Change of variables
| | Educational level: this is a tertiary (university) resource. |
| | Resource type: this resource is a lesson. |
| | Subject classification: this is a mathematics resource . |
| | Completion status: this resource is ~25% complete. |
School:Mathematics > Differential Equations > Ordinary differential equations > Change of variables
Definition
In a differential equation, if a certain term appears many different times, a substitution can be made similar to a 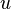 -substitution.
-substitution.
Solution
- Substitute a term for a variable (e.g.
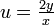 ).
). - Implicitly differentiate the variable (e.g.
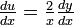 ).
). - Solve for the derivative that needs to be solved (e.g.
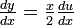 ).
). - Solve the original equation in terms of
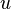 and then use the substitution for
and then use the substitution for 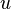 to get the original equation back in terms of
to get the original equation back in terms of 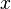 and
and 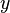 .
.
This article is issued from Wikiversity - version of the Friday, March 07, 2014. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.