Fractals/Iterations in the complex plane/Mandelbrot set/lavaurs
< Fractals < Iterations in the complex plane < Mandelbrot set
This algorithm shows :
- how to compute angles of external rays landing of root points of Mandelbrot set
- how to draw diagram ( lamination on a circle) showing structure of Mandelbrot set
External angles (measured in turns modulo 1) landing on root points of period p components of Mandelbrot set are:
Arc (chord) consists of:
- two external angles landing on the same root point
- root point.
Names
- Quadratic Minor Lamination = QML. It is the collection of Minor Leaves of any quadratic invariant lamination. The minor leaf is the image of the longest leaf in the lamination. [1] An approximation of the Quadratic Minor Lamination contains only periodic minor leaves.
- lamination on the circle associated with Mandelbrot set
- abstract Mandelbrot set ( Thurston)
- pinching disk model of Mandelbrot set : after pinching ( glue) all points of circle, which are connected by arcs. It is space homeomorphic to Mandelbrot set[2]
Mathematical description
- draw unit circle
- connect angles of period two : 1/3 and 2/3 with arc in unit circle perpendicular to the boundary
- for next period connect 2 angles of the same period (first and second) with arc, such that :
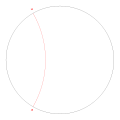 period 2
period 2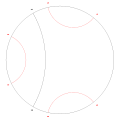 period 3
period 3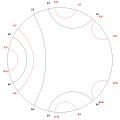 period 4
period 4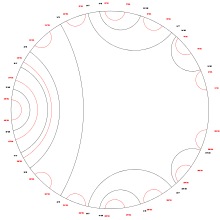 period 5
period 5
Programmer's description
- draw main circle with center (x0, y0) and radius r0 in the middle of your image
- choose period, for example p=3
- compute pairs of angles ( in turns)
- for each pair (alpha,beta) draw an arc using part of new circle, which is orthogonal[5] [6]to main circle in 2 points : c1,c2
Computing pair of angles
(to do )
Drawing arcs connecting angles
Converting units of angles
First units are in turns ( list of pairs of angles )
Using ttr function:
(defun ttr (turn)
" Turns to Radians"
(* turn (* 2 pi) ))
convert them to radians:
(alpha (ttr ( first angle-list)))
Computing points of intersection
Main circle (x0,y0,r0) and new orthogonal circle ( x,y,r) have 2 common points :
- c1 = (a,b) = (x0 + r0 * cos(alpha) , y0 + r0 * sin(alpha))
- c2 = (x0 + r0 * cos(beta) , y0 + r0 * sin(beta))
(ca (cos alpha))
(sa (sin alpha))
; first common point
(a (+ x0 (* r0 ca))) ; a = x0 + r0 * cos(alpha)
(b (+ y0 (* r0 sa))) ; b = y0 + r0 * sin(alpha)
Computing orthogonal circle
Radius and center
At points of intersection radius r0 and new radius or orthogonal circle are also orthogonal. Center of new circle ( x,y) is on the line through point (x0,y0) and slope defined by angle gamma :
gamma = alpha + (balpha - alpha)/2
(gamma (+ alpha (/ (- balpha alpha) 2))) ; angle between alpha and balpha
Using this information one can compute new circle : (x,y,r)
new angles
One has:
- main circle (x0, y0m r0)
- new circle (x, y, r)
- point of intersections c1 and c2 and its angles : alpha and beta
Because arc will be drawn using new circle one has to compute (convert) new angles ( angles measured in new circle) :
angle of point c1 = (a,b) measured in new circle units.
(phi (atan r0 r))) ; phi = (new-alpha - new-balpha)
(balha (+ pi gamma phi)) ; new balpha
(alpha (- (+ pi gamma) phi)) ; new alpha
Drawing arc
It depends of available procedures.
From point to point
Easiest case is drawing arc from point c1 to c2.
Postscript
In postscript there is arct procedure : [7]
x1 y1 x2 y2 r arct
So in Lisp one can directly create ps file and use this procedure :
; code by Copyright 2009 Rubén Berenguel
; http://www.mostlymaths.net/2009/08/lavaurs-algorithm.html
(defun DrawArc (alpha balpha R)
"Generate the postscript arcs using arct
x1 y1 x2 y2 r arct "
(format t "newpath ~A ~A moveto 300 300 ~A ~A ~A arct"
(+ 300 (* 100 (cos balpha)))
(+ 300 (* 100 (sin balpha)))
(+ 300 (* 100 (cos alpha)))
(+ 300 (* 100 (sin alpha)))
R))
SVG
In SVG there is the elliptical arc curve command.[8] [9][10][11][12][13]
It is a version of path command that draws an elliptical arc from the current point to (x, y).
The size and orientation of the ellipse are defined by two radii (rx, ry) and an x-axis-rotation, which indicates how the ellipse as a whole is rotated relative to the current coordinate system.
The center (cx, cy) of the ellipse is calculated automatically to satisfy the constraints imposed by the other parameters.
large-arc-flag and sweep-flag contribute to the automatic calculations and help determine how the arc is drawn.
rx ry x-axis-rotation large-arc-flag sweep-flag x y
<path d="M 100,100 a100,100 0 0,0 100,50" fill="none" stroke="red" stroke-width="6" />
<?xml version="1.0" standalone="no"?>
<svg width="800px" height="800px" version="1.1" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg">
<path d="M100 100
A 100 100 0 0 0 162.55 162.45
" stroke="black" fill="none" stroke-width="2" fill-opacity="0.5"/>
</svg>
SVG path elements :
- M100 100 specifies an absolute start point (100,100) for the circular arc
- A 100 100 means that both the major axis and the minor axis of this circular arc have the same length = 100
- 0 0 0 are x-axis-rotation large-arc-flag sweep-flag
- 162.55 162.45 is an end point of arc
So one can draw arc by writing path command to svg file like that :
(format stream-name "<path d=\"M~,0f ~,0f A~,0f ~,0f 0 0 0 ~,0f ~,0f\" />~%"
(first arc-list)
(second arc-list)
(third arc-list)
(third arc-list)
(fourth arc-list) ;
(fifth arc-list))
Remember that initial coordinate system in SVG has the origin at the top/left with the x-axis pointing to the right and the y-axis pointing down. [14]
For drawing all arcs it may be not important, but labels with angels will be wrong.
From angle to angle
This case is harder, because one must convert angles from main circle to new, orthogonal circle. When angles are converted then :
- move current point to first point of arc ( intersection). Here c1 = (a,b)
- draw an arc. It is easier to draw arc clockwise instead of counterclockwise
In Vecto Common Lisp package there is arcn procedure [15]
(vecto:move-to ( sixth arc-list) (seventh arc-list)) ; beginning of arc is point (a,b)
(vecto:arcn
( first arc-list) ; x
(second arc-list) ; y
(third arc-list) ; radius
(fourth arc-list) ; angle1
(fifth arc-list))) ; angle2
(vecto:stroke)
Examples of code
- Common Lisp code :
- for drawing poscript files by Ruben Berenguel[16]
- for drawing png files using Vecto package
- for drawing svg files
- Haskell code with SVG output by Claude Heiland-Allen
- c++ code from demo 4 page 7 from program Mandel by Wolf Jung
References
- ↑ [Freddie Exall : An Introduction to Equivalant Matings]
- ↑ A. DOUADY, Algorithms for computing angles in the Mandelbrot set (Chaotic Dynamics and Fractals, ed. Barnsley and Demko, Acad. Press, 1986, pp. 155-168).
- ↑ Lavaurs, P., "Une description combinatoire de l'involution define par M sur les rationnels a denominateur impair," C. R. Acad. Sci. Paris 303 (1986), 143-146.
- ↑ Combinatorics in the Mandelbrot Set - Lavaurs Algorithm by Michael Frame, Benoit Mandelbrot, and Nial Neger
- ↑ Constructing orthogonal circle from Fractal Geometry at Yale University by Michael Frame, Benoit Mandelbrot (1924-2010), and Nial Neger. Version : November 7, 2010
- ↑ Orthogonal Circle at planetmath.org
- ↑ Postscript Operators at Joint Stock Company
- ↑ SVG documentation : The elliptical arc curve commands
- ↑ svg basics description of arcs
- ↑ Elliptical arc implementation notes
- ↑ Paths at mozilla developer center
- ↑ arc at Pilat Informative Educative
- ↑ oreilly documentation
- ↑ The initial coordinate system - SVG documentation at w3.org
- ↑ arcn procedure from Vecto Common Lisp package by Zach Beane.
- ↑ lavaurs algorithm by Ruben Berenguel
See also