Robotics/Components/Actuation Devices/Pneumatics Hydraulics
< Robotics < Components < Actuation DevicesPneumatic and hydraulic systems are actuators which provide linear movement. Hydraulic systems, especially, can produce extremely high forces.
Pneumatic systems
The Pneumatic Actuator is sometimes called a Pneumatic Ram. The basic Pnuematic Ram consists of 3 main parts. These 3 parts are the Cylinder, Piston and Rod.
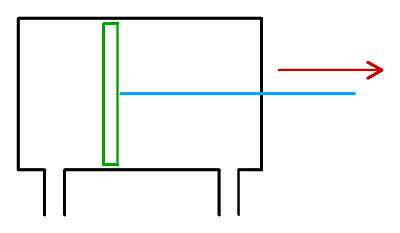
The Cylinder, which is black in the diagram, is where the process takes place. Most of the cylinders in use for hobby robotics are constructed of stainless steel and depending on the type of ram it will either feature one or two ports for compressed air.
The Piston, marked in green, is similar to one that you would find in a car engine. It essentially provides a surface for the compressed gas to act upon.
The Ram , marked in blue, is connected to the piston and transfers the force from the piston to the mechanism that needs moving.
There are several different types of cylinders:
- Single acting cylinder: This cylinder has one input and has a spring. If the pressure is released from the cylinder the spring pushes the piston rod back to its starting position.
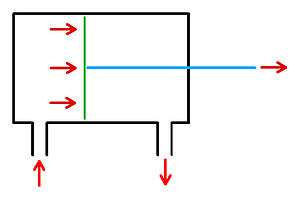
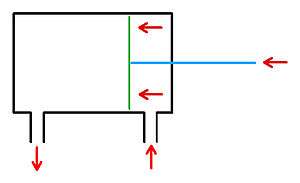
- Double acting cylinder. This type of cylinder is moved by pressurizing one side at a time of the piston. (see images below).
Applications
Pneumatics are useful for generating linear motion.
- Movement of a lever in a walker robot design.
- Closing a gripper
Design Considerations
The use of Pnuematics requires a supply of compressed gas. For a stationary robot on a production line a compressor could be set up nearby to supply it however this isn't possible for a robot that is on the move. The solution is to have a container that holds compressed air. If lots of compressed air is required the addition of a compressor into the design may be required however bear in mind that a compressor will consume a large amount of power.
Calculating Output Force
The force a cylinder can be expressed as
- F: Force in Newtons
- p: Air pressure in cylinder in Pascals. Pressure can be obtained through use of a Pressure Gauge in the air circuit before the Ram.
- A: Surface area of the piston in square meters. This can be obtained from the manufacturers specifications.
Notes
- ^ Note: the surface area of the rod side of the piston is smaller than the other side.