Quizbank/Calculus Physics/T4study
< Quizbank < Calculus PhysicsCalcIIT4_Study
If you are reading this as a Wikiversity page, proper pagebreaks should result if printed using your browser's print option. On Chrome, Explorer, and Firefox, this option is available in the upper right hand corner of your screen. But, pagebreaks do not render properly if you use "Printable version" on Wikiversity's Print/export option on the left-hand sidebar.
- This document contains either a study guide OR pairs of exams taken from the same exam bank
- If two exams have the same s-number, then v1 and v2 have the same questions, presented in different (random) order.
- Exams with different s-numbers have different questions and may not have the same difficulty.
- Click items in the table of contents and appropriate page should be reached. This feature should allow you to print only those pages that you need.
- At the end of this document
- Attribution for the quizzes identifies where the questions were obtained
- Study guide links reading materials and/or relevant equations.
CalcIIT4_Study-v1s1
1. Two orbiting satellites are orbiting at a speed of 52 km/s perpendicular to a magnetic field of 41 μT. They are connected by a cable that is 33 km long. A voltmeter is attached between a satellite and one end of the cable. The voltmeter's internal impedance far exceeds the net resistance through the ionosphere that completes the circuit. What is the measured voltage?
- ___a) 4.79 x 104 volts.
- ___b) 5.81 x 104 volts.
- ___c) 7.04 x 104 volts.
- ___d) 8.52 x 104 volts.
- ___e) 1.03 x 105 volts.
2. An loop of wire with 43 turns has a radius of 0.27 meters, and is oriented with its axis parallel to a magetic field of 0.68 Tesla. What is the induced voltage if this field is reduced to 36% of its original value in 3.8 seconds?
- ___a) 6.34 x 10-1 volts
- ___b) 7.68 x 10-1 volts
- ___c) 9.31 x 10-1 volts
- ___d) 1.13 x 100 volts
- ___e) 1.37 x 100 volts
3. A circlular capactitor of radius 4.2 m has a gap of 12 mm, and a charge of 94 μC. What is the electric field between the plates?
- ___a) 1.92E+05 N/C (or V/m)
- ___b) 2.32E+05 N/C (or V/m)
- ___c) 2.81E+05 N/C (or V/m)
- ___d) 3.41E+05 N/C (or V/m)
- ___e) 4.13E+05 N/C (or V/m)
4. A circlular capactitor of radius 4.1 m has a gap of 8 mm, and a charge of 24 μC. Compute the surface integral 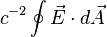 over an inner face of the capacitor.
over an inner face of the capacitor.
- ___a) 2.05E-11 Vs2m-1
- ___b) 2.49E-11 Vs2m-1
- ___c) 3.02E-11 Vs2m-1
- ___d) 3.65E-11 Vs2m-1
- ___e) 4.43E-11 Vs2m-1
5. A circlular capactitor of radius 4.7 m has a gap of 19 mm, and a charge of 27 μC. The capacitor is discharged through a 6 kΩ resistor. What is the decay time?
- ___a) 1.60E-04 s
- ___b) 1.94E-04 s
- ___c) 2.35E-04 s
- ___d) 2.85E-04 s
- ___e) 3.45E-04 s
6. A circlular capactitor of radius 3.1 m has a gap of 9 mm, and a charge of 85 μC. The capacitor is discharged through a 5 kΩ resistor. What is what is the maximum magnetic field at the edge of the capacitor? (There are two ways to do this; you should know both.)
- ___a) 2.33E-08 Tesla
- ___b) 2.93E-08 Tesla
- ___c) 3.69E-08 Tesla
- ___d) 4.65E-08 Tesla
- ___e) 5.85E-08 Tesla
7.
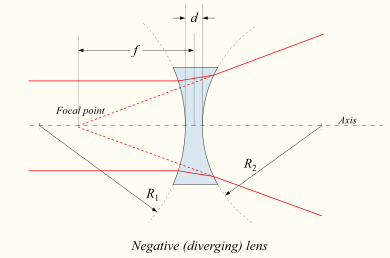
Shown is a corrective lens by a person who needs glasses. This ray diagram illustrates
- ___ a) how a nearsighted person might see a distant object
- ___ b) how a farsighted person might see an object that is too close for comfort
- ___ c) how a farsighted person might see a distant object
- ___ d) how a nearsighted person might see an object that is too close for comfort
8.
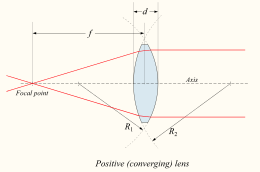
Shown is a corrective lens by a person who needs glasses. This ray diagram illustrates
- ___ a) how a farsighted person might see an object that is too close for comfort
- ___ b) how a nearsighted person might see a distant object
- ___ c) how a farsighted person might see a distant object
- ___ d) how a nearsighted person might see an object that is too close for comfort
9. In optics, normal means
- ___ a) to the right of the optical axis
- ___ b) perpendicular to the surface
- ___ c) to the left of the optical axis
- ___ d) parallel to the surface
10. The law of reflection applies to
- ___ a) flat surfaces
- ___ b) telescopes but not microscopes
- ___ c) curved surfaces
- ___ d) both flat and curved surfaces
- ___ e) only light in a vacuum
11. When light passes from air to glass
- ___ a) it bends towards the normal
- ___ b) the frequency increases
- ___ c) it does not bend
- ___ d) the frequency decreases
- ___ e) it bends away from the normal
12. When light passes from glass to air
- ___ a) it bends towards the normal
- ___ b) it does not bend
- ___ c) the frequency increases
- ___ d) the frequency decreases
- ___ e) it bends away from the normal
13. An important principle that allows fiber optics to work is
- ___ a) the invariance of the speed of light
- ___ b) total external refraction
- ___ c) partial internal absorption
- ___ d) the Doppler shift
- ___ e) total internal reflection
14. The focal point is where
- ___ a) rays meet whenever they are forming an image
- ___ b) the center of the lens
- ___ c) rays meet if they were parallel to the optical axis before striking a lens
- ___ d) rays meet whenever they pass through a lens
- ___ e) rays meet if they are parallel to each other
15. An object is placed 6.3 cm to the left of a diverging lens with a focal length of 8.9 cm. How far is the image from the lens?
- ___a) 1.17 x 100 cm
- ___b) 2.07 x 100 cm
- ___c) 3.69 x 100 cm
- ___d) 6.56 x 100 cm
- ___e) 1.17 x 101 cm
16. An object is placed 4.15 cm to the left of a converging lens with a focal length of 3.6 cm. How far is the image from the lens?
- ___a) 8.59 x 100 cm
- ___b) 1.53 x 101 cm
- ___c) 2.72 x 101 cm
- ___d) 4.83 x 101 cm
- ___e) 8.59 x 101 cm
17. An object of height 0.75 cm is placed 147 cm behind a diverging lens with a focal length of 86 cm. What is the height of the image?
- ___a) 2.77 x 10-1 cm
- ___b) 3.32 x 10-1 cm
- ___c) 3.99 x 10-1 cm
- ___d) 4.78 x 10-1 cm
- ___e) 5.74 x 10-1 cm
18. An object is placed 13.7 cm to the left of a diverging lens with a focal length of 17.7 cm. On the side, at a distance of 5.5 cm from the diverging lens is a converging lens with focal length equal to 4 cm. How far is the final image from the converging lens?
- ___a) 5.73 x 10-2 cm
- ___b) 1.81 x 10-1 cm
- ___c) 5.73 x 10-1 cm
- ___d) 1.81 x 100 cm
- ___e) 5.73 x 100 cm
19. Which lens has the shorter focal length?
- ___ a) They have the same focal lengh.
- ___ b)

- ___ c)
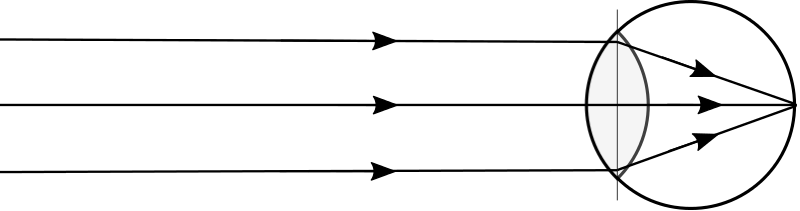
20. ![]() If this represents the eye looking at an object, where is this object?
If this represents the eye looking at an object, where is this object?
- ___ a) at infinity
- ___ b) very far away
- ___ c) One focal length in front of the eye
- ___ d) directly in front of the eye (almost touching)
- ___ e) Two (of the other answers) are true
21. After passing through a the lens of a camera or the eye, the focal point is defined as where the rays meet.
- ___ a) true
- ___ b) false
22. ![]() Mr. Smith is gazing at something as shown in the figure to the left. Suppose he does not refocus, but attempts to stare at the star shown in the figures below. Which diagram depicts how the rays from the star would travel if he does not refocus?
Mr. Smith is gazing at something as shown in the figure to the left. Suppose he does not refocus, but attempts to stare at the star shown in the figures below. Which diagram depicts how the rays from the star would travel if he does not refocus?
- ___ a)

- ___ b)
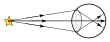
- ___ c)

Key to CalcIIT4_Study-v1s1
1. Two orbiting satellites are orbiting at a speed of 52 km/s perpendicular to a magnetic field of 41 μT. They are connected by a cable that is 33 km long. A voltmeter is attached between a satellite and one end of the cable. The voltmeter's internal impedance far exceeds the net resistance through the ionosphere that completes the circuit. What is the measured voltage?
- -a) 4.79 x 104 volts.
- -b) 5.81 x 104 volts.
- +c) 7.04 x 104 volts.
- -d) 8.52 x 104 volts.
- -e) 1.03 x 105 volts.
2. An loop of wire with 43 turns has a radius of 0.27 meters, and is oriented with its axis parallel to a magetic field of 0.68 Tesla. What is the induced voltage if this field is reduced to 36% of its original value in 3.8 seconds?
- -a) 6.34 x 10-1 volts
- -b) 7.68 x 10-1 volts
- -c) 9.31 x 10-1 volts
- +d) 1.13 x 100 volts
- -e) 1.37 x 100 volts
3. A circlular capactitor of radius 4.2 m has a gap of 12 mm, and a charge of 94 μC. What is the electric field between the plates?
- +a) 1.92E+05 N/C (or V/m)
- -b) 2.32E+05 N/C (or V/m)
- -c) 2.81E+05 N/C (or V/m)
- -d) 3.41E+05 N/C (or V/m)
- -e) 4.13E+05 N/C (or V/m)
4. A circlular capactitor of radius 4.1 m has a gap of 8 mm, and a charge of 24 μC. Compute the surface integral 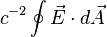 over an inner face of the capacitor.
over an inner face of the capacitor.
- -a) 2.05E-11 Vs2m-1
- -b) 2.49E-11 Vs2m-1
- +c) 3.02E-11 Vs2m-1
- -d) 3.65E-11 Vs2m-1
- -e) 4.43E-11 Vs2m-1
5. A circlular capactitor of radius 4.7 m has a gap of 19 mm, and a charge of 27 μC. The capacitor is discharged through a 6 kΩ resistor. What is the decay time?
- -a) 1.60E-04 s
- +b) 1.94E-04 s
- -c) 2.35E-04 s
- -d) 2.85E-04 s
- -e) 3.45E-04 s
6. A circlular capactitor of radius 3.1 m has a gap of 9 mm, and a charge of 85 μC. The capacitor is discharged through a 5 kΩ resistor. What is what is the maximum magnetic field at the edge of the capacitor? (There are two ways to do this; you should know both.)
- -a) 2.33E-08 Tesla
- -b) 2.93E-08 Tesla
- +c) 3.69E-08 Tesla
- -d) 4.65E-08 Tesla
- -e) 5.85E-08 Tesla
7.

Shown is a corrective lens by a person who needs glasses. This ray diagram illustrates
- + a) how a nearsighted person might see a distant object
- - b) how a farsighted person might see an object that is too close for comfort
- - c) how a farsighted person might see a distant object
- - d) how a nearsighted person might see an object that is too close for comfort
8.

Shown is a corrective lens by a person who needs glasses. This ray diagram illustrates
- + a) how a farsighted person might see an object that is too close for comfort
- - b) how a nearsighted person might see a distant object
- - c) how a farsighted person might see a distant object
- - d) how a nearsighted person might see an object that is too close for comfort
9. In optics, normal means
- - a) to the right of the optical axis
- + b) perpendicular to the surface
- - c) to the left of the optical axis
- - d) parallel to the surface
10. The law of reflection applies to
- - a) flat surfaces
- - b) telescopes but not microscopes
- - c) curved surfaces
- + d) both flat and curved surfaces
- - e) only light in a vacuum
11. When light passes from air to glass
- + a) it bends towards the normal
- - b) the frequency increases
- - c) it does not bend
- - d) the frequency decreases
- - e) it bends away from the normal
12. When light passes from glass to air
- - a) it bends towards the normal
- - b) it does not bend
- - c) the frequency increases
- - d) the frequency decreases
- + e) it bends away from the normal
13. An important principle that allows fiber optics to work is
- - a) the invariance of the speed of light
- - b) total external refraction
- - c) partial internal absorption
- - d) the Doppler shift
- + e) total internal reflection
14. The focal point is where
- - a) rays meet whenever they are forming an image
- - b) the center of the lens
- + c) rays meet if they were parallel to the optical axis before striking a lens
- - d) rays meet whenever they pass through a lens
- - e) rays meet if they are parallel to each other
15. An object is placed 6.3 cm to the left of a diverging lens with a focal length of 8.9 cm. How far is the image from the lens?
- -a) 1.17 x 100 cm
- -b) 2.07 x 100 cm
- +c) 3.69 x 100 cm
- -d) 6.56 x 100 cm
- -e) 1.17 x 101 cm
16. An object is placed 4.15 cm to the left of a converging lens with a focal length of 3.6 cm. How far is the image from the lens?
- -a) 8.59 x 100 cm
- -b) 1.53 x 101 cm
- +c) 2.72 x 101 cm
- -d) 4.83 x 101 cm
- -e) 8.59 x 101 cm
17. An object of height 0.75 cm is placed 147 cm behind a diverging lens with a focal length of 86 cm. What is the height of the image?
- +a) 2.77 x 10-1 cm
- -b) 3.32 x 10-1 cm
- -c) 3.99 x 10-1 cm
- -d) 4.78 x 10-1 cm
- -e) 5.74 x 10-1 cm
18. An object is placed 13.7 cm to the left of a diverging lens with a focal length of 17.7 cm. On the side, at a distance of 5.5 cm from the diverging lens is a converging lens with focal length equal to 4 cm. How far is the final image from the converging lens?
- -a) 5.73 x 10-2 cm
- -b) 1.81 x 10-1 cm
- -c) 5.73 x 10-1 cm
- -d) 1.81 x 100 cm
- +e) 5.73 x 100 cm
19. Which lens has the shorter focal length?
- - a) They have the same focal lengh.
- + b)

- + b)
- - c)

- - c)
20. ![]() If this represents the eye looking at an object, where is this object?
If this represents the eye looking at an object, where is this object?
- - a) at infinity
- - b) very far away
- - c) One focal length in front of the eye
- - d) directly in front of the eye (almost touching)
- + e) Two (of the other answers) are true
21. After passing through a the lens of a camera or the eye, the focal point is defined as where the rays meet.
- - a) true
- + b) false
22. ![]() Mr. Smith is gazing at something as shown in the figure to the left. Suppose he does not refocus, but attempts to stare at the star shown in the figures below. Which diagram depicts how the rays from the star would travel if he does not refocus?
Mr. Smith is gazing at something as shown in the figure to the left. Suppose he does not refocus, but attempts to stare at the star shown in the figures below. Which diagram depicts how the rays from the star would travel if he does not refocus?
- + a)

- + a)
- - b)
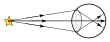
- - b)
- - c)

- - c)
- Attribution (for quiz questions) under CC-by-SA license
- http://en.wikiversity.org/w/index.php?title=Physics_equations/23-Electromagnetic_Induction,_AC_Circuits,_and_Electrical_Technologies/Q:spaceTetherAndSimpleLoop&oldid=1418578
- https://en.wikiversity.org/w/index.php?title=Physics_equations/24-Electromagnetic_Waves/Q:displacementCurrent&oldid=1282320
- https://en.wikiversity.org/wiki/Physics_equations/25-Geometric_Optics/Q:image
- http://en.wikiversity.org/w/index.php?title=Physics_equations/25-Geometric_Optics/Q:thinLens&oldid=1378617
- http://en.wikiversity.org/w/index.php?title=Physics_equations/25-Geometric_Optics/Q:vision&oldid=1378615
- Study guide
- http://en.wikiversity.org/wiki/Physics_equations/Sheet/All_chapters
- https://en.wikiversity.org/wiki/Light_and_optics
- http://en.wikiversity.org/wiki/Physics_equations/Sheet/All_chapters
http://en.wikiversity.org/wiki/Light_and_optics