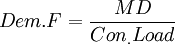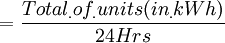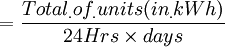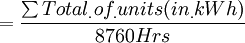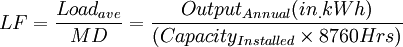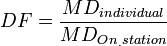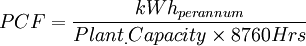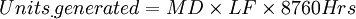Power Generation-variable load
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Part 1: Definitions
help | edit
|
|
Part 2: Introduction
Objectives of a Power station: The power station is constructed, comissioned and operated to supply required power to consumers with generators running at rated capacity for maximum efficiency. we saw in lesson one that the fundamental problem in generation, transmission and distribution of electrical energy is the fact that electrical energy can not be stored. It must be generated, transmitted and distributed as and when needed. This lesson looks at problems associated with variable loads on power stations, and discusses the complexities met in deciding the make, size and capacity of Generators (Generating units) that must be installed in a power plant to successfully meet these varying energy demands on a day to day basis. Variable load: The load on a power station varies from time to time due to uncertain demands of consumers. Energy demand of one consumer at any given time is distinct/differs from the energy demand of another consumer. This results in the total demand on the power station to vary over a given period of time and may necesitate the following:
In order to study the pattern and effect of the varying load, station engineers use load curves. help | edit
|
|
Part 4: Generating units & Meeting Loads
Selecting generating units: The following must be considered when selecting the number and size of Generating units (Generators):
Meeting Load: The best method to meet load requirements on power station is to Interconnect two different power stations in paralell as follows:
-- Generally thermal & Nuclear power stations.
-- Generally Hydro, Pumped storage & gas turbine power stations. Careful study of load curves must be undertaken before deciding which type of station will be used for what purpose as this is greatly dependant on enviromental issues and availability of fuel used by a particular power station. help | edit
|
|
Part 6: Example
Power Generation-variable load/Part6 help | edit
|
|
Part 8: Refferences & Exercise 7
Refferences:
Execise 7:
|
|
Part 3: Load curves
A load curve is a graph showing the variation of load on the power station with respect to time. the following load curves are used in power stations:
help | edit
|
|
Part 5: The Power grid
The power grid is constructed by connecting several generating stations together in parallel. This method has helped solve most transmission and distribution problems facing power engineers. Below are the advantages of using a power grid:
Sharing of load among stations allows for more efficient stations to work constantly at high load factors and less efficient stations to be used for peak supply only.
Different stations have different load curves thus the total maximum demand of the system is decreased, thus effectively increasing the diversity factor of the system.
The stand-by capacity required of individual plants is reduced when they are interconnected in a grid.
If major breakdown occurs on one station, supply is maintained by other stations.
Excess load can be shared from highly stressed plants to plant with lower peak loads ( Identified from load curves ).
Older plants which are less efficient can still be used to carry peak loads of short durations. help | edit
|
|
Part 7: Example
Power Generation-variable load/Part7 help | edit
|
|
Part 9: Completion list
Once you finish your Exercises you can post your score here!
To post your score just e-mail your course co-ordinator your name and score Click Here
|
| |
|
|
|
|
| | Resource type: this resource contains a lecture or lecture notes. |