Fractals/Iterations in the complex plane/Mandelbrot set/centers
< Fractals < Iterations in the complex plane < Mandelbrot setname ( synonims )
- center of hyperbolic component of Mandelbrot set
- Nucleus of a Mu-Atom [1]
definition
A center of a hyperbolic component H is a parameter ( or point of parameter plane ) such that the corresponding periodic orbit has multiplier= 0." [2]
Initial domain
- "All centers of M of any period are contained in the interior of M, so that the circle C = {z ∈ C: |z − 0.75| = 2} surrounds all centers. "
- "one can exploit the real symmetry of M and only use starting points with non-negative imaginary parts; "[3]
Period
Period of center = period of critical orbit = period of hyperbolic component
Number of components
Equation :
where :
- N(p) is a number of all components of Mandelbrot set for given period p.
- p is a period
- s is a sum of numbers of its components for each divisor[4] of period smaller then period p
All values are positive integers
Program in Maxima CAS :
N(p) := block( [a:2^(p-1),f:0], for f in divisors(p) do if f < p then a : a - N(f), return(a) );
One can run it :
for p:1 thru 50 step 1 do display(N(p));
N(1)=1 N(2)=1 N(3)=3 N(4)=6 N(5)=15 N(6)=27 N(7)=63 N(8)=120 N(9)=252 N(10)=495 N(11)=1023 N(12)=2010 N(13)=4095 N(14)=8127 N(15)=16365 N(16)=32640 N(17)=65535 N(18)=130788 N(19)=262143 N(20)=523770 N(21)=1048509 N(22)=2096127 N(23)=4194303 N(24)=8386440 N(25)=16777200 N(26)=33550335 N(27)=67108608 N(28)=134209530 N(29)=268435455 N(30)=536854005 N(31)=1073741823 N(32)=2147450880 N(33)=4294966269 N(34)=8589869055 N(35)=17179869105 N(36)=34359605280 N(37)=68719476735 N(38)=137438691327 N(39)=274877902845 N(40)=549755289480 N(41)=1099511627775 N(42)=2199022198821 N(43)=4398046511103 N(44)=8796090925050 N(45)=17592186027780 N(46)=35184367894527 N(47)=70368744177663 N(48)=140737479934080 N(49)=281474976710592 N(50)=562949936643600
or :
sum(N(p),p,1,50);
result :
1125899873221781
How to compute centers ?
Methods :
- all centers for given period
- solving or [5]
- showing results in graphical form
- using numerical methods[6][7]
- "quick and dirty" algorithm : check if then colour c-point with colour n. Here n is a period of attracting orbit and eps is a radius of circle around attracting point = precision of numerical comutations
- finding all roots of polynomial
- atom domains
- Myrberg's method [8][9]
- interval arithmetics and a divide and conquere strategy[10]
- solving or [5]
- one center for given period near given point
- some steps of Newton method for solving
System of equations defining centers
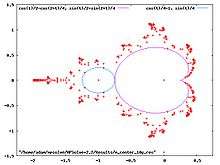
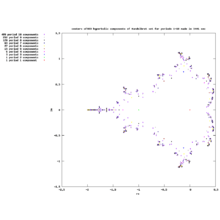
Center of hyperbolic component is a point of parameter plain, for which periodic z-cycle is superattracting. It gives a system of 2 equations defining centers of period hyperbolic components :
- first defines periodic point ,
- second makes point superattracting.
see definitions for details.
Solving system of equations
Second equation can be solved when critical point is in this cycle :
To solve system put into first equation.
Equation defining centers
One gets equation :
Centers of components are roots of above equation.
Because one can remove z from these equations :
- for period 1 : z^2+c=z and z=0 so
- for period 2 : (z^2+c)^2 +c =z and z=0 so
- for period 3 : ((z^2+c)^2 +c)^2 +c = z and z=0 so
Here is Maxima functions for computing above functions :
P[n]:=if n=1 then c else P[n-1]^2+c;
Reduced equation defining centers
Set of roots of above equation contains centers for period p and its divisors. It is because :
where :
- is irreducible divisors [11] of [12]
- capital Pi notation of iterated multiplication is used
- means here : for all divisors of ( from 1 to p ). See table of divisors.
For example :
So one can find irreducible polynomials using :
Here is Maxima function for computing :
GiveG[p]:= block( [f:divisors(p), t:1], /* t is temporary variable = product of Gn for (divisors of p) other than p */ f:delete(p,f), /* delete p from list of divisors */ if p=1 then return(Fn(p,0,c)), for i in f do t:t*GiveG[i], g: Fn(p,0,c)/t, return(ratsimp(g)) )$
Here is a table with degree of and for periods 1-10 and precision needed to compute roots of these functions.
| period | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 16 |
| 2 | 2 | 1 | 16 |
| 3 | 4 | 3 | 16 |
| 4 | 8 | 6 | 16 |
| 5 | 16 | 15 | 16 |
| 6 | 32 | 27 | 16 |
| 7 | 64 | 63 | 32 |
| 8 | 128 | 120 | 64 |
| 9 | 256 | 252 | 128 |
| 10 | 512 | 495 | 300 |
| 11 | 1024 | 1023 | 600 |
Here is a table of greatest coefficients.
| period | ||
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 2 | 0 | 1 |
| 3 | 1 | 2 |
| 4 | 1 | 3 |
| 5 | 3 | 116 |
| 6 | 4 | 5892 |
| 7 | 11 | 17999433372 |
| 8 | 21 | 106250977507865123996 |
| 9 | 44 | 16793767022807396063419059642469257036652437 |
| 10 | 86 | 86283684091087378792197424215901018542592662739248420412325877158692469321558575676264 |
| 11 | 179 | 307954157519416310480198744646044941023074672212201592336666825190665221680585174032224052483643672228833833882969097257874618885560816937172481027939807172551469349507844122611544 |
Precision can be estimated as bigger than size of binary form of greatest coefficient :
| period | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 16 |
| 2 | 1 | 1 | 16 |
| 3 | 3 | 2 | 16 |
| 4 | 6 | 2 | 16 |
| 5 | 15 | 7 | 16 |
| 6 | 27 | 13 | 16 |
| 7 | 63 | 34 | 32 |
| 8 | 120 | 67 | 64 |
| 9 | 252 | 144 | 128 |
| 10 | 495 | 286 | 300 |
| 11 | 1023 | 596 | 600 |
Here is Maxima code for
period_Max:11; /* ----------------- definitions -------------------------------*/ /* basic function = monic and centered complex quadratic polynomial http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Complex_quadratic_polynomial */ f(z,c):=z*z+c $ /* iterated function */ fn(n, z, c) := if n=1 then f(z,c) else f(fn(n-1, z, c),c) $ /* roots of Fn are periodic point of fn function */ Fn(n,z,c):=fn(n, z, c)-z $ /* gives irreducible divisors of polynomial Fn[p,z=0,c] */ GiveG[p]:= block( [f:divisors(p),t:1], g, f:delete(p,f), if p=1 then return(Fn(p,0,c)), for i in f do t:t*GiveG[i], g: Fn(p,0,c)/t, return(ratsimp(g)) )$ /* degree of function */ GiveDegree(_function,_var):=hipow(expand(_function),_var); log10(x) := log(x)/log(10); /* ------------------------------*/ file_output_append:true; /* to append new string to file */ grind:true; for period:1 thru period_Max step 1 do ( g[period]:GiveG[period], /* function g */ d[period]:GiveDegree(g[period],c), /* degree of function g */ cf[period]:makelist(coeff(g[period],c,d[period]-i),i,0,d[period]), /* list of coefficients */ cf_max[period]:apply(max, cf[period]), /* max coefficient */ disp(cf_max[period]," ",ceiling(log10(cf_max[period]))), s:concat("period:",string(period)," cf_max:",cf_max[period]), stringout("max_coeff.txt",s)/* save output to file as Maxima expressions */ );
Graphical methods for finding centers
All these methods shows centers for period n and its divisors.
.gif)

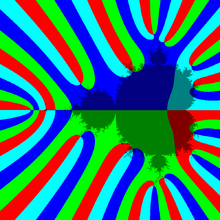
color is proportional to magnitude of zn
- color is proportional to magnitude of zn[13]
- Parameter plane is scanned for points c for which orbit of critical point vanishes [14]
- youtube video : Mandelbrot Oscillations [15]
color shows in which quadrant zn lands
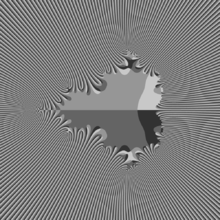
This is radial nth-decomposition of exterior of Mandelbrot set ( compare it with n-th decomposition of LSM/M )
4 colors are used because there are 4 quadrants :
- re(z_n) > 0 and im(z_n) > 0 ( 1-st quadrant )
- re(z_n) < 0 and im(z_n) > 0 ( 2-nd quadrant )
- re(z_n) < 0 and im(z_n) < 0 ( 3-rd quadrant )
- re(z_n) > 0 and im(z_n) < 0 (4-th quadrant ).
"... when the four colors are meeting somewhere, you have a zero of q_n(c), i.e., a center of period dividing n. In addition, the light or dark color shows if c is in M." ( Wolf Jung )
Here is fragment of c code for computing 8-bit color for point c = cx + cy * i :
/* initial value of orbit = critical point Z= 0 */
Zx=0.0;
Zy=0.0;
Zx2=Zx*Zx;
Zy2=Zy*Zy;
/* the same number of iterations for all points !!! */
for (Iteration=0;Iteration<IterationMax; Iteration++)
{
Zy=2*Zx*Zy + Cy;
Zx=Zx2-Zy2 +Cx;
Zx2=Zx*Zx;
Zy2=Zy*Zy;
};
/* compute pixel color (8 bit = 1 byte) */
if ((Zx>0) && (Zy>0)) color[0]=0; /* 1-st quadrant */
if ((Zx<0) && (Zy>0)) color[0]=10; /* 2-nd quadrant */
if ((Zx<0) && (Zy<0)) color[0]=20; /* 3-rd quadrant */
if ((Zx>0) && (Zy<0)) color[0]=30; /* 4-th quadrant */
One can also find cpp code in function quadrantqn from class mndlbrot in mndlbrot.cpp file from source code of program Mandel by Wolf Jung[16]
The differences from standard loop are :
- there is no bailout test (for example for max value of abs(zn) ). It means that every point has the same number of iterations. For large n overflow is possible. Also one can't use test Iteration==IterationMax
- Iteration limit is relatively small ( start for example IterationMax = 8 )
See also code in Sage[17]
Newton method
Newton method for finding one root
Lists of centers
- centers for periods 1-20 ( sum = 1 045 239 ) by James Artherton. Made with custom software using 320 bit fixed point math (approx. 92 decimal digits) and a quadtree subdivision of the grid to increase the search resolution in areas with higher root density. This adapts to very fine resolution in the tips of the antennae.[19]
- largest islands by Robert P Munafo[20][21]
- a database of all islands up to period 16, found by tracing external rays (period, islandhood, angled internal address, lower external angle numerator, denominator, upper numerator, denominator, orientation, size, centre realpart, imagpart)[22]
- real centers of components computed by Jay R. Hill[23]
- collection of centers lists[24]
references
- ↑ Nucleus - From the Mandelbrot Set Glossary and Encyclopedia, by Robert Munafo, (c) 1987-2015.
- ↑ Surgery in Complex Dynamics by Carsten Lunde Petersen, online paper
- ↑ NEWTON’S METHOD IN PRACTICE: FINDING ALL ROOTS OF POLYNOMIALS OF DEGREE ONE MILLION EFFICIENTLY by DIERK SCHLEICHER AND ROBIN STOLL
- ↑ divisor in wikipedia
- ↑ FF Topic: The Mandelbrot Polynomial Roots Challenge (Read 5233 times)
- ↑ Piers Lawrence and Rob Corless : Mandelbrot Polynomials and Matrices. 1 ; 048 ; 575 roots of period 21
- ↑ IAP Poster 2013
- ↑ [http://www.iec.csic.es/~gerardo/publica/Alvarez98a.pdf Determination of Mandelbrot Set's Hyperbolic Component Centres by G Alvarez, M Romera, G Pastor and F Montoya. Chaos, Solitons & Fractals 1998, Vol 9 No 12 pp 1997-2005]
- ↑ Myrberg, P J, Iteration der reelen polynome zweiten GradesIII, Ann. Acad. Sci. Fennicae, A. I no. 348, 1964.
- ↑ evaldraw script that can compute 1 million root by knighty
- ↑ irreducible divisors at wikipedia
- ↑ V Dolotin , A Morozow : On the shapes of elementary domains or why Mandelbrot set is made from almost ideal circles ?
- ↑ [http://www.cerebralmastication.com/2009/02/mandelbrot-set-in-r/ Mandelbrot Set in R by J.D. Long]
- ↑ Fractal Stream help file
- ↑ youtube video : Mandelbrot Oscillations
- ↑ Multiplatform cpp program Mandel by Wolf Jung
- ↑ Formation of Escape-Time Fractals By Christopher Olah
- ↑ [http://www.dhushara.com/DarkHeart/DarkHeart.htm _3__The_Dark Exploding the Dark Heart of Chaos by Chris King March-Dec 2009]
- ↑ Fractal Dragons by James Artherton
- ↑ Largest Islands by Robert P. Munafo, 2010 Oct 21
- ↑ mrob : largest-islands.txt
- ↑ a database of all islands up to period 16, found by tracing external rays by Claude
- ↑ real centers of components computed by Jay R. Hill
- ↑ mset centers