Object Oriented Enterprise Modelling/Object Oriented Business Process Modelling
< Object Oriented Enterprise ModellingOOEM/BPM Notation
| Notation | Bedeutung | Konformität |
|---|---|---|
| |
Basic symbols - note the distinction between classes (no underline) and instances (underline) | UML standard |
| |
UML standard | |
| |
extension to UML, we expect it in UML 3.0 | |
| |
UML standard (introduced for activity diagrams) | |
| |
UML stereotypes vs. new symbols (OOEM/BPM) | suggested UML usage conforming to standard |
| |
specific UML usage conforming to standard | |
| |
specific UML usage conforming to standard | |
| |
UML usage | |
| |
specific UML usage conforming to standard | |
| |
specific UML usage conforming to standard | |
| |
A step is the explicitly performed change between an initial and a final constellation | specific UML usage conforming to standard |
| |
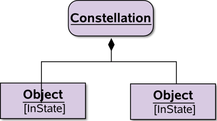
Same as above, but with instances instead of classes | specific UML usage conforming to standard |
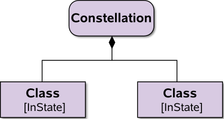 |
extension to UML | |
 |
A constellation is an aggregation of certain objects within certain states | extension to UML |
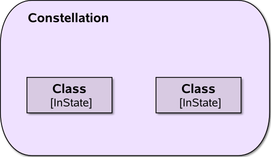 |
An alternative notation for a constellation | extension to UML |
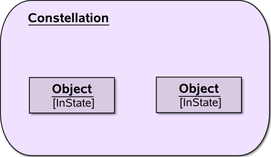 |
extension to UML | |
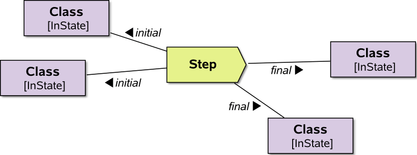 |
Constellations can be shown in detail | UML standard |
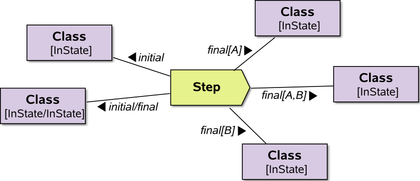 |
Steps can have different (mutually exclusive) final constellations; individual classes/instances may be shared by these constellations | UML standard |
| |
All standard UML notation is valid, e.g. constraints | UML standard |
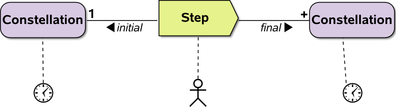 |
Of course actors and timing constraints can be placed here; optionally with nice symbols | UML standard |
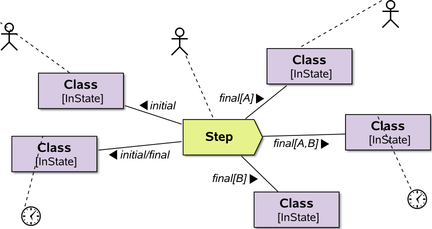 |
A more complex example of annotations | UML standard |
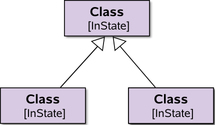 |
extension to UML | |
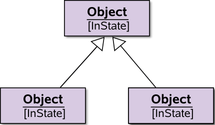 |
extension to UML | |
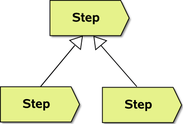 |
Steps can be derived from as is true for any normal class; derivation of classes and instances within a certain state expresses a substate relationship | extension to UML |
| |
Partially completed work can be shown in a natural way | extension to UML |
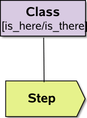 |
extension to UML | |
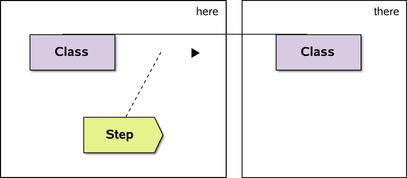 |
A notation for location changes, as a special case of state changes | extension to UML |
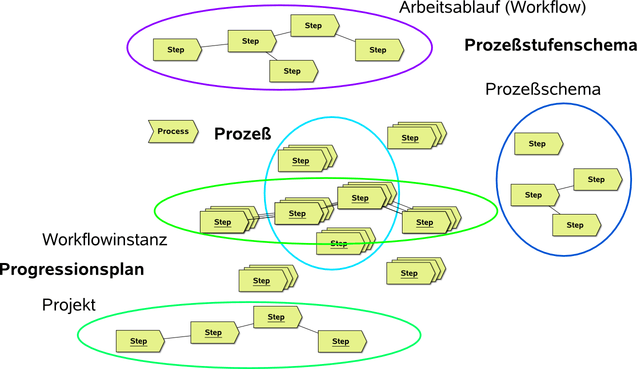
Prozeß-Begriffe
This article is issued from Wikiversity - version of the Friday, May 15, 2009. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.