Fractals/Iterations in the complex plane/MandelbrotSetExterior
< Fractals < Iterations in the complex planeColouring of exterior of Mandelbrot set can be :
- non-smooth :
- boolean ( bETM/M )
- discrete ( LSM/M = iETM/M)
- Smooth :
One can also draw curves :
- external rays
- equipotential lines ( closed curves - quasi circles)
Escape time or dwell
Here for given point c on parameter plane one checks how critical point behaves on dynamical plane under forward iteration. If you change initial point you will get different result [4]
To draw given plane one needs to check/scan (all) its points. See here for more details ( optimisation) Read definitions first.
Boolean escape time
Here complex plane consists of 2 sets : Mandelbrot set and its complement :
ASCI graphic ( on screen)
// http://mrl.nyu.edu/~perlin/
main(k){float i,j,r,x,y=-16;while(puts(""),y++<15)for(x
=0;x++<84;putchar(" .:-;!/>)|&IH%*#"[k&15]))for(i=k=r=0;
j=r*r-i*i-2+x/25,i=2*r*i+y/10,j*j+i*i<11&&k++<111;r=j);}
-- Haskell code by Ochronus
-- http://blog.mostof.it/mandelbrot-set-in-ruby-and-haskell/
import Data.Complex
mandelbrot a = iterate (\z -> z^2 + a) a !! 500
main = mapM_ putStrLn [[if magnitude (mandelbrot (x :+ y)) < 2 then '*' else ' '
| x <- [-2, -1.9685 .. 0.5]]
| y <- [1, 0.95 .. -1]]
; common lisp
(loop for y from -1.5 to 1.5 by 0.05 do
(loop for x from -2.5 to 0.5 by 0.025 do
(let* ((c (complex x y)) ; parameter
(z (complex 0 0))
(iMax 20) ; maximal number of iterations
(i 0)) ; iteration number
(loop while (< i iMax ) do
(setq z (+ (* z z) c)) ; iteration
(incf i)
(when (> (abs z) 2) (return i)))
; color of pixel
(if (= i iMax) (princ (code-char 42)) ; inside M
(princ (code-char 32))))) ; outside M
(format t "~%")) ; new line
Comparison programs in various languages [5][6]
Graphic file ( PPM )
Here are various programs for creating pbm file [7]
C
This is complete code of C one file program.
- It makes a ppm file which consists an image. To see the file (image) use external application ( graphic viewer).
- Program consists of 3 loops:
- iY and iX, which are used to scan rectangle area of parameter plane
- iterations.
For each point of screen (iX,iY) it's complex value is computed c=cx+cy*i.
For each point c is computed iterations of critical point
It uses some speed_improvement. Instead of checking :
sqrt(Zx2+Zy2)<ER
it checks :
(Zx2+Zy2)<ER2 // ER2 = ER*ER
It gives the same result but is faster.
/*
c program:
--------------------------------
1. draws Mandelbrot set for Fc(z)=z*z +c
using Mandelbrot algorithm ( boolean escape time )
-------------------------------
2. technique of creating ppm file is based on the code of Claudio Rocchini
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Image:Color_complex_plot.jpg
create 24 bit color graphic file , portable pixmap file = PPM
see http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Portable_pixmap
to see the file use external application ( graphic viewer)
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
int main()
{
/* screen ( integer) coordinate */
int iX,iY;
const int iXmax = 800;
const int iYmax = 800;
/* world ( double) coordinate = parameter plane*/
double Cx,Cy;
const double CxMin=-2.5;
const double CxMax=1.5;
const double CyMin=-2.0;
const double CyMax=2.0;
/* */
double PixelWidth=(CxMax-CxMin)/iXmax;
double PixelHeight=(CyMax-CyMin)/iYmax;
/* color component ( R or G or B) is coded from 0 to 255 */
/* it is 24 bit color RGB file */
const int MaxColorComponentValue=255;
FILE * fp;
char *filename="new1.ppm";
char *comment="# ";/* comment should start with # */
static unsigned char color[3];
/* Z=Zx+Zy*i ; Z0 = 0 */
double Zx, Zy;
double Zx2, Zy2; /* Zx2=Zx*Zx; Zy2=Zy*Zy */
/* */
int Iteration;
const int IterationMax=200;
/* bail-out value , radius of circle ; */
const double EscapeRadius=2;
double ER2=EscapeRadius*EscapeRadius;
/*create new file,give it a name and open it in binary mode */
fp= fopen(filename,"wb"); /* b - binary mode */
/*write ASCII header to the file*/
fprintf(fp,"P6\n %s\n %d\n %d\n %d\n",comment,iXmax,iYmax,MaxColorComponentValue);
/* compute and write image data bytes to the file*/
for(iY=0;iY<iYmax;iY++)
{
Cy=CyMin + iY*PixelHeight;
if (fabs(Cy)< PixelHeight/2) Cy=0.0; /* Main antenna */
for(iX=0;iX<iXmax;iX++)
{
Cx=CxMin + iX*PixelWidth;
/* initial value of orbit = critical point Z= 0 */
Zx=0.0;
Zy=0.0;
Zx2=Zx*Zx;
Zy2=Zy*Zy;
/* */
for (Iteration=0;Iteration<IterationMax && ((Zx2+Zy2)<ER2);Iteration++)
{
Zy=2*Zx*Zy + Cy;
Zx=Zx2-Zy2 +Cx;
Zx2=Zx*Zx;
Zy2=Zy*Zy;
};
/* compute pixel color (24 bit = 3 bytes) */
if (Iteration==IterationMax)
{ /* interior of Mandelbrot set = black */
color[0]=0;
color[1]=0;
color[2]=0;
}
else
{ /* exterior of Mandelbrot set = white */
color[0]=255; /* Red*/
color[1]=255; /* Green */
color[2]=255;/* Blue */
};
/*write color to the file*/
fwrite(color,1,3,fp);
}
}
fclose(fp);
return 0;
}
Integer escape time = LSM/M = dwell bands
 Number of details is proportional to maximal number of iterations
Number of details is proportional to maximal number of iterations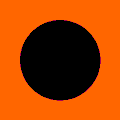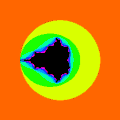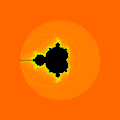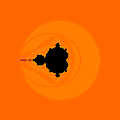 Mandelbrot animation based on a static number of iterations per pixel. Here you can see why offset is sometimes used ( because - color gradient changes : for high MaxIteration disapears.
Mandelbrot animation based on a static number of iterations per pixel. Here you can see why offset is sometimes used ( because - color gradient changes : for high MaxIteration disapears.
Here color is proportional to last iteration ( of final_n, final iteration).[9]
This is also called Level Set Method ( LSM )
C

Difference between Mandelbrot algorithm and LSM/M is in only in part instruction, which computes pixel color of exterior of Mandelbrot set. In LSM/M is :
if (Iteration==IterationMax)
{ /* interior of Mandelbrot set = black */
color[0]=0;
color[1]=0;
color[2]=0;
}
/* exterior of Mandelbrot set = LSM */
else if ((Iteration%2)==0)
{ /* even number = black */
color[0]=0; /* Red */
color[1]=0; /* Green */
color[2]=0; /* Blue */
}
else
{/* odd number = white */
color[0]=255; /* Red */
color[1]=255; /* Green */
color[2]=255; /* Blue */
};
Here is faster C function which can be used instead of above C++ function:
int GiveEscapeTime(double C_x, double C_y, int iMax, double _ER2)
{
int i;
double Zx, Zy;
double Zx2, Zy2; /* Zx2=Zx*Zx; Zy2=Zy*Zy */
Zx=0.0; /* initial value of orbit = critical point Z= 0 */
Zy=0.0;
Zx2=Zx*Zx;
Zy2=Zy*Zy;
for (i=0;i<iMax && ((Zx2+Zy2)<_ER2);i++)
{
Zy=2*Zx*Zy + C_y;
Zx=Zx2-Zy2 +C_x;
Zx2=Zx*Zx;
Zy2=Zy*Zy;
};
return i;
}
C++
Here is C++ function which can be used to draw LSM/M :
int iterate_mandel(complex C , int imax, int bailout)
{
int i;
std::complex Z(0,0); // initial value for iteration Z0
for(i=0;i<=imax-1;i++)
{
Z=Z*Z+C; // overloading of operators
if(abs(Z)>bailout)break;
}
return i;
}
I think that it can't be coded simpler (it looks better than pseudocode), but it can be coded in other way which can be executed faster .
Here is faster code :
// based on cpp code by Geek3
inline int fractal(double cx, double cy, int max_iters)
// gives last iteration
{
double zx = 0, zy = 0;
if (zx * zx + zy * zy > 4) return(0); // it=0
for (int it = 1; it < max_iters; it++)
{ double zx_old = zx;
zx = zx * zx - zy * zy;
zy = 2 * zx_old * zy;
zx += cx;
zy += cy;
if (zx * zx + zy * zy > 4.0) return(it);
}
return(max_iters);
}
See also :
GLSL
Java
//Java code by Josef Jelinek
// http://java.rubikscube.info/
int mandel(double cx, double cy) {
double zx = 0.0, zy = 0.0;
double zx2 = 0.0, zy2 = 0.0;
int iter = 0;
while (iter < iterMax && zx2 + zy2 < 4.0) {
zy = 2.0 * zx * zy + cy;
zx = zx2 - zy2 + cx;
zx2 = zx * zx;
zy2 = zy * zy;
iter++;
}
return iter;
}
Java Script
Here is JavaScript function which does not give last iteration but LastIteration modulo maxCol. It makes colour cycling ( if maxCol < maxIt ).
function iterate(Cr,Ci) {
// JavaScript function by Evgeny Demidov
// http://www.ibiblio.org/e-notes/html5/fractals/mandelbrot.htm
var I=0, R=0, I2=0, R2=0, n=0;
if (R2+I2 > max) return 0;
do { I=(R+R)*I+Ci; R=R2-I2+Cr; R2=R*R; I2=I*I; n++;
} while ((R2+I2 < max) && (n < maxIt) );
if (n == maxIt) return maxCol; else return n % maxCol;
}
Above functions do not use explicit definition of complex number.
Lisp program
Whole Lisp program making ASCII graphic based on code by Frank Buss [10] [11]
; common lisp
(loop for y from -1.5 to 1.5 by 0.1 do
(loop for x from -2.5 to 0.5 by 0.04 do
(let* ((i 0)
(z (complex x y))
(c z))
(loop while (< (abs
(setq z (+ (* z z) c)))
2)
while (< (incf i) 32))
(princ (code-char (+ i 32))))) ; ASCII chars <= 32 contains non-printing characters
(format t "~%"))
MathMap plugin for Gimp
filter mandelbrot (gradient coloration)
c=ri:(xy/xy:[X,X]*1.5-xy:[0.5,0]);
z=ri:[0,0]; # initial value z0 = 0
# iteration of z
iter=0;
while abs(z)<2 && iter<31
do
z=z*z+c; # z(n+1) = fc(zn)
iter=iter+1
end;
coloration(iter/32) # color of pixel
end
Pov-Ray
Pov-Ray has a built-in function mandel[12]
Matemathica
Here is code by Paul Nylander
Level Curves of escape time Method = LCM/M
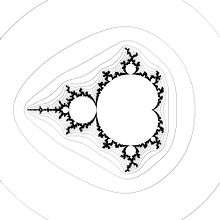
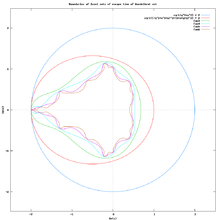
Lemniscates are boundaries of Level Sets of escape time ( LSM/M ). They can be drawn using :
- edge detection of Level sets.
- Algorithm described in paper by M. Romera et al.[13] This method is fast and allows looking for high iterations.
- boundary trace[14]
- drawing curves , see explanation and source code. This method is very complicated for iterations > 5.
Decomposition of exterior of Mandelbrot set
Decomposition is modification of escape time algorithm.
The target set is divided into parts (2 or more). Very large escape radius is used, for example ER = 12.
Binary decomposition of LSM/M
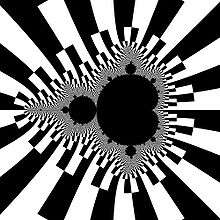
Here target set on dynamic plane is divided into 2 parts (binary decomposition = 2-decomposition ):
- upper half ( white)
- lower half (black)
Division of target set induces decomposition of level sets into parts:
- which is colored white,
- which is colored black.
External rays of angles (measured in turns):
can be seen.
Difference between binary decomposition algorithm and Mandel or LSM/M is in only in part of instruction , which computes pixel color of exterior of Mandelbrot set. In binary decomposition is :
if (Iteration==IterationMax)
{ /* interior of Mandelbrot set = black */
color[0]=0;
color[1]=0;
color[2]=0;
}
/* exterior of Mandelbrot set = LSM */
else if (Zy>0)
{
color[0]=0; /* Red */
color[1]=0; /* Green */
color[2]=0; /* Blue */
}
else
{
color[0]=255; /* Red */
color[1]=255; /* Green */
color[2]=255; /* Blue */
};
also GLSL code from Fragmentarium :
#include "2D.frag"
#group Simple Mandelbrot
// maximal number of iterations
uniform int iMax; slider[1,100,1000] // increase iMax
// er2= er^2 wher er= escape radius = bailout
uniform float er2; slider[4.0,1000,10000] // increase er2
// compute color of pixel
vec3 color(vec2 c) {
vec2 z = vec2(0.0); // initial value
// iteration
for (int i = 0; i < iMax; i++) {
z = vec2(z.x*z.x-z.y*z.y,2*z.x*z.y) + c; // z= z^2+c
if (dot(z,z)> er2) // escape test
// exterior
if (z.x>0){ return vec3( 1.0);} // upper part of the target set
else return vec3(0.0); //lower part of the target set
}
return vec3(0.0); //interior
}
Point c is plotting white or black if imaginary value of last iteration ( Zy) is positive or negative.[15]
nth-decomposition
This method is extension of binary decomposition.
The target set T = { z : |zn| > R } with a very large escape radius ( for example R = 12 ) is divided into more then 2 parts ( for example 8).[16]
Real Escape Time
Other names of this method/algorithm are :
- Normalized Iteration Count Algorithm
- Continuous coloring
- smooth colour gradient
- fractional iterations
- fractional escape time
Here color of exterior of Mandelbrot set is proportional not to Last Iteration ( which is integer number) but to real number :
Other methods and speedups
Colouring formula in Ultrafractal :[17]
smooth iter = iter + 1 + ( log(log(bailout)-log(log(cabs(z))) )/log(2)
where :
- log(log(bailout) can be precalculated
C
To use log2 function add :
#include <math.h>
at the beginning of program.
if (Iteration==IterationMax)
{ /* interior of Mandelbrot set = black */
color[0]=0;
color[1]=0;
color[2]=0;
}
/* exterior of Mandelbrot set */
else GiveRainbowColor((double)(Iteration- log2(log2(sqrt(Zx2+Zy2))))/IterationMax,color);
where :
- Zx2 = Zx*Zx
- Zy2 = Zy*Zy
Here is another version by Tony Finch[18]
while (n++ < max &&
x2+y2 < inf) {
y = 2*x*y + b;
x = x2-y2 + a;
y2 = y*y;
x2 = x*x;
}
nu = n - log(log(x2+y2)/2)/ log(2);
based on equation [19]
C++
// based on cpp code by Geek3 from http://en.wikibooks.org/wiki/File:Mandelbrot_set_rainbow_colors.png
sqrxy = x * x + y * y;
double m = LastIteration + 1.5 - log2(log2(sqrxy));
Matemathica
Here is code by Paul Nylander. It uses different formula :
Python
Python code using mpmath library[20]
def mandelbrot(z):
c = z
for i in xrange(ITERATIONS):
zprev = z
z = z*z + c
if abs(z) > ESCAPE_RADIUS:
return ctx.exp(1j*(i + 1 - ctx.log(ctx.log(abs(z)))/ctx.log(2)))
return 0
Distance estimation DEM/M
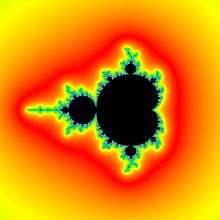 Exterior DEM/M
Exterior DEM/M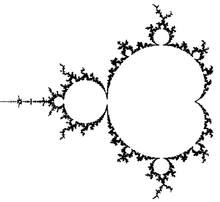 simple boundary with DEM/M
simple boundary with DEM/M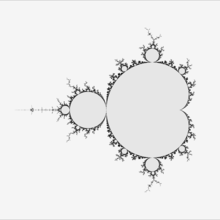 Boundary with DEM/M and Sobel filter
Boundary with DEM/M and Sobel filter
Variants :
- exterior DEM/M
- interior DEM/M
Complex potential
Complex potential is a complex number, so it has a real (real potential) and an imaginary part(external angle). One can take its curl, divergence or its absolute value. So on one image one can use more than one variable to color image.[21]
Real potential = CPM/M
In Fractint :
potential = log(modulus)/2^iterations
One can use real potential to:
- smooth (continuous) coloring[22]
- discrete coloring ( level sets of potential)
- 3D view
Here is Delphi function which gives level of potential :
Function GiveLevelOfPotential(potential:extended):integer;
var r:extended;
begin
r:= log2(abs(potential));
result:=ceil(r);
end;
/******************************************************************/
// /fractint/common/calcfrac.c
/*
CALCFRAC.C contains the high level ("engine") code for calculating the
fractal images (well, SOMEBODY had to do it!).
Original author Tim Wegner, but just about ALL the authors have contributed
SOME code to this routine at one time or another, or contributed to one of
the many massive restructurings.
The following modules work very closely with CALCFRAC.C:
FRACTALS.C the fractal-specific code for escape-time fractals.
FRACSUBR.C assorted subroutines belonging mainly to calcfrac.
CALCMAND.ASM fast Mandelbrot/Julia integer implementation
Additional fractal-specific modules are also invoked from CALCFRAC:
LORENZ.C engine level and fractal specific code for attractors.
JB.C julibrot logic
PARSER.C formula fractals
and more
-------------------------------------------------------------------- */
/* Continuous potential calculation for Mandelbrot and Julia */
/* Reference: Science of Fractal Images p. 190. */
/* Special thanks to Mark Peterson for his "MtMand" program that */
/* beautifully approximates plate 25 (same reference) and spurred */
/* on the inclusion of similar capabilities in FRACTINT. */
/* */
/* The purpose of this function is to calculate a color value */
/* for a fractal that varies continuously with the screen pixels */
/* locations for better rendering in 3D. */
/* */
/* Here "magnitude" is the modulus of the orbit value at */
/* "iterations". The potparms[] are user-entered paramters */
/* controlling the level and slope of the continuous potential */
/* surface. Returns color. - Tim Wegner 6/25/89 */
/* */
/* -- Change history -- */
/* */
/* 09/12/89 - added floatflag support and fixed float underflow */
/* */
/******************************************************************/
static int _fastcall potential(double mag, long iterations)
{
float f_mag,f_tmp,pot;
double d_tmp;
int i_pot;
long l_pot;
if(iterations < maxit)
{
pot = (float)(l_pot = iterations+2);
if(l_pot <= 0 || mag <= 1.0)
pot = (float)0.0;
else /* pot = log(mag) / pow(2.0, (double)pot); */
{
if(l_pot < 120 && !floatflag) /* empirically determined limit of fShift */
{
f_mag = (float)mag;
fLog14(f_mag,f_tmp); /* this SHOULD be non-negative */
fShift(f_tmp,(char)-l_pot,pot);
}
else
{
d_tmp = log(mag)/(double)pow(2.0,(double)pot);
if(d_tmp > FLT_MIN) /* prevent float type underflow */
pot = (float)d_tmp;
else
pot = (float)0.0;
}
}
/* following transformation strictly for aesthetic reasons */
/* meaning of parameters:
potparam[0] -- zero potential level - highest color -
potparam[1] -- slope multiplier -- higher is steeper
potparam[2] -- rqlim value if changeable (bailout for modulus) */
if(pot > 0.0)
{
if(floatflag)
pot = (float)sqrt((double)pot);
else
{
fSqrt14(pot,f_tmp);
pot = f_tmp;
}
pot = (float)(potparam[0] - pot*potparam[1] - 1.0);
}
else
pot = (float)(potparam[0] - 1.0);
if(pot < 1.0)
pot = (float)1.0; /* avoid color 0 */
}
else if(inside >= 0)
pot = inside;
else /* inside < 0 implies inside=maxit, so use 1st pot param instead */
pot = (float)potparam[0];
i_pot = (int)((l_pot = (long)(pot * 256)) >> 8);
if(i_pot >= colors)
{
i_pot = colors - 1;
l_pot = 255;
}
if(pot16bit)
{
if (dotmode != 11) /* if putcolor won't be doing it for us */
writedisk(col+sxoffs,row+syoffs,i_pot);
writedisk(col+sxoffs,row+sydots+syoffs,(int)l_pot);
}
return(i_pot);
}
External angle and external ( parameter) ray
First find angle of last iteration. It is easy to compute and shows some external rays as a borders of level sets.
- binary decomposition of LSM/M (see above)
- nth-decomposition : color of exterior is proportional to quadrant in which last iteration lands. ( see below )
Then one go futher.
- automatically calculate external angles from nucleus and period by Claude Heiland-Allen [23]
Methods
- newton method
- lines perpendicular ot equipotential lines [27]
- field line calculations, images and videos by Michael T Everest
- field lines by Chris M. Thomasson [28]
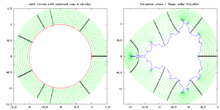
Tests
The Wolf Jung test

The external parameter rays for angles (in turns)
- 321685687669320/2251799813685247 (period 51, lands on c1 = -0.088891642419446 +0.650955631292636i )
- 321685687669322/2251799813685247 ( period 51 lands on c2 = -0.090588078906990 +0.655983860334813i )
- 1/7 ( period 3, lands on c3 = -0.125000000000000 +0.649519052838329i )
Angles differ by about , but the landing points of the corresponding parameter rays are about 0.035 apart. [29]
It can be computed with Maxima CAS :
(%i1) c1: -0.088891642419446 +0.650955631292636*%i; (%o1) 0.650955631292636*%i−0.088891642419446 (%i2) c2:-0.090588078906990 +0.655983860334813*%i; (%o2) 0.655983860334813*%i−0.09058807890699 (%i3) abs(c2-c1); (%o3) .005306692383854863 (%i4) c3: -0.125000000000000 +0.649519052838329*%i$ (%i5) abs(c3-c1); (%o5) .03613692356607755 (%i6) a3:1/7$ (%i7) float(abs(a3-a1)); (%o7) 4.440892098500628*10^−16
Informations from W Jung program :
The angle 1/7 or p001 has preperiod = 0 and period = 3. The conjugate angle is 2/7 or p010 . The kneading sequence is AA* and the internal address is 1-3 . The corresponding parameter rays are landing at the root of a satellite component of period 3. It is bifurcating from period 1.
The angle 321685687669320/2251799813685247 or p001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001000 has preperiod = 0 and period = 51. The conjugate angle is 321685687669319/2251799813685247 or p001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001000111 . The kneading sequence is AAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAABB* and the internal address is 1-49-50-51 . The corresponding parameter rays are landing at the root of a primitive component of period 51.
The angle 321685687669322/2251799813685247 or p001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001010 has preperiod = 0 and period = 51. The conjugate angle is 321685687669329/2251799813685247 or p001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001010001 . The kneading sequence is AABAABAABAABAABAABAABAABAABAABAABAABAABAABAABAABAA* and the internal address is 1-3-51 . The corresponding parameter rays are landing at the root of a satellite component of period 51. It is bifurcating from period 3.
The test by G. Pastor and Miguel Romera
The external parameter rays for angles (in turns)
- 6871947673/34359738367 ( period 35 )
- 9162596898/34359738367 ( period 35 )
the central babies Mandelbrot sets of the cauliflowers located at -0.153756141 + 1.030383223i
(not that 34359738367 = 2^35 - 1)
test by M. Romera,1 G. Pastor, A. B. Orue,1 A. Martin, M.-F. Danca,and F. Montoya

G Pastor gave an example of external rays for which the resolution of the IEEE 754 is not sufficient [30]:
- ( period 3, lands on root point of period 3 component c3 = -0.125000000000000 +0.649519052838329i )
One can analyze these angles using program by Claude Heiland-Allen :
./bin/mandelbrot_describe_external_angle ".(001)"
binary: .(001)
decimal: 1/7
preperiod: 0
period: 3
./bin/mandelbrot_describe_external_angle
".(001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001010)"
binary:
.(001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001010)
decimal:
33877456965431938318210482471113262183356704085033125021829876006886584214655562/237142198758023568227473377297792835283496928595231875152809132048206089502588927
preperiod: 0
period: 267
./bin/mandelbrot_describe_external_angle
".(001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001010001)"
binary:
.(001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001001010001)
decimal:
33877456965431938318210482471113262183356704085033125021829876006886584214655569/237142198758023568227473377297792835283496928595231875152809132048206089502588927
preperiod: 0
period: 267
./bin/mandelbrot_describe_external_angle
".(0010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010001)"
binary:
.(0010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010001)
decimal:
67754913930863876636420964942226524366713408170066250043659752013773168429311121/474284397516047136454946754595585670566993857190463750305618264096412179005177855
preperiod: 0
period: 268
./bin/mandelbrot_describe_external_angle
".(0010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010)"
binary:
.(0010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010010)
decimal:
67754913930863876636420964942226524366713408170066250043659752013773168429311122/474284397516047136454946754595585670566993857190463750305618264096412179005177855
preperiod: 0
period: 268
Landing points of above rays are roots with angled internal addresses ( description by Claude Heiland-Allen) :
- the upper one will be 1 -> 1/3 -> 3 -> 1/(period/3) -> period because it's the nearest bulb to the lower root cusp of 1/3 bulb and child bulbs of 1/3 bulb have periods 3 * denominator(internal angle) ie, 1 -> 1/3 -> 3 -> 1/89 -> 267
- the lower one will be 1 -> floor(period/3)/period -> period because it's the nearest bulb below the 1/3 cusp ie, 1 -> 89/268 -> 268
- the middle ray .(001) lands at the root of 1 -> 1/3 -> 3, from the cusp on the lower side (which is on the right in a standard unrotated view)
References
- ↑ Mathematics of Divergent Fractals by
- ↑ wikipedia : Orbit trap
- ↑ Mandelbrot Orbit Trap Rendering! Programming How-To Video by DKM101
- ↑ Java program by Dieter Röß showing result of changing initial point of Mandelbrot iterations
- ↑ Fractal Benchmark by Erik Wrenholt
- ↑ 12-minute Mandelbrot: fractals on a 50 year old IBM 1401 mainframe
- ↑ The Computer Language Benchmarks Game
- ↑ example-code-from-presentation-ways-of-seeing-julia-sets by ed Burke
- ↑ Computing the Mandelbrot set by Andrew Williams
- ↑ LIsp Program by Frank Buss
- ↑ Mandelbrot Set ASCII art at Bill Clementson's blog
- ↑ mandel function from 2.5.11.14 Fractal Patterns at Pov-Ray docs
- ↑ Drawing the Mandelbrot set by the method of escape lines. M. Romera et al.
- ↑ http://www.metabit.org/~rfigura/figura-fractal/math.html boundary trace by Robert Figura
- ↑ http://web.archive.org/20010415125044/www.geocities.com/CapeCanaveral/Launchpad/5113/fr27.htm| An open letter to Dr. Meech from Joyce Haslam in FRACTAL REPORT 27
- ↑ mandelbrot set n-th-decomposition
- ↑ fractalforums : What range/precision for fractional escape counts for Mandelbrot/Julia sets?
- ↑ Making Mandelbrot Set Movies by Tony Finch
- ↑ Linas Vepstas. Renormalizing the mandelbrot escape.
- ↑ mpmath Python library
- ↑ | The Mandelbrot Function by John J. G. Savard
- ↑ Smooth colouring is the key to the Mandelbrot set by Tony Finch
- ↑ calculate external angles from nucleus and period by Claude Heiland-Allen
- ↑ An algorithm to draw external rays of the Mandelbrot set by Tomoki Kawahira
- ↑ Wolf Jung explanation
- ↑ Claude Heiland-Allenmandelbrot_set_newton_basins by
- ↑ [http://www.hindawi.com/journals/mpe/2013/105283/ A Method to Solve the Limitations in Drawing External Rays of the Mandelbrot Set M. Romera,1 G. Pastor, A. B. Orue,1 A. Martin, M.-F. Danca,and F. Montoya ]
- ↑ Fractal forum : Plotting field lines during iteration...
- ↑ Wolf Jung's test for precision of drawing parameter rays
- ↑ A Method to Solve the Limitations in Drawing External Rays of the Mandelbrot Set M. Romera,1 G. Pastor, A. B. Orue,1 A. Martin, M.-F. Danca,and F. Montoya