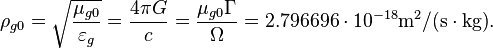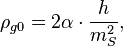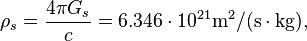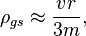Physics/Essays/Fedosin/Gravitational characteristic impedance of free space
< Physics < Essays < FedosinThe Gravitational characteristic impedance of free space, 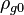 is a physical constant that relates the magnitudes of the gravitational field strength
is a physical constant that relates the magnitudes of the gravitational field strength 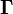 and the gravitational torsion field
and the gravitational torsion field 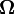 in covariant theory of gravitation (the gravitoelectric and gravitomagnetic fields in gravitoelectromagnetism) in gravitational radiation travelling through free space:
in covariant theory of gravitation (the gravitoelectric and gravitomagnetic fields in gravitoelectromagnetism) in gravitational radiation travelling through free space:
where
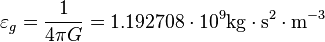 is the gravitoelectric gravitational constant in the set of selfconsistent gravitational constants,
is the gravitoelectric gravitational constant in the set of selfconsistent gravitational constants,
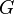 is the gravitational constant,
c is the speed of light,
is the gravitational constant,
c is the speed of light,
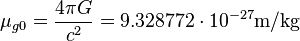 is the gravitomagnetic gravitational constant.
is the gravitomagnetic gravitational constant.
As in electromagnetism, the characteristic impedance of free space plays a central role in all radiation problems, such as in a comparison of the radiation resistance of gravity-wave antennas to the value of this impedance in order to estimate the coupling efficiency of these antennas to free space. The numerical value of this impedance is extremely small, but the impedance of all material objects must be “impedance matched” to this extremely small quantity before significant power can be transferred efficiently from gravitational waves to these detectors.
The gravitational characteristic impedance of free space may be connected with other constants:
where 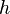 is the Planck constant,
is the Planck constant,
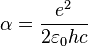 is the fine structure constant for the elementary charge
is the fine structure constant for the elementary charge  ,
,
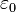 is the vacuum permittivity,
is the vacuum permittivity,
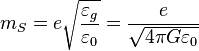 is the Stoney mass.
is the Stoney mass.
The gravitational characteristic impedance of free space for the atoms and nucleons level of matter is:
where 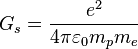 is the strong gravitational constant,
is the strong gravitational constant, 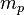 and
and 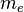 are the masses of proton and electron.
are the masses of proton and electron.
History
Due to McDonald [1] first who used Maxwell equations to describe gravity was Oliver Heaviside. [2] The point is that in the weak gravitational field the standard theory of gravity could be written in the form of Maxwell-like gravitational equations. [3]
In the 80-ties Maxwell-like equations were considered in the Wald book of general relativity. [4] In the 90-ties Kraus [5] first introduced the gravitational characteristic impedance of free space, which was detailed later by Kiefer [6], and now by Raymond Y. Chiao, [7] [8] [9] [10] [11] who is developing the ways of experimental determination of the gravitational waves.
Typical gravitational impedance at the megascopic scale
In the general case only planets (with their sattelites) and stars could be considered "as free, as possible" to be used as some "antenna" to the gravitational waves detection. Spherical megascopic bodies have the folloving characteristic impedance:
where
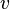 is the equatorial velocity,
is the equatorial velocity,  is the spherical body radius and
is the spherical body radius and 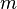 is the body mass.
is the body mass.
- Solar planetary system
| Object | Radius, m | Equator velocity, m/s | Mass, kg | Impedance |  |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Human | 2 | 1 | 100 | 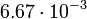 |
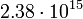 |
| Sun | 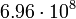 |
317.4 | 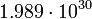 |
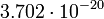 |
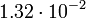 |
| Mercury | 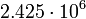 |
2.99 | 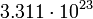 |
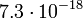 |
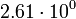 |
| Venus | 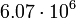 |
1.807 | 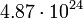 |
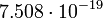 |
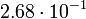 |
| Earth | 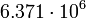 |
465 | 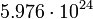 |
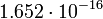 |
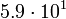 |
| Mars | 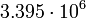 |
240.6 | 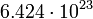 |
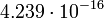 |
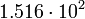 |
| Jupiter | 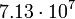 |
12644 | 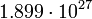 |
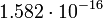 |
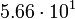 |
| Saturn | 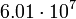 |
10248 | 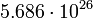 |
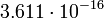 |
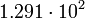 |
| Uranus | 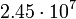 |
3952 | 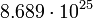 |
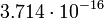 |
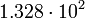 |
| Neptune | 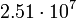 |
2771 | 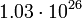 |
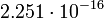 |
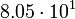 |
Planetary data were taken from the textbook. [12] As could be seen from the Table, only the Mercury has characteristic impedance close to the free space value.
- Planet's satellites
| Object | Radius, m | Equator velocity, m/s | Mass, kg | Impedance | 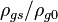 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moon | 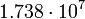 |
4.36 | 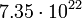 |
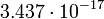 |
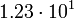 |
| Titan | 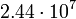 |
276.8 | 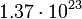 |
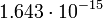 |
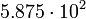 |
| Ganymede | 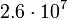 |
1116 | 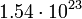 |
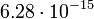 |
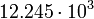 |
| Callisto | 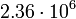 |
252.7 | 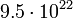 |
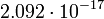 |
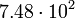 |
Satellites' data were taken from the textbook. [12] As could be seen from the Table, only the Moon has the closest value of characteristic impedance about 12-times greater then for free space.
- Stars
| Object | Radius, m | Equator velocity, m/s | Mass, kg | Impedance | 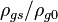 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sun | 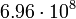 |
317.4 | 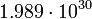 |
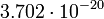 |
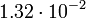 |
| O5 | 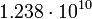 |
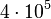 |
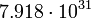 |
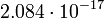 |
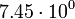 |
| F5 | 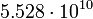 |
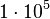 |
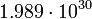 |
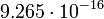 |
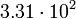 |
| Globular cluster | 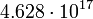 |
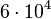 |
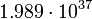 |
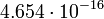 |
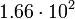 |
In this table designations "O5" and "F5" define stellar types. [12] As it is seen from the Table, some stars could have characteristic impedance value about the same as the impedance of free space.
See also
- Selfconsistent gravitational constants
- Maxwell-like gravitational equations
- Quantum Gravitational Resonator
- Vacuum constants
References
- ↑ K.T. McDonald, Am. J. Phys. 65, 7 (1997) 591-2.
- ↑ O. Heaviside, Electromagnetic Theory (”The Electrician” Printing and Publishing Co., London, 1894) pp. 455-465.
- ↑ W. K. H. Panofsky and M. Phillips, Classical Electricity and Magnetism (Addison-Wesley, Reading, MA, 1955), p. 168, 166.
- ↑ R. M. Wald, General Relativity (University of Chicago Press, Chicago, 1984).
- ↑ J. D. Kraus, IEEE Antennas and Propagation. Magazine 33, 21 (1991).
- ↑ C. Kiefer and C. Weber, Annalen der Physik (Leipzig) 14, 253 (2005).
- ↑ Raymond Y. Chiao. "Conceptual tensions between quantum mechanics and general relativity: Are there experimental consequences, e.g., superconducting transducers between electromagnetic and gravitational radiation?" arXiv:gr-qc/0208024v3 (2002). [PDF
- ↑ R.Y. Chiao and W.J. Fitelson. Time and matter in the interaction between gravity and quantum fluids: are there macroscopic quantum transducers between gravitational and electromagnetic waves? In Proceedings of the “Time & Matter Conference” (2002 August 11-17; Venice, Italy), ed. I. Bigi and M. Faessler (Singapore: World Scientific, 2006), p. 85. arXiv: gr-qc/0303089. PDF
- ↑ R.Y. Chiao. Conceptual tensions between quantum mechanics and general relativity: are there experimental consequences? In Science and Ultimate Reality, ed. J.D. Barrow, P.C.W. Davies, and C.L.Harper, Jr. (Cambridge:Cambridge University Press, 2004), p. 254. arXiv:gr-qc/0303100.
- ↑ Raymond Y. Chiao. "New directions for gravitational wave physics via “Millikan oil drops” arXiv:gr-qc/0610146v16 (2009). PDF
- ↑ Stephen Minter, Kirk Wegter-McNelly, and Raymond Chiao. Do Mirrors for Gravitational Waves Exist? arXiv:gr-qc/0903.0661v10 (2009). PDF
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 12.2 Allen C.W.(1973). Astrophysical quantities. 3-d edition. University of London, The Athlone Press.