Mechanics
| |
Subject classification: this is a physics resource . |
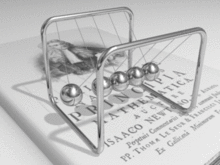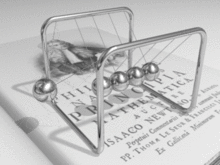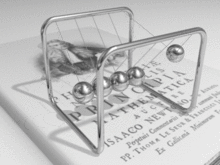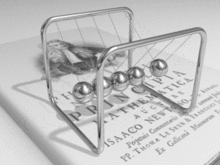
Animation of Newton's cradle from the Newton's book Principia Mathematica.
Mechanics is the branch of physics which studies massive bodies that are influenced by mass-based forces and moved.
The discipline has its roots in ancient Greece where Aristotle studied the way bodies behaved when they were thrown through the air (e.g. a stone). However it was Galileo, Kepler and especially Newton who laid the foundation for much of the so called Newtonian mechanics we know today.
Mechanics is the original discipline of physics, dealing with the macroscopic world. Mechanics encompasses the movement of all matter possessing mass in the universe under the four forces: gravity, the strong and weak interactions, and the electromagnetic interaction.
Some aspects of classical mechanics
- Astrodynamics, spacecraft navigation, etc.
- Solid mechanics, elasticity, the properties of (semi-)rigid bodies
- Acoustics, sound in solids, fluids, etc.
- Hydraulics, fluids in equilibrium
- Applied / Engineering mechanics
- Statistical mechanics, large assemblies of particles
- Relativistic or Einsteinian mechanics, universal gravitation
Quantum mechanics
The following are categorized as being part of Quantum mechanics:
- Particle physics, the motion, structure, and reactions of particles
- Nuclear physics, the motion, structure, and reactions of nuclei
- Condensed matter physics, quantum gases, solids, liquids, etc.
- Quantum statistical mechanics, large assemblies of particles
This article is issued from Wikiversity - version of the Saturday, December 06, 2014. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.