Advanced ANOVA/One-way ANOVA
< Advanced ANOVA
This tutorial teaches use of one-way ANOVA, a statistical technique for testing mean differences betweeen three or more independent groups on a single dependent variable. Practical exercises are based on using SPSS. |
Purpose
- Assesses the statistical significance of differences between three or more group means for a single dependent variable
- Extension of a t-test
- Use one-way ANOVA in preference to multiple pairwise comparisons (t-tests) because:
- Computationally easier
- Limits the probability of type I and type II errors.
- With multiple comparisons, if they are all independent (which is unlikley) in a series of 100 tests we would expect to get five Type I errors with a .05 level of significance
- By simultaneously computing all possible comparisons in a single significance test, the ANOVA avoids these inflated error rates
- However, use of one-way ANOVA limits error rates at the expense of specificity - statistic tells us that there is a significant difference somewhere among the sample means, but does not tell us which means differ significantly (have to use post-hoc and a priori comparison procedures)
- Use one-way ANOVA in preference to multiple pairwise comparisons (t-tests) because:
Examples
- Experimental study: Examine reaction time under different levels of alcohol consumption by randomly assigning participants to four conditions (none, low, medium, and high alcohol)
- Quasi-experimental study: Examine whether students with behaviour problems behave better in classrooms where teachers have a humanistic philosophy and have control of their classrooms. Classify teachers as (1) humanists with control, (2) strict disciplinarians, and (3) laissez-faire.
General steps
- Establish hypothesis/hypotheses
- Examine assumptions - If assumptions are not met, use the Kruskal-Wallis non-parametric procedure
- Examine descriptive statistics, particularly the four moments (M, SD, Skewness, Kurtosis) overall, and also for each group
- Examine graphs, e.g.,:
- Histograms
- Normal probability plot
- Error-bar graph
- Conduct inferential test (ANOVA) and interpret significance of F
- Conduct follow-up tests (planned contrasts or post-hoc tests) if F is significant
- Calculate and interpret effect sizes
- Eta-square (omnibus - equivalent to R2)
- Standardised mean effect size (difference b/w two means) - e.g., Cohen's d
Visual ANOVA
- Understanding ANOVA Visually (may require viewing with Internet Explorer)
- Under what conditions would F be the smallest?
- Under what conditions would F be the largest?
- Now explore the same ideas with this more advanced Visualisation Tool for One-way and Two-way ANOVA Applet
Error bar graphs
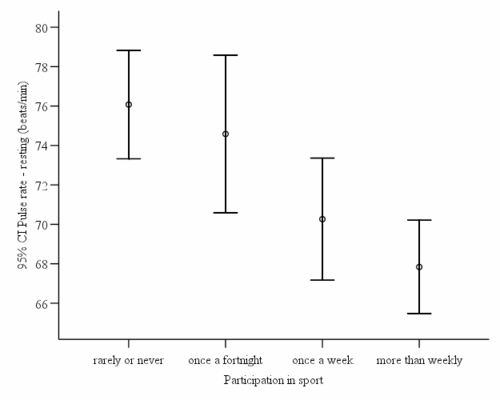
Error-bar graph showing mean pulse rates and 95% confidence intervals by exercise level.
- Use any dataset
- Conduct a one-way ANOVA and graphically present the means and confidence intervals using an Error Bar Graph - is this error bar chart consistent with the statistical results?
- Why?
- Why not?
Data
See also
External links
- ANOVA (ucspace)
This article is issued from Wikiversity - version of the Tuesday, September 16, 2014. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.