Angular Velocity
Angular velocity is a pseudovector physical quantity which specifies the angular speed of an object and the axis about which it is rotating.
It has the units radians (the unit for angles used in circular motion physics) per second or just rad s-1. From this we can easily derive the formulae for angular velocity:
In a basic form, angular velocity can be expressed as
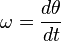
where ω is angular velocity, dθ is the angle covered by the object in question and dt is the time taken for this angle to be covered.
Angular velocity can also be expressed in a number of different ways shown below (relating to other physical quantities such as linear velocity):
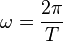
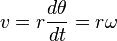
where v is linear velocity, r is the radius of the circle and T is the time period.
Angular acceleration is also related to angular velocity through a similar method to linear acceleration,
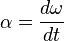
this can also be shown in terms of the second derivative of linear velocity:
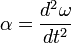
where α represents the angular acceleration (rad s-2).