) 4.8 x 10-5 m
5. A dense rope is connected to a rope with less density (i.e. fewer kilograms per meter). If the rope is stretched and a wave is sent along high density rope,
- - a) the low density rope supports a wave with a higher frequency
- - b) the low density rope supports a wave with a lower frequency
- + c) the low density rope supports a wave with a higher speed
- - d) the low density rope supports a wave with a lower speed
6. What happens to the wavelength on a wave on a stretched string if the wave passes from lightweight (low density) region of the rope to a heavy (high density) rope?
- + a) the wavelength gets longer
- - b) the wavelength gets shorter
- - c) the wavelength stays the same
7. ![]() Two signals (dashed) add to a solid
Two signals (dashed) add to a solid
- - a) dissonance
- + b) fifth
- - c) octave
8. While standing 0.66 km from a cliff, you measure the echo time to be 3.768 seconds. What is the temperature?
- +a) 3.26 x 101Celsius
- -b) 3.77 x 101Celsius
- -c) 4.35 x 101Celsius
- -d) 5.03 x 101Celsius
- -e) 5.81 x 101Celsius
9. A spring with spring constant 7.7 kN/m undergoes simple harmonic motion with a frequency of 4.4 kHz. The maximum force is 9.4 N. What is the total energy?
- -a) 5.74 x 10-5 J
- -b) 1.81 x 10-4 J
- -c) 5.74 x 10-4 J
- -d) 1.81 x 10-3 J
- +e) 5.74 x 10-3 J
10. A spring of spring constant 2.1 kN/m causes a mass to move with a period of 1.4 ms. The maximum displacement is 6.6 mm. What is the maximum kinetic energy?
- -a) 1.45 x 10-3 J
- -b) 4.57 x 10-3 J
- -c) 1.45 x 10-2 J
- +d) 4.57 x 10-2 J
- -e) 1.45 x 10-1 J
11. A tuning fork with a frequency of 440 Hz is played simultaneously with a tuning fork of 442 Hz. How many beats are heard in 10 seconds?
- - a) 30
- + b) 20
- - c) 40
- - d) 50
- - e) 60
12. When a wave is reflected off a stationary barrier, the reflected wave
- - a) has higher frequency than the incident wave
- + b) has lower amplitude than the incident wave
- - c) both of these are true
13. ![]() These two pulses will collide and produce
These two pulses will collide and produce
- - a) negative diffraction
- + b) positive interference
- - c) positive diffraction
- - d) negative interference
14. What is the speed of a transverse wave on a string if the string is 0.58 m long, clamped at both ends, and harmonic number 4 has a frequency of 543 Hz?
- -a) 8.86 x 101 unit
- -b) 1.07 x 102 unit
- -c) 1.3 x 102 unit
- +d) 1.57 x 102 unit
- -e) 1.91 x 102 unit
15. If a source of sound is moving towards you, the pitch becomes
- + a) higher
- - b) unchanged
- - c) lower
TrigPhysT1_151021-v2s3
1. If a source of sound is moving towards you, the pitch becomes
- ___ a) unchanged
- ___ b) higher
- ___ c) lower
2. A dense rope is connected to a rope with less density (i.e. fewer kilograms per meter). If the rope is stretched and a wave is sent along high density rope,
- ___ a) the low density rope supports a wave with a higher speed
- ___ b) the low density rope supports a wave with a higher frequency
- ___ c) the low density rope supports a wave with a lower frequency
- ___ d) the low density rope supports a wave with a lower speed
3. What is the speed of a transverse wave on a string if the string is 0.5 m long, clamped at both ends, and harmonic number 4 has a frequency of 316 Hz?
- ___a) 7.9 x 101 unit
- ___b) 9.57 x 101 unit
- ___c) 1.16 x 102 unit
- ___d) 1.4 x 102 unit
- ___e) 1.7 x 102 unit
4. ![]() Two signals (dashed) add to a solid
Two signals (dashed) add to a solid
- ___ a) octave
- ___ b) dissonance
- ___ c) fifth
5. A spring with spring constant 9.6 kN/m is attached to a 9.1 gram mass. The maximum acelleration is 1.6 m/s2. What is the maximum displacement?
- ___a) 4.8 x 10-7 m
- ___b) 1.52 x 10-6 m
- ___c) 4.8 x 10-6 m
- ___d) 1.52 x 10-5 m
- ___e) 4.8 x 10-5 m
6. What happens to the wavelength on a wave on a stretched string if the wave passes from lightweight (low density) region of the rope to a heavy (high density) rope?
- ___ a) the wavelength stays the same
- ___ b) the wavelength gets longer
- ___ c) the wavelength gets shorter
7. A spring with spring constant 7.7 kN/m undergoes simple harmonic motion with a frequency of 4.4 kHz. The maximum force is 9.4 N. What is the total energy?
- ___a) 5.74 x 10-5 J
- ___b) 1.81 x 10-4 J
- ___c) 5.74 x 10-4 J
- ___d) 1.81 x 10-3 J
- ___e) 5.74 x 10-3 J
8. When a wave is reflected off a stationary barrier, the reflected wave
- ___ a) has lower amplitude than the incident wave
- ___ b) has higher frequency than the incident wave
- ___ c) both of these are true
9. A tuning fork with a frequency of 440 Hz is played simultaneously with a tuning fork of 442 Hz. How many beats are heard in 10 seconds?
- ___ a) 40
- ___ b) 60
- ___ c) 20
- ___ d) 50
- ___ e) 30
10. A spring of spring constant 8.7 kN/m causes a mass to move with a period of 5.2 ms. The maximum displacement is 7.1 mm. What is the maximum kinetic energy?
- ___a) 2.19 x 10-1 J
- ___b) 6.93 x 10-1 J
- ___c) 2.19 x 100 J
- ___d) 6.93 x 100 J
- ___e) 2.19 x 101 J
11. If you start moving towards a source of sound, the pitch becomes
- ___ a) higher
- ___ b) lower
- ___ c) unchanged
12. ![]() These two pulses will collide and produce
These two pulses will collide and produce
- ___ a) positive interference
- ___ b) positive diffraction
- ___ c) negative interference
- ___ d) negative diffraction
13. While standing 0.62 km from a cliff, you measure the echo time to be 3.648 seconds. What is the temperature?
- ___a) 1.47 x 101Celsius
- ___b) 1.7 x 101Celsius
- ___c) 1.97 x 101Celsius
- ___d) 2.27 x 101Celsius
- ___e) 2.62 x 101Celsius
14. ![]() These two pulses will collide and produce
These two pulses will collide and produce
- ___ a) positive diffraction
- ___ b) negative interference
- ___ c) positive interference
- ___ d) negative diffraction
15. ![]() These two pulses will collide and produce
These two pulses will collide and produce
- ___ a) negative interference
- ___ b) positive interference
- ___ c) negative diffraction
- ___ d) positive diffraction
Key to TrigPhysT1_151021-v2s3
1. If a source of sound is moving towards you, the pitch becomes
- - a) unchanged
- + b) higher
- - c) lower
2. A dense rope is connected to a rope with less density (i.e. fewer kilograms per meter). If the rope is stretched and a wave is sent along high density rope,
- + a) the low density rope supports a wave with a higher speed
- - b) the low density rope supports a wave with a higher frequency
- - c) the low density rope supports a wave with a lower frequency
- - d) the low density rope supports a wave with a lower speed
3. What is the speed of a transverse wave on a string if the string is 0.5 m long, clamped at both ends, and harmonic number 4 has a frequency of 316 Hz?
- +a) 7.9 x 101 unit
- -b) 9.57 x 101 unit
- -c) 1.16 x 102 unit
- -d) 1.4 x 102 unit
- -e) 1.7 x 102 unit
4. ![]() Two signals (dashed) add to a solid
Two signals (dashed) add to a solid
- - a) octave
- - b) dissonance
- + c) fifth
5. A spring with spring constant 9.6 kN/m is attached to a 9.1 gram mass. The maximum acelleration is 1.6 m/s2. What is the maximum displacement?
- -a) 4.8 x 10-7 m
- +b) 1.52 x 10-6 m
- -c) 4.8 x 10-6 m
- -d) 1.52 x 10-5 m
- -e) 4.8 x 10-5 m
6. What happens to the wavelength on a wave on a stretched string if the wave passes from lightweight (low density) region of the rope to a heavy (high density) rope?
- - a) the wavelength stays the same
- + b) the wavelength gets longer
- - c) the wavelength gets shorter
7. A spring with spring constant 7.7 kN/m undergoes simple harmonic motion with a frequency of 4.4 kHz. The maximum force is 9.4 N. What is the total energy?
- -a) 5.74 x 10-5 J
- -b) 1.81 x 10-4 J
- -c) 5.74 x 10-4 J
- -d) 1.81 x 10-3 J
- +e) 5.74 x 10-3 J
8. When a wave is reflected off a stationary barrier, the reflected wave
- + a) has lower amplitude than the incident wave
- - b) has higher frequency than the incident wave
- - c) both of these are true
9. A tuning fork with a frequency of 440 Hz is played simultaneously with a tuning fork of 442 Hz. How many beats are heard in 10 seconds?
- - a) 40
- - b) 60
- + c) 20
- - d) 50
- - e) 30
10. A spring of spring constant 8.7 kN/m causes a mass to move with a period of 5.2 ms. The maximum displacement is 7.1 mm. What is the maximum kinetic energy?
- +a) 2.19 x 10-1 J
- -b) 6.93 x 10-1 J
- -c) 2.19 x 100 J
- -d) 6.93 x 100 J
- -e) 2.19 x 101 J
11. If you start moving towards a source of sound, the pitch becomes
- + a) higher
- - b) lower
- - c) unchanged
12. ![]() These two pulses will collide and produce
These two pulses will collide and produce
- + a) positive interference
- - b) positive diffraction
- - c) negative interference
- - d) negative diffraction
13. While standing 0.62 km from a cliff, you measure the echo time to be 3.648 seconds. What is the temperature?
- +a) 1.47 x 101Celsius
- -b) 1.7 x 101Celsius
- -c) 1.97 x 101Celsius
- -d) 2.27 x 101Celsius
- -e) 2.62 x 101Celsius
14. ![]() These two pulses will collide and produce
These two pulses will collide and produce
- - a) positive diffraction
- + b) negative interference
- - c) positive interference
- - d) negative diffraction
15. ![]() These two pulses will collide and produce
These two pulses will collide and produce
- - a) negative interference
- + b) positive interference
- - c) negative diffraction
- - d) positive diffraction
- Attribution (for quiz questions) under CC-by-SA license
- http://en.wikiversity.org/w/index.php?title=Physics_equations/18-Electric_charge_and_field/Q:findE&oldid=1378605
- http://en.wikiversity.org/wiki/How_things_work_college_course/Waves_(Physics_Classroom)
- Study guide
- http://en.wikiversity.org/wiki/Physics_equations/Sheet/All_chapters
- http://www.physicsclassroom.com/class/waves