Geometry for Elementary School/Solids
< Geometry for Elementary SchoolIn this section, we will talk about solids. A three-dimensional space is a space that goes in all directions forever.
Solids
Solids are shapes that you can actually touch. They have three dimensions, which means that the have length, width and height. These shapes are what make up our daily life, and are very useful. Points on a solid must not be coplanar or colinear. The edge of solids are called the edge, and the surfaces are called faces. The corners, like angles and plane figures, are called vertices.
A solid with only straight edges is called a polyhedron(pol-ee-HEE-dron). The plural form of polehedron is polyhedra(pol-ee-HEE-drah). Your chocolate bars are polyhedra, The Great Pyramids are polyhedra – a lot of things are. We will go into detail about them later.
When dealing with these solid figures, there are two measurements we will need to know: the total surface area and the volume. The former is the sum of the faces of the solid; the latter is how big the solid is.
Polyhedra
We will talk about polyhedra in this section. The first thing we will need to know about polyhedra is how to classify them. First, we can classify them by the number of faces:
- A tetrahedron is a polyhedron with four faces. Tetrahedrons, interestingly enough, are always rectangular pyramids.
- A pentahedron os a polyhedron with five faces.
- A hexahedron is a polyhedron with six faces.
- A heptahedron is a polyhedron with seven faces.
- The list goes on with the same prefixes as the polygons.
- There are no triahedrons. This is because one cannot arrange any polyhedron with three faces. Cylinders don't count as they are not polyhedra.
Secondly, we can classify them by the way they look:

- Prisms are shapes with a flat top and a flat base. The bases must be on parallel planes. Their number of faces is always the same as two added to the number of sides on the base. The number of edges is three times that of the number of sides on the base, while the number of vertices is two times the number of sides on the base. Prisms can be divided by the shape of the base: triangular, quadrilateral, pentagonal, etc. They can be stacked together but cannot be rolled. Note that cylinders are not counted.
- Pyramids are shapes with a pointy top and a flat base. Their number of faces is always the same as one added to the number of sides on the base. The number of edges is twice of the number of sides of the base, while the number of vertices is one added to the number of sides on the base. They can neither be stacked together nor rolled. Pyramids can be divided by the shape of the base, like Prisms. Note that cones are not counted.
There is one interesting thing about convex polyhedra. A convex polyhedron is a polyhedron where any line joining any of the vertices will not stick out. According to the Euler's formula, the number of faces plus the number of vertices in minus the number of edges in such a polyhedron is always the same 2. Here is an example to try out.
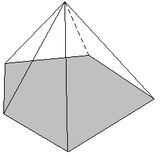
Look at the pentagonal pyramid on the right. Assuming it is convex, does it follow the Euler's formula?
The final thing we need to know about polyhedra is their total surface area and volume. You will only need to know about prisms for the volume. To find the total surface area of any polyhedron, add up all the faces. Look out for congruent faces and don't forget to check whether you've found all the faces by using the formulae given above – that is, when you are facing a pyramid or prism. Otherwise you can just count. As for the volume of prisms, simply find the area of the base and multiply it by the height. With cuboids, it's easy. Just multiply the length, width/breadth and height. With a cube it's the easiest: cube an edge, any edge!
Other kinds of solids
Of course, there are other kinds of solids apart from the polyhedra. They include the sphere, the cone, the cylinder and the ellipsoid. The sphere is a shape that is like a ball. All of the points on a sphere are the same distance from the centre of the sphere. The cone is a shape with a round, flat base and a pointy top. The cylinder is a shape where the top and the base are both circles, and the bases are parallel. The ellipsoid looks like a squashed sphere.
All of the shapes mentioned above can roll. Only the cylinder can be stacked together. You need not learn much about them in elementary school, apart from their names and appearances.
Cross-sections

A cross-section is the shape formed after cutting a solid. Take cutting a birthday cake as an example. When you cut the cake into half, there is a rectangle formed on each half. This is called a cross-section. Some people simply call them sections. This is also correct, but less common. When a series of identical cross-sections can be formed after cutting a solid in the same direction but a different position, uniform cross-sections are formed. This can only be done when cutting a prism or cylinder with the direction parallel to the bases.
Although it is not important to remember the kinds of cross-sections formed, it can be helpful to remember a few. Let us assume that all the shapes are put 'upright' before cutting. When cutting a prism or cylinder, cutting horizonally will result in a series of uniform cross-sections which are congruent to the base. Cutting vertically will result in a number of different rectangles, while cutting obliquely can result in a parallelogram (when four surfaces are involved in a prism), a triangle (when three surfaces are involved in a prism, such as cutting off a corner), what look like arches (in a cylinder where two surfaces are involved), or an ellipse (in a cylinder where only the lateral face is involved).
When cutting a pyramid or cone, cutting horizontally will result in shapes that are similar to the base. (When shapes are similar, it means that they have the same shape but different size. See the chapter on similarity for details.) When cutting a pyramid vertically, a triangle or a parallelogram can be formed depending on the situation. If you cut a corner or cut right across the middle (i.e. three surfaces are involved), then a triangle will be formed. Otherwise, a parallelogram will be formed. On cones, cutting vertically will result in a triangle in the same situation, but otherwise, will result in what looks like an arch. When you cut a pyramid obliquely, the shapes formed can vary a lot!
Finally, if you cut a sphere, you always get a circle. For other shapes, try imagining them yourself!