Trigonometry/Trigonometric identities
< TrigonometryWhat is an identity?
An identity is an equation that holds true for all values of the variables appearing in it, because it either is a definition or is the logical consequence of a definition. An example of a definitional identity is 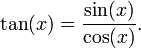 An example of an identity that can logically be proven to hold for all values of its variable is the Pythagorean identity expressed in trigonometric form:
An example of an identity that can logically be proven to hold for all values of its variable is the Pythagorean identity expressed in trigonometric form: 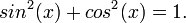
Next Page: Graphs of Sine and Cosine Functions
Previous Page: Right Angle Trigonometry
Home: Trigonometry
This article is issued from Wikibooks. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.