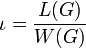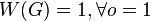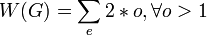Transportation Geography and Network Science/Characterizing Graphs
< Transportation Geography and Network Sciencebeta index
The beta index (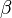 ) measures the connectivity relating the number of edges to the number of nodes. It is given as:
) measures the connectivity relating the number of edges to the number of nodes. It is given as:
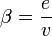
where e = number of edges (links), v = number of vertices (nodes)
The greater the value of 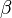 , the greater the connectivity. As transport networks develop and become more efficient, the value of
, the greater the connectivity. As transport networks develop and become more efficient, the value of 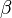 should rise.
should rise.
cyclomatic number
The cyclomatic number (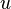 ) is the maximum number of independent cycles in a graph.
) is the maximum number of independent cycles in a graph.

where p = number of graphs or subgraphs.
alpha index
The alpha index (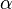 ) is the ratio of the actual number of circuits in a network to the maximum possible number of circuits in that network. It is given as:
) is the ratio of the actual number of circuits in a network to the maximum possible number of circuits in that network. It is given as:
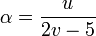
Values range from 0%—no circuits—to 100%—a completely interconnected network.
gamma index
The gamma index (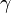 ) measures the connectivity in a network. It is a measure of the ratio of the number of edges in a network to the maximum number possible in a planar network (
) measures the connectivity in a network. It is a measure of the ratio of the number of edges in a network to the maximum number possible in a planar network (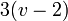 )
)
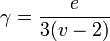
The index ranges from 0 (no connections between nodes) to 1.0 (the maximum number of connections, with direct links between all the nodes).
Completeness
The number of links in a real world network is typically less than the maximum number of links and the completeness index used here captures this difference. This measure is estimated at the metropolitan level.
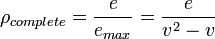
 refers to the number of links or street segments in the network and
refers to the number of links or street segments in the network and 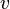 refers to the number of intersections or nodes in the network. Compare with the
refers to the number of intersections or nodes in the network. Compare with the 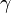 index above.
index above.
König number
The König number (or associated number) is the number of edges from any node in a network to the furthest node from it. This is a topological measure of distance, in edges rather than in kilometres. A low associated number indicates a high degree of connectivity; the lower the König number, the greater the Centrality of that node.
eta index
The eta index (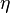 ) measure the length of the graph over the number of edges.
) measure the length of the graph over the number of edges.
theta index
The theta index (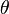 ) measure the traffic (Q(G)) per vertex.
) measure the traffic (Q(G)) per vertex.
iota index
The iota index ( ) measures the ratio between the length of its network and its weighted vertices.
) measures the ratio between the length of its network and its weighted vertices.