Fractals/Mathematics/sequences
< Fractals < MathematicsDefinition
types of sequences
Integer sequences
Fraction sequences
Farey sequence
The Farey sequence of order n is the sequence of completely reduced vulgar fractions between 0 and 1 which when in lowest terms have denominators less than or equal to n, arranged in order of increasing size.
Each Farey sequence starts with the value 0, denoted by the fraction 0⁄1, and ends with the value 1, denoted by the fraction 1⁄1 (although some authors omit these terms).
Farey Addition = the mediant of two fractions :
Terms
- next term = child
- Previous terms = parents[1]
Farey tree = Farey sequence as a tree
| Sorted |
|---|
F1 = {0/1, 1/1}
F2 = {0/1, 1/2, 1/1}
F3 = {0/1, 1/3, 1/2, 2/3, 1/1}
F4 = {0/1, 1/4, 1/3, 1/2, 2/3, 3/4, 1/1}
F5 = {0/1, 1/5, 1/4, 1/3, 2/5, 1/2, 3/5, 2/3, 3/4, 4/5, 1/1}
F6 = {0/1, 1/6, 1/5, 1/4, 1/3, 2/5, 1/2, 3/5, 2/3, 3/4, 4/5, 5/6, 1/1}
F7 = {0/1, 1/7, 1/6, 1/5, 1/4, 2/7, 1/3, 2/5, 3/7, 1/2, 4/7, 3/5, 2/3, 5/7, 3/4, 4/5, 5/6, 6/7, 1/1}
F8 = {0/1, 1/8, 1/7, 1/6, 1/5, 1/4, 2/7, 1/3, 3/8, 2/5, 3/7, 1/2, 4/7, 3/5, 5/8, 2/3, 5/7, 3/4, 4/5, 5/6, 6/7, 7/8, 1/1}
|
Sequences on the parameter plane
sequence from Siegel disk to Lea-Fatou flower
- plain Siegel disk
- digitated Siegel disk[2]
- virtual Siegel disk
- ? Leau-Fatou flower ?
Sharkovsky ordering
It is the infinite sequence of positive integers. It starts from 3 and ends in 1. It contains ininitely many subsequences.
"The Sharkovski ordering :
- begins with the odd numbers >= 3,
- then twice these numbers,
- then 4 times them,
- then 8 times them,
- etc.,
- ending with the powers of 2 in decreasing order, ending with 2^0 = 1."[3]
sequence of fraction in the elephant valley
In the elephant valley[4][5] ( from parameter plane ) there is a sequence of componts with period p : from 1/2 to 1/p
Note that :
- internal ray 0/1 = 1/1
- internal angle 1/p means that ray goes from period 1 component ( parent period = 1) to period p component ( child period = p)
- as child period grows computations are harder
- exponential growth[6] of . One can easly create a numeric value that is too large to be represented within the available storage space ( integer overflow[7] ). For example is to big for short ( 16 bit ) and long ( 32 bit) integer.
The upper principal sequence of rotational number around the main cardioid of Mandelbrot set[8]
| n | rotation number = 1/n | parameter c |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | 1/2 | -0.75 |
| 3 | 1/3 | 0.64951905283833*i-0.125 |
| 4 | 1/4 | 0.5*i+0.25 |
| 5 | 1/5 | 0.32858194507446*i+0.35676274578121 |
| 6 | 1/6 | 0.21650635094611*i+0.375 |
| 7 | 1/7 | 0.14718376318856*i+0.36737513441845 |
| 8 | 1/8 | 0.10355339059327*i+0.35355339059327 |
| 9 | 1/9 | 0.075191866590218*i+0.33961017714276 |
| 10 | 1/10 | 0.056128497072448*i+0.32725424859374 |
See :
- Slide show of rescaled limbs converging to the Lavaurs elephant - video by Wolf Jung made with Mandel
sequence of fractions tending to the golden mean ( Golden Ratio Conjugate )
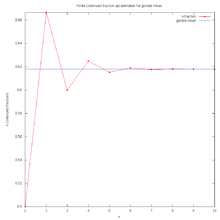
n = 1 ; p_n/q_n = 1.0000000000000000000 = 1 / 1 n = 2 ; p_n/q_n = 0.5000000000000000000 = 1 / 2 n = 3 ; p_n/q_n = 0.6666666666666666667 = 2 / 3 n = 4 ; p_n/q_n = 0.6000000000000000000 = 3 / 5 n = 5 ; p_n/q_n = 0.6250000000000000000 = 5 / 8 n = 6 ; p_n/q_n = 0.6153846153846153846 = 8 / 13 n = 7 ; p_n/q_n = 0.6190476190476190476 = 13 / 21 n = 8 ; p_n/q_n = 0.6176470588235294118 = 21 / 34 n = 9 ; p_n/q_n = 0.6181818181818181818 = 34 / 55 n = 10 ; p_n/q_n = 0.6179775280898876404 = 55 / 89 n = 11 ; p_n/q_n = 0.6180555555555555556 = 89 / 144 n = 12 ; p_n/q_n = 0.6180257510729613734 = 144 / 233 n = 13 ; p_n/q_n = 0.6180371352785145888 = 233 / 377 n = 14 ; p_n/q_n = 0.6180327868852459016 = 377 / 610 n = 15 ; p_n/q_n = 0.6180344478216818642 = 610 / 987 n = 16 ; p_n/q_n = 0.6180338134001252348 = 987 / 1597 n = 17 ; p_n/q_n = 0.6180340557275541796 = 1597 / 2584 n = 18 ; p_n/q_n = 0.6180339631667065295 = 2584 / 4181 n = 19 ; p_n/q_n = 0.6180339985218033999 = 4181 / 6765 n = 20 ; p_n/q_n = 0.6180339850173579390 = 6765 / 10946 n = 21 ; p_n/q_n = 0.6180339901755970865 = 10946 / 17711 n = 22 ; p_n/q_n = 0.6180339882053250515 = 17711 / 28657 n = 23 ; p_n/q_n = 0.6180339889579020014 = 28657 / 46368 n = 24 ; p_n/q_n = 0.6180339886704431856 = 46368 / 75025 n = 25 ; p_n/q_n = 0.6180339887802426829 = 75025 / 121393 n = 26 ; p_n/q_n = 0.6180339887383030068 = 121393 / 196418 n = 27 ; p_n/q_n = 0.6180339887543225376 = 196418 / 317811 n = 28 ; p_n/q_n = 0.6180339887482036214 = 317811 / 514229 n = 29 ; p_n/q_n = 0.6180339887505408394 = 514229 / 832040 n = 30 ; p_n/q_n = 0.6180339887496481015 = 832040 / 1346269 n = 31 ; p_n/q_n = 0.6180339887499890970 = 1346269 / 2178309 n = 32 ; p_n/q_n = 0.6180339887498588484 = 2178309 / 3524578 n = 33 ; p_n/q_n = 0.6180339887499085989 = 3524578 / 5702887 n = 34 ; p_n/q_n = 0.6180339887498895959 = 5702887 / 9227465 n = 35 ; p_n/q_n = 0.6180339887498968544 = 9227465 / 14930352 n = 36 ; p_n/q_n = 0.6180339887498940819 = 14930352 / 24157817 n = 37 ; p_n/q_n = 0.6180339887498951409 = 24157817 / 39088169 n = 38 ; p_n/q_n = 0.6180339887498947364 = 39088169 / 63245986 n = 39 ; p_n/q_n = 0.6180339887498948909 = 63245986 / 102334155 n = 40 ; p_n/q_n = 0.6180339887498948319 = 102334155 / 165580141 n = 41 ; p_n/q_n = 0.6180339887498948544 = 165580141 / 267914296 n = 42 ; p_n/q_n = 0.6180339887498948458 = 267914296 / 433494437 n = 43 ; p_n/q_n = 0.6180339887498948491 = 433494437 / 701408733 n = 44 ; p_n/q_n = 0.6180339887498948479 = 701408733 / 1134903170 n = 45 ; p_n/q_n = 0.6180339887498948483 = 1134903170 / 1836311903
This is a sequence of rational numbers ( Julia sets are parabolic). It's limit is an irrational number ( Julia set has a Siegel disk).
More
- orbit
References
- ↑ Finding parents in the Farey tree by Claude Heiland-Allen
- ↑ scholarpedia : Siegel_disks , Quadratic_Siegel_disks, Digitation
- ↑ The On-Line Encyclopedia of Integer Sequences : A005408 = The odd numbers: a(n) = 2n+1
- ↑ muency : elephant valley
- ↑ Visual Guide To Patterns In The Mandelbrot Set by Miqel
- ↑ integer number in wikipedia
- ↑ Integer overflow in wikipedia
- ↑ Mandel Set Combinatorics : Principal Series