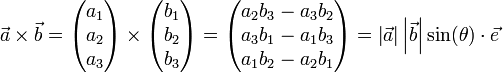Statics/Equations of Statics
< StaticsCondition Of Equilibrium
When forces are in equilibrium, that is, there is no net force and the summation of the particle's moment, taken at any point, is equal to 0.
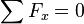
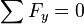
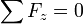
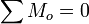
Newton's Second Law of Motion

Trigonometry
Sine Law
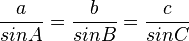
Cosine Law
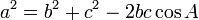
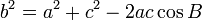
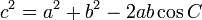
Vector Relations
Dot Product
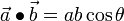
Cross Product
This article is issued from Wikibooks. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.