Structural Biochemistry/Cell Signaling Pathways/Respiratory System
< Structural Biochemistry < Cell Signaling PathwaysCapillary Exchange
Capillary exchange is where an exchange between blood and extracellular fluid occurs. It contains small precapillary spincters by the ateriole end: - When spincters are relaxed, there is more blood flowing through the capillary bed. - When spincters are contracted, there is less blood flowing through the capillary bed. - Constriction and dilation also impact capillary blood flow.
Hydrostatic pressure tends to be higher inside the capillary at the arteriole end and lower at the venous end. This causes fluid to move out of the capillaries at the arteriole end. On the other hand, osmotic pressure tends to be lower outside of the capillary at the arteriole end and higher at the venous end. This causes the fluid to enter the capillaries again at the venous end. The plasma proteins creates osmotic pressure and are unable to pass through the capillary wall, making the blood more concentrated.
Blood Composition
Erythrocytes (red blood cells) - Erythrocytes do not have any type or organelles. They transport oxygen and carbon dioxide and use glycolosis for metabolism. They look like a flat biconcave disk, which maximizes the surface area to increase diffusion of gases. Their life span is 3-4 months and a spherical shape is observed when they are ready to die.
Leukocytes (white blood cells) There are different kinds of white blood cells: Lymphocytes: play a role in defense and immunity, responsible for the production of antibodies Monocytes: also participate in defense and immunity Eosinophils: respond to allergic reactions Neutrophils: fight infections and are usually inert Basophils: participate in the secretion and storage of histamine
Platelets (fragments which trigger blood clotting) Blood clotting is an example of a positive feedback loop. It is a mechanism that converts prothrombin to thrombin which in turn converts fibrinogen to fibrin. The main requirement for this mechanism is the presence of vitamin K and calcium.
Plasma (The plasma is made up of ions, plasma proteins, nutrients, water, hormones, and respiratory gases. The proteins found in the plasma include albumin, fibrinogen, and immunoglobulins).
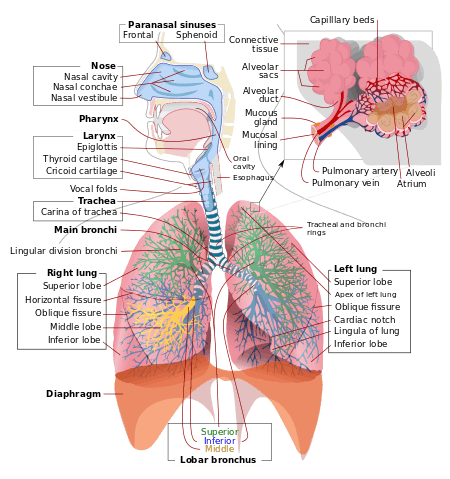
Respiratory System Function
- The respiratory system's function is to allow gas exchange to all parts of the body. The space between the alveoli and the capillaries, the anatomy or structure of the exchange system, and the precise physiological uses of the exchanged gases vary depending on the organism. In humans and other mammals, for example, the anatomical features of the respiratory system include airways, lungs, and the respiratory muscles. Molecules of oxygen and carbon dioxide are passively exchanged by diffusion between the gaseous external environment and the blood. This exchange process occurs in the alveolar region of the lungs.
- Muscle action changes the volume of the rib cage and the chest cavity, and the lungs match these volume changes. The inner layer of the lung's double-walled sac adheres to the outside of the lungs, and the outer layer adheres to the wall of the chest cavity. A thin space filled with fluid separates the two layers. Because of surface tension, the two layers are like two plates of glass stuck together by a film of water: The layers can slide smoothly past each other, but they cannot be pulled apart easily. surface tension couples movement of the lungs to movement of the rib cage.
- Lung Volume increases as a result of contraction of the rib muscles and the diaphragm, a sheet of skeletal muscle that forms the bottom wall of the chest cavity. contraction of the rib muscles expands the rib cage by pulling the ribs upward and the breastbone outward. At the same time, the chest cavity expands as the diaphragm contracts and descends like a piston.All these changes increase the lung volume, and as a result, air pressure within the alveoli becomes lower than atmospheric pressure. Because gas flows from a region of higher pressure to a region of lower pressure, air rushes through the nostrils and mouth and down the breathing tubes to the alveoli. During exhalation, the rib muscles and diaphragm relax, lung volume is reduced, and the increased air pressure within the alveoli forces air up the breathing tubes and out of the body.
A More in Depth look at the Anatomy of the Respiratory System
- The main purpose of breathing is in fact to simply supply the body with sufficient oxygen and remove excess amounts of Carbon Dioxide. The process of respiration can be observed at two levels, one large and one small. At the lungs (large level), gas exchange occurs through the process of breathing. At a more cellular level (small level), oxygen performs its role of transforming the food we eat into must needed energy, producing carbon dioxide as a certain by-product.
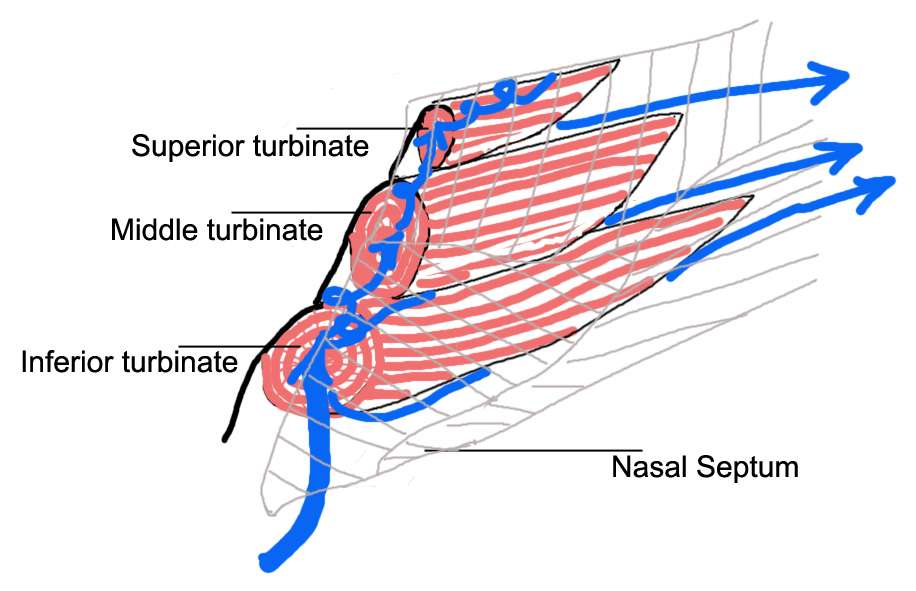
The Nose
- The picture above gives a detailed look at the nose. It is important to note that the nose is not simply a passageway to our throat, but that the nose is a critical aspect of the skull that provides and extensive passage array with inner walls covered by mucus. These walls are supplied with heat-radiating blood vessels. As a matter of fact, the nose can be looked at as an air-conditioner that prepares prepares the air before being taken into the lungs. There are three processes that occur when air is brought in through the nose, which include warming, filtering, and humidifying.
- Warming: The air is warmed by blood vessels, so that it is always at the right temperature before entering the lungs. As labeled on the figure above, the three turbinates (superior, middle, and inferior), serve a critical function in the nose: They are shelves at the side of the nose that warm inhaled air before it enters the lungs. They are also covered by millions of cilia that defend the body against irritants in the inhaled air. They seem to enlarge when someone catches a cold, but no matter how trouble these turbinates may cause, it is crucial not to just get rid of them.
- Filtering: The dust particles taken in are trapped by tiny hairs in the nose in addition to mucus, so that the air is rather clean when taken into the lungs. The nasal septum, as shown above, actually separates the left and right airways of the nose, dividing the two nostrils that are involved throughout nose filtering.
- humidifying: The air is 100% humidified by the mucus in the nose. After these three processes occur, the "treated" air is passed through the lungs and into the trachea.
The Bronchial Tubes
- The inner lining of the bronchial tubes is a membrane called the bronchial mucosa. In terms of function, these tubes carry air into the tiny branches and smaller cells of the lungs after the air has passed through the mouth, nasal passages, and windpipe (trachea). There exists a layer of smooth muscle which is capable of contracting, thus producing airway narrowing. Mucus glands inside the layers of the bronchial tubes can produce a large amount of thick mucus when stimulated.
The Alveoli (Site of gas exchange)
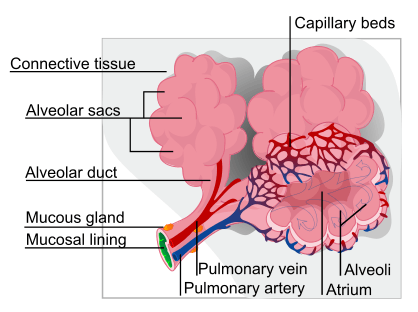
- At the end of the small bronchioles exist millions of air sacs or alveoli. They have large gas space in between with thin blood space provide surface area and is also necessary for air to diffuse. This is explained by the ratio between surface area to volume ratio where when dividing large area into small volumes, the surface area increases. In addition, the thin membrane allow for better diffusion. In a way that is easier to understand, these air sacs can compared to grapes hanging off a stem. The one cell thick walls of the alveoli allow oxygen and carbon dioxide to pass through. Outside the lungs exist a network of air sacs called capillaries which also have walls one cell thick. The alveoli contain oxygen rich air, but carbon dioxide depleted air. The blood in the capillaries, however, contain more carbon dioxide than oxygen. Gas tries to equalize pressure levels, as oxygen passes into the carbon dioxide rich capillaries. At the same time, carbon dioxide passes from the blood and into the alveoli. This allows for gas equilibrium. The next step involves the exit of carbon dioxide through exhalation. This particular gas exchange occurs at the large (lung) level. Oxygen is then bound to hemoglobin in the bloodstream, as it travels from the lungs to the heart. Hemoglobin then performs its role of being a very efficient oxygen carrier, as it is pumped throughout the body supplying oxygen to oxygen-depleted tissues and muscles.
The Second Level (Cellular Gas Exchange)
- In contrast to the large (lung) level, tissue cells have high levels of carbon dioxide and low levels of oxygen. Though the process of equilibrium is the same, the tissue cells use oxygen to make energy and as a result, carbon dioxide and water are produced. They pass from the cell to the bloodstream and oxygen enters to produce energy. This particular gas exchange cycle repeats more than 60 times a minute at both large and small levels.