Information Systems/Operating Systems
< Information Systems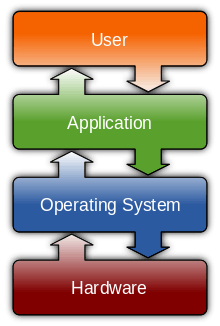
An operating system (OS) is a collection of software that manages computer hardware resources and provides common services for computer programs. The operating system is a vital component of the system software in a computer system. Application programs usually require an operating system to function.[1]
Objectives and Skills
Objectives and skills for the operating systems portion of CLEP Information Systems include:[2]
- Concepts of computer architectures (mainframe, client/server, operating systems)
- Basic user functions of a desktop operating system (memory management, file management, interfaces, types of OS)
Readings
- Read Wikibooks: Introduction to Computer Information Systems/System Software.
- Read Wikipedia: Operating system.
Multimedia
- Watch YouTube: Operating Systems Introduction.
- Watch YouTube: Introduction to Operating Systems.
- Watch YouTube: Operating System Basics.
- Watch YouTube: Operating System Functions.
- Watch YouTube: Types of Operating Systems.
- Watch YouTube: The History of Operating Systems.
Activities
- Complete the tutorial GCFLearnFree: Understanding Operating Systems.
- Determine whether your computer is running a 32 or 64-bit operating system:
- Windows: Review Microsoft: Is my PC running the 32-bit or 64-bit version of Windows?.
- OS X: Review Apple: Mac OS X: 64-bit kernel frequently asked questions.
- Linux: Review How to Check Linux Kernel is 32 bit or 64 bit.
- Use your system's monitoring utilities to review active processes and resources in use:
- Windows: Review Wikipedia: Windows Task Manager and Wikipedia: Resource Monitor and run both utilities.
- OS X: Review Wikipedia: Activity Monitor and run the utility.
- Linux: Review GNOME: System Monitor and run the utility.
- Review Wikipedia: Device Manager and Microsoft: Update a driver for hardware that isn't working properly. Run Device Manager on a Windows system Use Device Manager to check for updated drivers for all display adapters, network adapters, and sound controllers.
- Examine system health and recent events for your system:
- Windows: Review Microsoft: How to Use Reliability Monitor and Wikipedia: Event Viewer and run the utilities.
- OS X: Review Wikipedia: Console (OS X) and run the utility.
- Linux: Review RedHat: Viewing Log Files and run the Log Viewer.
- Review the lesson summary, key terms, review questions, and assessments below.
Lesson Summary
- An operating system is software that manages computer hardware and software resources and provides common services for computer programs.[3]
- The operating system provides an Interface between the user and the system.[4]
- The operating system coordinates hardware components.[5]
- The operating system provides an environment for software applications to function.[6]
- The operating system monitors system health and functionality.[7]
- The operating system provides a file structure for data management.[8]
- Popular computer operating systems include Windows, OS X, Linux, and Chrome OS.[9]
- A mobile operating system, also referred to as mobile OS, is an operating system that operates a smartphone, tablet, PDA, or other mobile device.[10]
- Popular mobile operating systems include Android, iOS and to a lesser extent Windows Phone and Blackberry.[11]
- OS X, Linux, Android, Chrome OS and iOS are based on Unix.[12]
- Popular distributions of Linux include Red Hat, Debian, Ubuntu, Linux Mint and Google's Android.[13]
- Open-source software is computer software with its source code made available with a license in which the copyright holder provides the rights to study, change and distribute the software to anyone and for any purpose.[14]
- Proprietary software or closed source software is computer software licensed under exclusive legal right of the copyright holder with the intent that the licensee is given the right to use the software only under certain conditions, and restricted from other uses, such as modification, sharing, studying, redistribution, or reverse engineering.[15]
Key Terms
- 32-bit
- A computer architecture that supports at most 32-bit integers, memory addresses, and other data units, limiting integer values to -2,147,483,648 through 2,147,483,647 and memory addresses to 4 GiB (gigabytes or gibibytes).[16]
- 64-bit
- A computer architecture that supports at most 64-bit integers, memory addresses, and other data units, limiting integer values to over 18 quintillion and memory addresses to 16 EiB (exbibytes).[17]
- agent
- A computer program that acts on behalf of a user or other program.[18]
- Android
- A mobile operating system (OS) based on the Linux kernel and currently developed by Google.[19]
- Blackberry OS
- A proprietary mobile operating system developed by BlackBerry Ltd for its BlackBerry line of smartphone handheld devices.[20]
- booting
- The initialization of a computerized system.[21]
- Chrome OS
- An operating system based on the Linux kernel and designed by Google to work with web applications and installed applications, initially designed as a pure web thin client operating system.[22]
- command-line interface
- A means of interacting with a computer program where the user issues commands to the program in the form of successive lines of text.[23]
- compatibility
- The ability to run software on a given system.[24]
- copyright
- Used by proprietary software companies to prevent the unauthorized copying of their software and by open source licenses to enforce their terms.[25]
- cross-platform
- An attribute conferred to computer software or computing methods and concepts that are implemented and inter-operate on multiple computer platforms.[26]
- device driver
- A computer program that operates or controls a particular type of device that is attached to a computer, specifically hardware devices [27]
- DOS (Disk Operating System)
- An acronym for several computer operating systems that were operated by using the command line.[28]
- end-user license agreement (EULA)
- The contract between a licensor and purchaser, establishing the purchaser's right to use software.[29]
- file manager
- A computer program that provides a user interface to manage files and folders.[30]
- formatting
- The process of preparing a data storage device such as a hard disk drive, solid-state drive, floppy disk or USB flash drive for initial use.[31]
- fragmentation
- Occurs when a file system cannot or will not allocate enough contiguous space to store a complete file as a unit, but instead puts parts of it in gaps between existing files.[32]
- Graphical User Interface (GUI)
- A type of interface that allows users to interact with electronic devices through icons and visual indicators.[33]
- iOS
- A mobile operating system developed by Apple Inc. and distributed exclusively for Apple hardware, including iPods, iPhones, and iPads.[34]
- kernel
- A computer program that manages I/O requests from software, and translates them into data processing instructions for the central processing unit and other electronic components of a computer.[35]
- Linux
- A Unix-like computer operating system assembled under the model of free and open-source software development and distribution.[36]
- Mac OS
- A series of graphical user interface–based operating systems developed by Apple Inc. for their Macintosh line of computer systems, currently branded as OS X.[37]
- memory management
- Provides ways to dynamically allocate portions of memory to programs at their request, and free it for reuse when no longer needed.[38]
- menu bar
- A graphical control element that lists options or commands presented to an operator by a computer or communications system.[39]
- multi-tasking
- Performing multiple tasks over a certain period of time by executing them concurrently.[40]
- open source
- A development model that promotes universal access via a free license to a product's design, and universal redistribution of that design, including subsequent improvements to it by anyone.[41]
- OS X
- A series of Unix-based graphical interface operating systems developed and marketed by Apple Inc. designed to run on Mac computers.[42]
- paging
- A memory management scheme by which a computer stores and retrieves data from the secondary storage for use in main memory.[43]
- path
- The general form of the name of a file or directory, specifies a unique location in a file system.[44]
- platform
- Computer hardware architecture, an operating system, and runtime libraries in which a piece of software is designed to run.[45]
- root directory
- The first or top-most directory in a hierarchy.[46]
- safe mode
- A diagnostic mode of a computer operating system (OS). [47]
- shell
- A user interface used to access an operating system's services.[48]
- task manager
- A system monitor program used to provide information about the processes and programs running on a computer, as well as the general status of the computer.
- taskbar
- An element of a graphical user interface which typically shows which programs or applications are running on the device, as well as providing links or shortcuts to other programs or places. [49]
- Unix
- A family of multitasking, multi-user computer operating systems.[50]
- user interface
- The space where interactions between humans and machines occur.[51]
- virtual memory
- A memory management technique that is implemented using both hardware and software.[52]
- Windows
- A metafamily of graphical operating systems developed, marketed, and sold by Microsoft.[53]
- x64
- The 64-bit version of the x86 instruction set, supporting 64-bit addressing and processing, and fully backwards compatible with 16-bit and 32-bit x86 code.[54]
- x86
- A family of backward compatible instruction set architectures based on the Intel 8086 through 80486 CPUs supporting 16-bit and 32-bit addressing and processing.[55][56]
Review Questions
-
An operating system is _____.An operating system is software that manages computer hardware and software resources and provides common services for computer programs.
-
The operating system provides an interface between _____.The operating system provides an Interface between the user and the system.
-
The operating system coordinates _____.The operating system coordinates hardware components.
-
The operating system provides an environment for _____.The operating system provides an environment for software applications to function.
-
The operating system monitors _____.The operating system monitors system health and functionality.
-
The operating system provides a file structure for _____.The operating system provides a file structure for data management.
-
Popular computer operating systems include _____.Popular computer operating systems include Windows, OS X, Linux, and Chrome OS.
-
A mobile operating system, also referred to as mobile OS, is an operating system that operates _____.A mobile operating system, also referred to as mobile OS, is an operating system that operates a smartphone, tablet, PDA, or other mobile device.
-
Popular mobile operating systems include _____.Popular mobile operating systems include Android, iOS and to a lesser extent Windows Phone and Blackberry.
-
OS X, Linux, Android, Chrome OS and iOS are based on _____.OS X, Linux, Android, Chrome OS and iOS are based on Unix.
-
Popular distributions of Linux include _____.Popular distributions of Linux include Red Hat, Debian, Ubuntu, Linux Mint and Google's Android.
-
Open-source software is computer software with _____.Open-source software is computer software with its source code made available with a license in which the copyright holder provides the rights to study, change and distribute the software to anyone and for any purpose.
-
Proprietary software or closed source software is _____.Proprietary software or closed source software is computer software licensed under exclusive legal right of the copyright holder with the intent that the licensee is given the right to use the software only under certain conditions, and restricted from other uses, such as modification, sharing, studying, redistribution, or reverse engineering.
Assessments
- Flashcards: Quizlet: Information Systems - Operating Systems
- Quiz: Quizlet: Information Systems - Operating Systems
See Also
- Computer Software
- Using an Operating System
- IT Fundamentals/Operating Systems
- How Stuff Works: 5 Important Jobs Your Operating System Handles Without You Knowing
- How Stuff Works: How Operating Systems Work
- eHow.com: How does a computer operating system work?
- Nash Networks: The Pros and Cons of Operating Systems
References
- ↑ Wikipedia: Operating system
- ↑ CLEP: Information Systems
- ↑ Wikipedia: Operating system
- ↑ CompTIA IT Fundamentals Certification Exam Objectives (FC0-U51)
- ↑ CompTIA IT Fundamentals Certification Exam Objectives (FC0-U51)
- ↑ CompTIA IT Fundamentals Certification Exam Objectives (FC0-U51)
- ↑ CompTIA IT Fundamentals Certification Exam Objectives (FC0-U51)
- ↑ CompTIA IT Fundamentals Certification Exam Objectives (FC0-U51)
- ↑ Wikipedia: Operating system
- ↑ Wikipedia: Mobile operating system
- ↑ Wikipedia: Operating system
- ↑ Wikipedia: Operating system
- ↑ Wikipedia: Operating system
- ↑ Wikipedia: Open-source software
- ↑ Wikipedia: Proprietary software
- ↑ Wikipedia: 32-bit
- ↑ Wikipedia: 64-bit
- ↑ Wikipedia: Software agent
- ↑ Wikipedia: Android (operating system)
- ↑ Wikipedia: Blackberry OS
- ↑ Wikipedia: Booting
- ↑ Wikipedia: Chrome OS
- ↑ Wikipedia: Command-line interface
- ↑ Wikipedia: Computer compatibility
- ↑ Wikipedia: Software copyright
- ↑ Wikipedia: Cross-platform
- ↑ Wikipedia: Operating Systems
- ↑ Wikipedia: DOS
- ↑ Wikipedia: End-user license agreement
- ↑ Wikipedia: File manager
- ↑ Wikipedia: Disk formatting
- ↑ Wikipedia: Defragmentation
- ↑ [[|Wikipedia: Graphical user interface]]
- ↑ Wikipedia: iOS
- ↑ Wikipedia: Kernel (operating system)
- ↑ Wikipedia: Linux
- ↑ Wikipedia: Mac OS
- ↑ Wikipedia: Memory management
- ↑ Wikipedia: Menu bar
- ↑ Wikipedia: Computer multitasking
- ↑ Wikipedia: Open source
- ↑ Wikipedia: OS X
- ↑ Wikipedia: Paging
- ↑ Wikipedia: Path (computing)
- ↑ Wikipedia: Computing platform
- ↑ Wikipedia: Root directory
- ↑ Wikipedia: Safe mode
- ↑ Wikipedia: Shell (computing)
- ↑ Wikipedia: Taskbar
- ↑ Wikipedia:Unix
- ↑ Wikipedia: User interface
- ↑ Wikipedia: Virtual memory
- ↑ Wikipedia: Microsoft Windows
- ↑ Wikipedia: x86-64
- ↑ Wikipedia: x86
- ↑ Wikipedia: IA-32
This article is issued from Wikiversity - version of the Sunday, January 03, 2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.