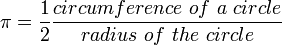Angles
| |
Subject classification: this is a mathematics resource . |
An angle can be defined as two rays sharing a common vertex.
Measurement of angles
An angle is measured by considering the ratio of an arc to the radius of the arc. A scaling constant k is multiplied for various units.
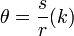 °
°
Units of measurement
There are various units of measurement for measuring angles, however the most commonly used are degrees or radians.
- Degrees - It is denoted by a small circle as a superscript (°). One full rotation is considered equal to 360 degrees. Degree is subdivided into minutes and seconds as:-
1° = 60' (60 arcminutes) = 3600" (3600 arcseconds)
- Radians - This is a number and is dimensionless. A full circle is equal to
(pronounced two pi) radians. This in conjunction with the formula for arc length defines the historically famous irrational number
(pronounced pi) as,
There are six types of angles: Acute, Obtuse, Straight, Right, Reflex and Complete.
- An Acute angle is less than 90° and more than 0°
- An Obtuse angle is more than 90° and less than 180°
- A Straight angle is 180°.
- A Right angle is 90°.
- A Reflex angle is more than 180°.
- A Complete angle is 360°.
This article is issued from Wikiversity - version of the Friday, June 28, 2013. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.