Computer Support/Hardware/Motherboards
< Computer Support < HardwareThis lesson covers motherboards.
Objectives and Skills
Objectives and skills for the motherboards portion of A+ certification include:[1]
- Explain the importance of motherboard components, their purpose, and properties.
- Sizes
- ATX
- Micro-ATX
- Mini-ITX
- ITX
- Expansion slots
- PCI
- PCI-X
- PCIe
- miniPCI
- RAM slots
- CPU sockets
- Chipsets
- North Bridge
- South Bridge
- Power connections and types
- Fan connectors
- Front/Top panel connectors
- USB
- Audio
- Power button
- Power light
- Drive activity lights
- Reset button
- Bus speeds
- Sizes
Readings
- Read Wikipedia: Motherboard.
- Read Wikipedia: Computer form factor.
- Read Wikipedia: ATX.
- Read Wikipedia: EPIA.
- Read Wikipedia: Expansion card.
- Read Wikipedia: CPU socket.
- Read Wikipedia: Northbridge (Computing).
- Read Wikipedia: Southbridge (Computing).
- Read Wikipedia: Computer form factor.
Multimedia
- Watch YouTube: An Overview of Motherboard Types - CompTIA A+ 220-901: 1.2.
- Watch YouTube: Motherboard Expansion Slots and Bus Speeds - CompTIA A+ 220-901: 1.2.
- Watch YouTube: Motherboard RAM Slots - CompTIA A+ 220-901: 1.2.
- Watch YouTube: CPU Sockets - CompTIA A+ 220-901: 1.2.
- Watch YouTube: Motherboard Chipsets - CompTIA A+ 220-901: 1.2.
- Watch YouTube: Motherboard Jumpers and Connectors - CompTIA A+ 220-901: 1.2.
Activities
- Read How Motherboards Work on HowStuffWorks Tech.
- Read How PCI Works on HowStuffWorks Tech.
- Read How PCI Express Works on HowStuffWorks Tech.
- Take the HowStuffWorks Tech CPU Quiz.
Lesson Summary

Motherboard for an Acer desktop personal computer, showing the typical components and interfaces that are found on a motherboard. This model was made by Foxconn in 2007, and follows the ATX layout (known as the "form factor") usually employed for desktop computers. It is designed to work with AMD's Athlon 64 processor
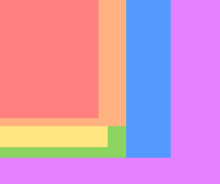
ATX motherboard size comparison; rear is on left.
FlexATX (229 × 191 mm)
microATX (244 × 244 mm)
Mini ATX (284 × 208 mm)
Standard ATX (305 × 244 mm)
Extended ATX (EATX) (305 × 330 mm)
WTX (356 × 425 mm)

ITX motherboard form factor comparison
- Motherboards are produced in a variety of sizes and shapes called computer form factor, some of which are specific to individual computer manufacturers. However, the motherboards used in IBM-compatible systems are designed to fit various case sizes. As of 2007, most desktop computer motherboards use the ATX standard form factor — even those found in Macintosh and Sun computers, which have not been built from commodity components. A case's motherboard and PSU form factor must all match, though some smaller form factor motherboards of the same family will fit larger cases. For example, an ATX case will usually accommodate a microATX motherboard. Laptop computers generally use highly integrated, miniaturized and customized motherboards. This is one of the reasons that laptop computers are difficult to upgrade and expensive to repair. Often the failure of one laptop component requires the replacement of the entire motherboard, which is usually more expensive than a desktop motherboard due to the large number of integrated components and their custom shape and size.[2]
- ATX (Advanced Technology eXtended) is a motherboard configuration specification developed by Intel in 1995 to improve on previous de facto standards like the AT design. It was the first major change in desktop computer enclosure, motherboard and power supply design in many years, improving standardization and interchangeability of parts. ATX is the most common motherboard design. Other standards for smaller boards (including microATX, FlexATX and mini-ITX) usually keep the basic rear layout but reduce the size of the board and the number of expansion slots. Dimensions of a full-size ATX board are 12 × 9.6 in (305 × 244 mm), which allows many ATX chassis to also accept microATX boards. The official ATX specifications were released by Intel in 1995 and have been revised numerous times since. The most recent ATX motherboard specification is version 2.2. The most recent ATX12V power supply unit specification is 2.31, released in February 2008.[3]
- VIA EPIA (VIA Embedded Platform Innovative Architecture) is a series of mini-ITX, em-ITX, nano-ITX, pico-ITX and pico-ITXe motherboards with integrated VIA processors. They are small in size and consume less power than computers of comparable capabilities.[4]
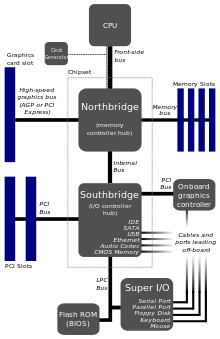
Block diagram of a modern motherboard, which supports many on-board peripheral functions as well as several expansion slots
- The expansion card (also expansion board, adapter card or accessory card) in computing is a printed circuit board that can be inserted into an electrical connector, or expansion slot on a computer motherboard, backplane or riser card to add functionality to a computer system via the expansion bus.[5]
- PCI, PCI-X, PCIe, miniPCI are common expansion cards.
- A CPU socket (central processing unit) or slot is an electrical component that attaches to a Printed Circuit Board (PCB) and is designed to house a CPU (also called a microprocessor). It is a special type of integrated circuit socket designed for very high pin counts. A CPU socket provides many functions, including a physical structure to support the CPU, support for a heat sink, facilitating replacement (as well as reducing cost), and most importantly, forming an electrical interface both with the CPU and the PCB. CPU sockets on the motherboard can most often be found in most desktop and server computers (laptops typically use surface mount CPUs), particularly those based on the Intel x86 architecture. A CPU socket type and motherboard chipset must support the CPU series and speed.[6]
- In a computer system, a chipset is a set of electronic components in an integrated circuit that manages the data flow between the processor, memory and peripherals. It is usually found on the motherboard. Chipsets are usually designed to work with a specific family of microprocessors. Because it controls communications between the processor and external devices, the chipset plays a crucial role in determining system performance.[7]
- A northbridge (or host bridge) is one of the two chips in the core logic chipset architecture on a PC motherboard. northbridge is connected directly to the CPU via the frontside bus (FSB) and thus responsible for tasks that require the highest performance.[8]
- The southbridge typically implements the slower capabilities of the motherboard in a northbridge/southbridge chipset computer architecture. The southbridge can usually be distinguished from the northbridge by not being directly connected to the CPU. Rather, the northbridge ties the southbridge to the CPU.[9]
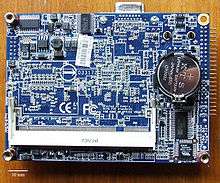
CMOS battery in a Pico ITX motherboard
- The memory battery (aka motherboard, CMOS, real-time clock (RTC), clock battery) is generally a CR2032 lithium coin cell. These cells last two to ten years, depending on the type of motherboard, ambient temperature and the length of time that the system is powered off. When replacing the cell, the system time and CMOS BIOS settings may revert to default values. This may be avoided by replacing the cell with the power supply master switch on. On ATX motherboards, this will supply 5V power to the motherboard even if it is apparently "switched off" and keep the CMOS memory energized.[10]

AMP Mate-N-Lok and Molex Standard .093" Pin and Socket power connectors.

ATX Connector
- Power connectors receive electrical power from the computer power supply and distribute it to the CPU, chipset, main memory, and expansion cards.[11]
- The ATX specification requires the power supply to produce three main outputs, +3.3 V, +5 V and +12 V. Low-power −12 V and 5 VSB (standby) supplies are also required. Originally, the motherboard was powered by one 20-pin connector. An ATX power supply provides a number of peripheral power connectors and (in modern systems) two connectors for the motherboard: a 4-pin auxiliary connector providing additional power to the CPU and a main 24-pin power supply connector, an extension of the original 20-pin version.[12]
- The Three-pin Molex KK family connector is used when connecting a fan to the motherboard or other circuit board. 4, 6 and 8 pin configurations of the same style of connector are used for additional CPU power and graphics card power. This is changing as power, signal and speed requirements increase in sophistication and electronic requirements.[13]
- Common front-panel connectors include USB ports, audio jacks for integrated sound hardware, power button, and power indication and drive activity LEDs.
- Front-side buses usually connect the CPU and the rest of the hardware via a chipset, which Intel implemented as a northbridge and a southbridge. Other buses like the Peripheral Component Interconnect (PCI), Accelerated Graphics Port (AGP), and memory buses all connect to the chipset in order for data to flow between the connected devices. These secondary system buses usually run at speeds derived from the front-side bus clock, but are not necessarily synchronized to it.[14]
- The frequency at which a processor (CPU) operates is determined by applying a clock multiplier to the front-side bus (FSB) speed in some cases. For example, a processor running at 3200 MHz might be using a 400 MHz FSB. This means there is an internal clock multiplier setting (also called bus/core ratio) of 8. That is, the CPU is set to run at 8 times the frequency of the front-side bus: 400 MHz × 8 = 3200 MHz. Different CPU speeds are achieved by varying either the FSB frequency or the CPU multiplier.[15]
- Setting an FSB speed is related directly to the speed grade of memory a system must use. The memory bus connects the northbridge and RAM, just as the front-side bus connects the CPU and northbridge. Often, these two buses must operate at the same frequency.[16]
- Similar to the memory bus, the PCI and AGP buses can also be run asynchronously from the front-side bus. In older systems, these buses are operated at a set fraction of the front-side bus frequency. This fraction was set by the BIOS. In newer systems, the PCI, AGP, and PCI Express peripheral buses often receive their own clock signals, which eliminates their dependence on the front-side bus for timing.[17]

The icon denoting the power or reset function on most devices
- The reset button could be an actual button or concept. The reset button would typically kick off a soft boot, instructing the computer to go through the process of shutting down, which would clear memory and reset devices to their initialized state. Contrary to the 'Power Button', which would simply remove power immediately.[18]
Key Terms
- Form factor
- the specification of a motherboard – the dimensions, power supply type, location of mounting holes, number of ports on the back panel, etc.[19]
- Expansion card
- a printed circuit board that can be inserted into an electrical connector, or expansion slot on a computer motherboard, backplane or riser card to add functionality to a computer system via the expansion bus.[20]
- CPU socket
- an electrical component that attaches to a Printed Circuit Board (PCB) and is designed to house a CPU[21]
- Chipset
- a set of electronic components in an integrated circuit that manages the data flow between the processor, memory and peripherals.[22]
- Connector
- joins two lengths of flexible copper wire or cable, or connect a wire or cable to an electrical terminal. Connectors consist of plugs (male-ended) and jacks (female-ended). Common motherboard connectors are Molex and Berg connectors.[23]
- Bus
- a communication system that transfers data between components inside a computer, or between computers. This expression covers all related hardware components (wire, optical fiber, etc.) and software, including communication protocols.[24]
References
- ↑ CompTIA: A+ Certification Exam Objectives - Exam 220-901
- ↑ Wikipedia: Motherboard#Form factor
- ↑ Wikipedia: ATX
- ↑ Wikipedia: EPIA
- ↑ Wikipedia: Expansion_card
- ↑ Wikipedia: CPU socket
- ↑ Wikipedia: Chipset
- ↑ Wikipedia: Northbridge (computing
- ↑ Wikipedia: Southbridge (computing)
- ↑ Wikipedia: Nonvolatile BIOS memory#CMOS battery
- ↑ Wikipedia: Motherboard#Design
- ↑ Wikipedia: ATX#Power supply
- ↑ Wikipedia: Computer fan#Connectors
- ↑ Wikipedia: Front-side bus#History
- ↑ Wikipedia: Front-side_bus#CPU
- ↑ Wikipedia: Memory bus speeds
- ↑ Wikipedia: Front-side bus#Peripheral buses
- ↑ Wikipedia: Reset button
- ↑ Wikipedia: Motherboard form factor
- ↑ Wikipedia: Expansion card
- ↑ Wikipedia: CPU socket
- ↑ Wikipedia: Chipset
- ↑ Wikipedia: Electrical connectors
- ↑ Wikipedia: Bus
This article is issued from Wikiversity - version of the Thursday, March 03, 2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.