Logical NNOR
☞ This page belongs to resource collections on Logic and Inquiry.
The logical NNOR (“Neither Nor”) is an operation on two logical values, typically the values of two propositions, that produces a value of true if and only if both of its operands are false. In other words, it produces a value of false if and only if at least one of its operands is true.
The truth table of 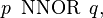 also written
also written 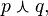 appears below:
appears below:
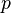 |
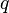 |
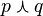 |
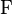 | 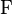 | 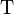 |
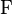 | 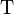 | 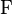 |
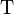 | 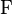 | 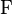 |
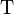 | 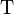 | 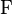 |
Syllabus
Focal nodes
Peer nodes
- Logical NNOR @ InterSciWiki
- Logical NNOR @ Subject Wikis
- Logical NNOR @ Wikiversity
- Logical NNOR @ Wikiversity Beta
Logical operators
Related topics
Relational concepts
Information, Inquiry
Related articles
Document history
Portions of the above article were adapted from the following sources under the GNU Free Documentation License, under other applicable licenses, or by permission of the copyright holders.
- Logical NNOR, InterSciWiki
- Logical NNOR, Wikinfo
- Logical NNOR, Wikiversity
- Logical NNOR, Wikiversity Beta
- Logical NNOR, Wikipedia
This article is issued from Wikiversity - version of the Thursday, November 05, 2015. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.