Amino acids
An amphoteric organic acid containing the amino group is an amino acid. Amino acids make up proteins.
Biochemistry
Def. a compound that releases at least one hydrogen ion (H+), or donates a proton, accepts an electron in reactions, when dissolved in water is called an acid.
Def. capable of reacting chemically either as an acid or a base is called amphoteric.
Organic chemistry
Def. any of various compounds derived from ammonia (NH3) by replacement of hydrogen (H) by one or more univalent hydrocarbon radicals is called an amine.
Def. a compound derived from ammonia by replacement of a hydrogen by a metal, containing the anion NH2- is called an amide.
Def. containing the group NH2 or a substituted group NHR or NR2 united to a radical group (R) other than an acid radical is called amino.
Most organic acids (carboxylic or fatty acids) contain the carboxyl group (-COOH).
Theoretical amino acids
Def. a simple organic compound containing both a carboxyl (-COOH) and an amino (-NH2) group is called an amino acid.
Electromagnetics
Chemistry
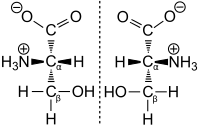
One way amino acids are classified is dextro (D) versus levo (L). This refers to the arrangement of certain radicals relative to the COOH portion.
Dextro has NH2 or the charged NH3+ on the right or on the bottom when the double bonded oxygen is on top.
Compounds
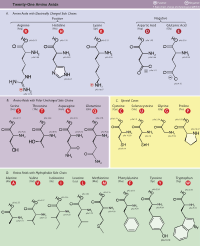
Def. 2-aminopropanoic acid with the chemical formula: CH3 CH(NH2)COOH is called alanine.
Def. 3-aminopropanoic acid, (NH2)CH2 CH2 COOH, is called β-alanine.
Def. 2-aminobutanedioic acid, COOHCH2 CH(NH2)COOH, or symmetrically HOOCCH(NH2)CH2COOH, is called aspartic acid.
Def. 2-aminopentanedioic acid, HOOC(CH2)2 (NH2)COOH, is called glutamic acid.
Def. 2-amino-3-hydroxypropanic acid, HO2CCH(NH2)CH2OH, is called serine.
Original research
- See also: Original research inquiry and Research
Hypothesis:
- Genes are used to produce amino acids.
- See also: Control groups and Proof of concept
See also
References
External links
- African Journals Online
- Bing Advanced search
- GenomeNet KEGG database
- Google Books
- Google scholar Advanced Scholar Search
- Home - Gene - NCBI
- International Astronomical Union
- JSTOR
- Lycos search
- NASA's National Space Science Data Center
- NCBI All Databases Search
- NCBI Site Search
- PubChem Public Chemical Database
- Questia - The Online Library of Books and Journals
- SAGE journals online
- The SAO/NASA Astrophysics Data System
- Scirus for scientific information only advanced search
- SpringerLink
- Taylor & Francis Online
- WikiDoc The Living Textbook of Medicine
- Wiley Online Library Advanced Search
- Yahoo Advanced Web Search
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
![]() This is a research project at http://en.wikiversity.org
This is a research project at http://en.wikiversity.org
| |
Educational level: this is a research resource. |
| |
Resource type: this resource is an article. |
| |
Resource type: this resource contains a lecture or lecture notes. |
| |
Subject classification: this is a biochemistry resource. |