Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants obtain and use energy from the Sun in conjunction with water and carbon dioxide to produce glucose and oxygen. The chemical equation is 6CO2 + 6H2O + energy from the Sun --> C6H12O6. Photosynthesis consists of two sets of reactions: the light-dependent reactions and the light-independent reactions (otherwise known as the Calvin Cycle).
Obtainment of Materials
Water
In a vascular plant, pipe-like tissues conduct water to different parts of the plant. In a non-vascular plant, water is unable to be conducted, and, therefore, must be absorbed from the plant's surroundings.
Carbon Dioxide
Stomata are pipe-like structures in the leaves that control the flow of carbon dioxide into a plant and the flow of oxygen outside of the plant.
Sunlight
Light is absorbed by molecules called pigments. In plants, the pigment that absorbs sunlight is chlorophyll. Chlorophyll absorbs light well in the blue-violet and red sections of the visible light spectrum, whereas it reflects light in the green section of the visible light spectrum, giving most plants a green color. Chlorophyll is found in the chloroplast.
-en.svg.png)
The Chloroplast
The chloroplast is where photosynthesis happens in plants.
The Thylakoid
- Contains chlorophyll
- Stacked into grana
- Light dependent reactions occur here
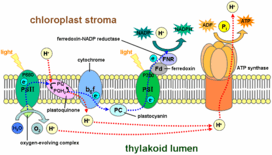
The Stroma
- The area of the chloroplast not taken up by the thylakoids
- The Calvin Cycle occurs here
The Process
There are two parts of photosynthesis, the light reactions and the dark reactions. The light reactions happen over the thylakoid membrane. It is made up of two photosystems. Photosystem II splits water, and raises the electrons to a higher energy level. In this process, oxygen is released, and two positive hydrogen ions are released into the intermembrane space. The electrons then carry another hydrogen ion from the stroma into the intermembrane space. This causes the electron to lose some of its energy. Photosystem I then raises the electron's energy level again, and it gets incorporated, along with a hydrogen ion, into NADPH. The hydrogen ions that were pushed over into the intermembrane space then go through the ATP synthase. The ATP synthase then merges ADP with another phosphate group, forming ATP. The ATP and NADPH formed by these reactions are needed in the dark reactions, also known as the Calvin Cycle.