Knowing How You Know
Introduction
.png)
How do you decide what to believe? How do you distinguish between fact and opinion? When you hear a claim, how do you assess the reliability of the sources? What do you consider to be a reliable rather than an unreliable information source? How do you gather and assess evidence for or against some proposition? If some trusted authority supports a particular belief and direct evidence you see disputes that belief, how do you resolve this discrepancy? Are your beliefs well-founded and consistent? What would cause you to change a belief?
| |
Completion status: this resource is considered to be complete. |
| |
Attribution: User lbeaumont created this resource and is actively using it. Please coordinate future development with him/her if possible. |
This course will help you explore these questions and develop your own well-considered rules for deciding what to believe. These rules are called your theory of knowledge, and when you have developed your own theory of knowledge you will finally know how you know.
The objectives of this course are:
- Examine how you decide what you believe,
- Explore the range of more reliable and less reliable information sources,
- Explore the tyranny of evidence,
- Survey example theories of knowledge,
- Develop your own Theory of Knowledge,
- Test and refine your Theory of Knowledge,
- Apply your Theory of Knowledge to improve the accuracy and consistency of your beliefs, and
- Align your beliefs with reality.
There are no specific prerequisites to this course.
This course is part of the Applied Wisdom curriculum.
If you wish to contact the instructor, please click here to send me an email.
Deciding what to Believe
How do you decide what to believe? Many people believe whatever they want to as they select information that seems to confirm what is convenient for them to believe and dismiss contrary or conflicting information. Other people listen to what their friends have to say, or follow the opinions of various celebrities. It might be that the group that shouts the loudest or most often or most cleverly gets your attention. Perhaps you are influenced by people in power, listening to what parents and teachers said when you were young, rebelling against them as an adolescent, and then choosing other authority figures to follow as an adult. People are often captivated by attractive, charming, glib, or charismatic people. Mystical language seems to seduce and entrance others. Many of us are members of some tribe which supports its own belief system. This might be a political party, an advocacy group, a professional society or industry group, a club, religious or cultural traditions, or proponents of some ideology.
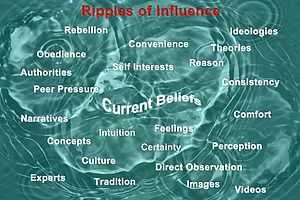
None of these approaches can accurately distinguish reliable information from rumor, myth, gossip, advertisement, propaganda, or other forms of unreliable, outdated, misleading, untrue, or deceptive misinformation. Also, because we are most comfortable when we are most certain, regardless of the validity of our beliefs, we naturally avoid or resist exposure to information that threatens our own tenuous certainty.[1]
The Supreme Court broadly upholds the first amendment protection of free speech. Hate speech, misleading information, and deliberate lies are all constitutionally protected forms of expression.[2] The Internet welcomes all contributors and as a result support for almost any belief, regardless of its truth, is easily found. This constant influx of unverified information makes it essential that we take personal responsibility to decide for ourselves what is reliable and what is not.
“You're entitled to your own opinions”, Senator Daniel Patrick Moynihan declares, “but you're not entitled to your own facts.” This succinctly captures the extent and boundaries of tolerance. While tolerance is essential in the realm of opinion, it has no place in the realm of fact. Of course you need to be able to distinguish fact from opinion to be tolerant.
Facts correspond with reality. Because we all live on the same earth, we all share the same reality, observed through our unique points of view. This is our common ground, we need to dig deeply to find that common ground and stand together on the bedrock of reality. Facts establish the middle ground. We can each choose to move toward the political left or the right, but we each must start from the facts while we constantly stay connected to the facts.
Taking responsibility for your own beliefs is not easy, but it is immensely rewarding. When you know how you know, you can be confident in what you know. You can then strive to purify the knowledge stream you accumulate and assimilate. When you know how you know you can easily identify the fools, fakers, and frauds among us, and confidently dispute, correct, dismiss, or avoid them.
Knowing how you know is a big step you can take now to reduce the influence of money and special interests in politics. Because you are less susceptible to misleading, manipulative, deceptive, and unhelpful influences, money spent by special interests on propaganda designed to support only their cause becomes less effective. You know how to make up your own mind based on a careful, accurate, nuanced, and balanced assessment of reliable information. Facts are stubborn. When you are justifiably confident in knowing what is true, what is false, and what you are unsure of you know when to stand firm, when to yield, and when to change your beliefs.
Assignment:
Your beliefs are what you accept as being true. This assignment begins to examine your beliefs.
Part 1:
- Write down a few of your own beliefs. Choose a range of more widely accepted and less widely accepted beliefs.
- For each of these beliefs, write down how you decided it is true.
- Optionally read this essay on the nature of beliefs.
- Optionally read this Wikipedia article on beliefs.
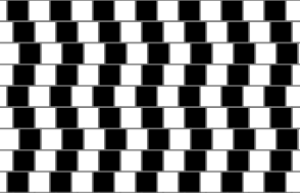
Part 2:
- Look at the checkered diagram on the right.
- Do you believe the horizontal lines are straight and parallel or do you believe they are tilted to the right or the left?
- Now look at the array from the side or use a straight edge or ruler to examine and measure the horizontal lines. It may be helpful to double click on the figure to examine a larger rendering of the image. You may find it best to print out the image and examine the hard copy rendering of it. Focus on the image one square at a time. Can you see the horizontal lines bend at any point? Do the horizontal lines seem parallel or tilted when you analyze them objectively?
- Based on what you learned in #3 above, look again at the figure. Do you now believe them to be parallel or tilted?
- Do you have more confidence in your conception of the figure or your perception of it?
What is a Theory of Knowledge?
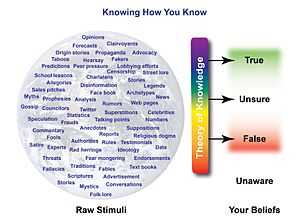
Our world is full of various stimuli that contend for our attention and masquerade as the truth. Unfortunately much of the information we are exposed to is unreliable and misleading. The diagram on the right illustrates our need to filter the raw stimuli we are exposed to in the world to arrive at our own beliefs. Our theory of knowledge is the process we use to analyze and integrate raw information sources into our beliefs about what is true, what is false, what we are unsure of, and what we are unaware of.
Your theory of knowledge is the set of rules you follow to decide what to believe. Since you have chosen your beliefs, you must have some theory of knowledge in some form, however it is unlikely you have given it much thought, written it down, tested it, refined it, or applied it conscientiously to evaluating your own beliefs.
Assignment
- Select 3 information sources from the following list to study.
- News, opinions, analysis, commentary, satire, testimonials, endorsements, threats, conversations, dialogue, rumors, gossip, folk lore, traditions, rules, superstitions, taboos, censorship, speculation, predictions, fear mongering, forecasts, propaganda, advertisement, sales pitches, advocacy, political talking points, religious dogma, scriptures, prophesies, ideology, text books, school lessons, numbers, data, statistics, lobbying efforts, reports, street lore, peer pressure, web pages, Facebook, twitter, hearsay, disinformation, stories, anecdotes, legends, fables, myths, allegories, intuition, feelings, premonitions, origin stories, archetypes, suppositions, fallacies, red herrings, authorities, experts, celebrities, councilors, mystics, clairvoyants, charlatans, fools, fakers, and frauds all contend for our attention and opportunities to exert their influence.
- For each of the sources chosen, identify why they may be influential, why they are memorable, why they seem credible, and why they may be misleading or untrue.
- Identify some belief you have accepted as true based on each of the sources studied above.
A Gallery of Example Theories of Knowledge
It will be helpful to study example Theories of Knowledge to prepare yourself to write your own.
Assignment:
Survey this gallery of example Theories of Knowledge to understand better how one might be designed and written down. If any of these appeals to you, feel free to adopt it. If you disagree with these, or believe you can improve on these, then please write your own, using the instructions given in the next section.
Developing your own Theory of Knowledge
I hope the background provided in this course so far motives you to create your own theory of knowledge. In this section you will examine how you decide what to believe and write it down; this is your own theory of knowledge. Let’s get started.
Assignment:
- Study the materials suggested in this annotated version of the template to expand your thinking about how best to decide what to believe.
- Answer the questions in this template to focus your thinking on this topic. Use the template to get started, and begin knowing how you know.
- Using your answers to the questions in the template as source material, write your theory of knowledge as a series of steps or decision rules.
Examining Ideologies
Please complete the module on Examining Ideologies along with the associated assignments.
Testing your Theory of Knowledge
Your theory of knowledge will get refined as you use it to decide what to believe. The next assignment provides some questions to use to gain experience using and testing your Theory of Knowledge.
Assignment
- Choose 5 questions from this list of general knowledge questions to research.
- Research answers to these questions using any sources deemed reliable by your own Theory of Knowledge.
- Refine your written Theory of Knowledge if you find it difficult to use, or if it gives surprising, conflicting, or unreliable results.
- Continue to align your beliefs with reality.
Applying your Theory of Knowledge
Use your theory of Knowledge every day to decide what to believe, and to refine and purify your knowledge stream.
Assignment
- Scan your own beliefs to identify some that may not be well justified.
- Subject beliefs you have held for some time to your newly-developed Theory of knowledge.
- Note if: 1) They are confirmed by your theory of knowledge, 2) your new theory of knowledge causes you to modify, doubt, or change your beliefs, or 3) you refine your theory of knowledge to better reflect your concept of truth.
Further Reading
Students interested in learning more about developing and applying a Theory of Knowledge may be interested in the following materials:
- Weston, Anthony (2000). A Rulebook for Arguments. Hackett Pub Co Inc. pp. 90. ISBN 978-0872205529.
- Copi, Irving M. (2001). Introduction to Logic. Prentice Hall. pp. 647. ISBN 978-0130337351.
- Cialdini, Robert B. (1993). Influence: The Psychology of Persuasion. Collins. pp. 336. ISBN 978-0688128166.
- Sewell, Keith (2012). Leaving Truth. eBookIt.com. pp. 70.
- Haidt, Jonathan (2012). The Righteous Mind: Why Good People Are Divided by Politics and Religion. Pantheon. pp. 448. ISBN 978-0307377906.
- de Bono, Edward (1999). Six Thinking Hats. Back Bay Books. pp. 192. ISBN 978-0316178310.
- Silver, Nate (2012). The Signal and the Noise: Why So Many Predictions Fail — but Some Don't. Penguin Press. pp. 544. ISBN 978-1594204111.
- Gore, Al (2008). The Assault on Reason. Penguin Books. pp. 308. ISBN 978-0143113621.
- Burton, Robert (March 2008). On Being Certain: Believing You Are Right Even When You're Not. St. Martin's Griffin. ISBN 978-0312541521.
- Tavris, Carol; Aronson, Elliot (March 2008). Mistakes Were Made (But Not by Me): Why We Justify Foolish Beliefs, Bad Decisions, and Hurtful Acts. Mariner Books. ISBN 978-0156033909.
- Wolpert, Lewis (July, 2008). Six Impossible Things Before Breakfast: The Evolutionary Origins of Belief. W. W. Norton & Company. pp. 256. ISBN 978-0393332032.
- Robert Kenner (July 7, 2015) (in English). Merchants of Doubt (DVD). Sony Pictures Home Entertainment.
- Gelwick, Richard (May 12, 2004). The Way of Discovery, an introduction to the thought of Michael Polanyi. Wipf & Stock. pp. 200. ISBN 978-1592446872.
- Noise to Wisdom—an appreciative inquiry about wisdom, Essay by Anne Adams November 2013,
- Critical Thinker Academy — Learn how to think, not what to think.
- Why we should trust scientists, TED Talk, May 2014, Naomi Oreskes
- (Evaluate the book: The Believing Brain: From Ghosts and Gods to Politics and Conspiracies---How We Construct Beliefs and Reinforce Them as Truths )
- (Evaluate the book: In the Mind's Eye: Truth Versus Perception: ELA Lessons for Gifted and Advanced Learners in Grades 6 by Emily Mofield )
References
- ↑ Burton, Robert (2008). On Being Certain: Believing You Are Right Even When You're Not. St. Martin's Press. pp. 272. ISBN 978-0312359201.
- ↑ see, for example: R.A.V. v. City of St. Paul and United States v. Alvarez