Computer Support/Hardware/CPUs
< Computer Support < HardwareThis lesson covers central processing units (CPUs).
Objectives and Skills
Objectives and skills for the CPUs portion of A+ certification include:[1]
- Install various types of CPUs and apply the appropriate cooling methods.
- Socket types
- Intel: 775, 1155, 1156, 1366, 1150, 2011
- AMD: AM3, AM3+, FM1, FM2, FM2+
- Characteristics
- Speeds
- Cores
- Cache size/type
- Hyperthreading
- Virtualization support
- Architecture (32-bit vs. 64-bit)
- Integrated GPU
- Disable execute bit
- Cooling
- Heat sink
- Fans
- Thermal paste
- Liquid-based
- Fanless/passive
- Socket types
Readings
- Read Wikipedia: Central processing unit.
- Read Wikipedia: Land grid array.
- Read Wikipedia: LGA 775.
- Read Wikipedia: LGA 1155.
- Read Wikipedia: LGA 1156.
- Read Wikipedia: LGA 1366.
- Read Wikipedia: LGA 1150.
- Read Wikipedia: LGA 2011.
- Read Wikipedia: Pin grid array.
- Read Wikipedia: Socket AM3.
- Read Wikipedia: Socket AM3+.
- Read Wikipedia: Socket FM1.
- Read Wikipedia: Socket FM2.
- Read Wikipedia: Socket FM2+.
- Read Wikipedia: Instructions per second.
- Read Wikipedia: Multi-core processor.
- Read Wikipedia: CPU cache.
- Read Wikipedia: Hyper-threading.
- Read Wikipedia: Virtualization.
- Read Wikipedia: Instruction set.
- Read Wikipedia: x86.
- Read Wikipedia: x86-64.
- Read Wikipedia: Graphics processing unit.
- Read Wikipedia: Land grid array.
- Read Wikipedia: Computer cooling.
- Read Wikipedia: Heat sink.
- Read Wikipedia: Air cooling.
- Read Wikipedia: Thermal grease.
- Read Wikipedia: Water cooling.
- Read Wikipedia: Passive cooling.
Multimedia
- Watch YouTube: An overview of CPU socket types - CompTIA A+ 220-901: 1.6.
- Watch YouTube: Understanding CPU characteristics - CompTIA A+ 220-901: 1.6.
- Watch YouTube: CPU Cooling Techniques - CompTIA A+ 220-901: 1.6.
Lesson Summary
- A CPU socket is made of plastic, with a lever or latch, and metal contacts for each of the pins or lands on the CPU. Many packages are keyed to ensure the proper insertion of the CPU. CPUs with a pin grid array package are inserted into the socket and the latch is closed. CPUs with a land grid array package are inserted into the socket, the latch plate is flipped into position atop the CPU, and the lever is lowered and locked into place, pressing the CPU's contacts firmly against the socket's lands and ensuring a good connection, as well as increased mechanical stability.[2]
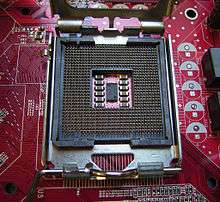
Socket 775 on a motherboard.

An example of a socket for a staggered pin grid array package.
- CPU clock speed, or clock rate, is measured in Hertz — generally in gigahertz, or GHz. A CPU’s clock speed rate is a measure of how many clock cycles a CPU can perform per second. For example, a CPU with a clock rate of 1.8 GHz can perform 1,800,000,000 clock cycles per second. Modern CPUs are becoming much more efficient. That is, they can get more work done per clock cycle. For example, Intel released Pentium 4 chips clocked at 3.6 GHz in 2006. It’s now the end of 2013 and the latest, fastest Intel Haswell Core i7 CPUs are clocked at 3.9 GHz from the factory. Does that mean CPU performance has only improved a tiny bit in seven years? Not at all! Instead, the Core i7 CPU can simply do much more during each clock cycle. It’s important to look not just at clock cycles but at the amount of work a CPU can do per clock cycle. All other things being equal, fewer clock cycles with more work are better than more clock cycles with less — fewer clock cycles means the CPU requires less power and produces less heat.[3]
- A multi-core processor is a single computing component with two or more independent actual processing units (called "cores"), which are the units that read and execute program instructions.[1] The instructions are ordinary CPU instructions such as add, move data, and branch, but the multiple cores can run multiple instructions at the same time, increasing overall speed for programs amenable to parallel computing.[2] Manufacturers typically integrate the cores onto a single integrated circuit die (known as a chip multiprocessor or CMP), or onto multiple dies in a single chip package.[4]
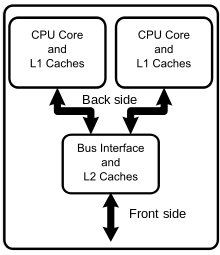
Diagram of a generic dual-core processor with CPU-local level-1 caches and a shared, on-die level-2 cache.
- When the processor needs to read from or write to a location in main memory, it first checks whether a copy of that data is in the cache. If so, the processor immediately reads from or writes to the cache, which is much faster than reading from or writing to main memory. Most modern desktop and server CPUs have at least three independent caches: an instruction cache to speed up executable instruction fetch, a data cache to speed up data fetch and store, and a translation lookaside buffer (TLB) used to speed up virtual-to-physical address translation for both executable instructions and data. The data cache is usually organized as a hierarchy of more cache levels (L1, L2, etc.; see also multi-level caches below). However, a TLB cache is part of the memory management unit (MMU) and not directly related to the CPU caches.[5]
- Hyper-threading (officially called Hyper-Threading Technology or HT Technology, and abbreviated as HTT or HT) is Intel's proprietary simultaneous multithreading (SMT) implementation used to improve parallelization of computations performed on x86 microprocessors. For each processor core that is physically present, the operating system addresses two virtual or logical cores, and shares the workload between them when possible. The main function of hyper-threading is to increase the number of independent instructions in the pipeline; it takes advantage of superscalar architecture, in which multiple instructions operate on separate data in parallel. With HTT, one physical core appears as two processors to the operating system, allowing concurrent scheduling of two processes per core. In addition, two or more processes can use the same resources: if resources for one process are not available, then another process can continue if its resources are available. In addition to requiring simultaneous multithreading (SMT) support in the operating system, hyper-threading can be properly utilized only with an operating system specifically optimized for it.[5] Furthermore, Intel recommends HTT to be disabled when using operating systems unaware of this hardware feature.[6]
- Computer hardware virtualization is the virtualization of computers as complete hardware platforms, certain logical abstractions of their componentry, or only the functionality required to run various operating systems. Virtualization hides the physical characteristics of a computing platform from the users, presenting instead another abstract computing platform.[1][2] At its origins, the software that controlled virtualization was called a "control program", but the terms "hypervisor" or "virtual machine monitor" became preferred over time.[7]
.svg.png)
Logical diagram of full virtualization.
- In computer architecture, 64-bit computing is the use of processors that have datapath widths, integer size, and memory address widths of 64 bits (eight octets). From the software perspective, 64-bit computing means the use of code with 64-bit virtual memory addresses. Without further qualification, a 64-bit computer architecture generally has integer and addressing registers that are 64 bits wide, allowing direct support for 64-bit data types and addresses.[8]
- In computer architecture, 32-bit integers, memory addresses, or other data units are those that are at most 32 bits (4 octets) wide. Memory as well as other digital electronic circuits and wiring was expensive during the first decades of 32-bit architectures (the 1960s to the 1980s). Older 32-bit processor families (or simpler and cheaper variants thereof) could therefore have many compromises and limitations in order to cut costs, such as buses narrower than 32 bits, limiting memory size or demanding more cycles for instruction fetch, execution and/or write back.[9]
- Integrated graphics solutions, shared graphics solutions, or integrated graphics processors (IGP) utilize a portion of a computer's system RAM rather than dedicated graphics memory. IGPs can be integrated onto the motherboard as part of the chipset, or within the same die as CPU (like AMD APU or Intel HD Graphics). Hybrid graphics cards are somewhat more expensive than integrated graphics, but much less expensive than dedicated graphics cards. These share memory with the system and have a small dedicated memory cache, to make up for the high latency of the system RAM.[10]
- The NX bit, which stands for No-eXecute, is a technology used in CPUs to segregate areas of memory for use by either storage of processor instructions (code) or for storage of data. An operating system with support for the NX bit may mark certain areas of memory as non-executable. The processor will then refuse to execute any code residing in these areas of memory. The general technique, known as executable space protection, is used to prevent certain types of malicious software from taking over computers by inserting their code into another program's data storage area and running their own code from within this section; one class of such attacks is known as the buffer overflow attack.[11]
- A heat sink is designed to maximize its surface area in contact with the cooling medium surrounding it, such as the air. Air velocity, choice of material, protrusion design and surface treatment are factors that affect the performance of a heat sink. Heat sink attachment methods and thermal interface materials also affect the die temperature of the integrated circuit. Thermal adhesive or thermal grease improve the heat sink's performance by filling air gaps between the heat sink and the heat spreader on the device. The Heat sink is usually made out of copper and aluminum.[12]

A fan-cooled heat sink on the processor of a personal computer. To the right is a smaller heat sink cooling another integrated circuit of the motherboard.
- As processors, graphics cards, RAM and other components in computers have increased in speed and power consumption, the amount of heat produced by these components as a side-effect of normal operation has also increased. These components need to be kept within a specified temperature range to prevent overheating, instability, malfunction and damage leading to a shortened component lifespan. While in earlier personal computers it was possible to cool most components using natural convection (passive cooling), many modern components require more effective active cooling. To cool these components, fans are used to move heated air away from the components and draw cooler air over them. Fans attached to components are usually used in combination with a heatsink to increase the area of heated surface in contact with the air, thereby improving the efficiency of cooling.[13]
- The principle used in a typical (active) liquid cooling system for computers is identical to that used in an automobile's internal combustion engine, with the water being circulated by a water pump through a waterblock mounted on the CPU (and sometimes additional components as GPU and northbridge[18] and out to a heat exchanger, typically a radiator. The radiator is itself sometimes cooled additionally by means of a fan. Also, a coolant reservoir is often also connected to the system.[14]
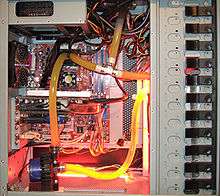
DIY Water cooling setup showing a 12 V pump, CPU Waterblock and the typical application of a T-Line
References
- ↑ CompTIA: A+ Certification Exam Objectives - Exam 220-901
- ↑ Wikipedia: CPU socket
- ↑ How-To Geek Why You Can’t Use CPU Clock Speed to Compare Computer Performance
- ↑ Wikipedia: Multi-core processor
- ↑ Wikipedia: CPU cache
- ↑ Wikipedia: Hyper-threading
- ↑ Wikipedia: Hardware virtualization
- ↑ Wikipedia: 64-bit computing
- ↑ Wikipedia: 32-bit
- ↑ Wikipedia: Graphics processing unit#Integrated graphics solutions
- ↑ Wikipedia: NX bit
- ↑ Wikipedia: Heat sink
- ↑ Wikipedia: Computer fan
- ↑ Wikipedia: Computer cooling#Liquid cooling
This article is issued from Wikiversity - version of the Tuesday, February 23, 2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.