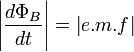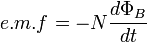Magnetism
| |
Subject classification: this is a physics resource . |
Faraday's Law
The magnitude induced EMF through a loop of conducting material is equal to the magnitude of the time derivative rate of change of the magnetic flux through that loop.
Lenz's Law
The polarity of the induced EMF is such that oppose the changes/current that causes it.
Magnetic Field Strength
Magnetic Field Strength is defined as the force on one metre of wire carrying a current of one amp at right angles to the magnetic field. Magnetic Field Strength is also called flux density and is measured in teslas, T.
This article is issued from Wikiversity - version of the Tuesday, January 05, 2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.