Logical XOR
| |
Resource type: this resource is a lesson. |
Welcome! This is a lesson in the Introductory Discrete Mathematics for Computer Science course here at Wikiversity.
Previous lesson: Logical OR
Introducing the Exclusive OR!
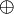 : This is the XOR operator. It is also called the exclusive OR, to distinguish it from the inclusive OR of the previous lesson. Like the inclusive OR, it is a diadic operator; unlike any other operator, it is true when one and only one input is true.
: This is the XOR operator. It is also called the exclusive OR, to distinguish it from the inclusive OR of the previous lesson. Like the inclusive OR, it is a diadic operator; unlike any other operator, it is true when one and only one input is true.
- Let
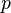 represent the statement: It is raining.
represent the statement: It is raining. - Let
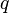 represent the statement: I am hungry.
represent the statement: I am hungry.
 represents the exclusive disjunction of statements
represents the exclusive disjunction of statements 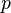 and
and 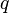 : It is raining OR I am hungry, But not both.
: It is raining OR I am hungry, But not both.
- Let
Truth Table
Its truth table is unique. Here it is!
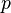 |
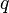 |
 |
|---|---|---|
| T | T | F |
| T | F | T |
| F | T | T |
| F | F | F |
Why XOR is Special
XOR is used for adding binary numbers, and is the fundamental arithmetic operation used by computers.
Next Lesson
Your next lesson is called Conditional Operator.
This article is issued from Wikiversity - version of the Friday, March 11, 2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.