Fractals/Computer graphic techniques/2D
< Fractals < Computer graphic techniquesIntro
All tasks ( image processing [1]) can be done using :
- own programs ( GUI or console )
- own programs and graphic libraries
- graphic programs like GIMP
- fractal programs like :
One can use free graphic libraries :
Creating graphic
Here are 3 targets / tasks :
- graphic file ( saving/ loading image )
- memory array ( processing image )
- screen pixels ( displaying image )
Graphic file
Memory array
Image in memory is a matrix :
- A 24-bit color image is an (Width x Height x 3) matrix.
- Gray-level and black-and-white images are of size (Width x Height) .
The color depth of the image :
- 8-bit for gray
- 24 or 32-bit for color,
- 1-bit for black and white.
Screen pixels
glxinfo | grep OpenGL
glxinfo | grep "direct rendering"
DRI
Direct Rendering Infrastructure (DRI2)[10]
Color

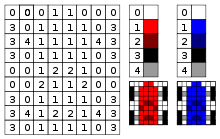
Curve
Field lines
Field line [11]
Tracing
Tracing curve [12]
Curve rasterisation
Ray
Ray can be parametrised with radius ( r)
Closed curve
Simple closed curve ("a connected curve that does not cross itself and ends at the same point where it begins" [13] = having no endpoints) can be parametrized with angle ( t).
Edge detection
- Boundary scanning method for Julia set - BSM/J
- Boundary scanning method for Mandelbrot set - BSM/M
- edge detection in Matlab [14]
 Level curves - edge detection ( 2 filters )
Level curves - edge detection ( 2 filters ) Edge detection of boundaries of level sets of escape time
Edge detection of boundaries of level sets of escape time
Sobel filter
Short introduction
Sobel filter G consist of 2 filters (masks):
- Gh for horizontal changes.
- Gv for vertical changes.
Sobel kernels
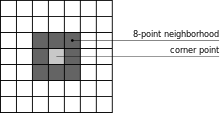
The Sobel kernel contains weights for each pixel from the 8-point neighbourhood of a tested pixel. These are 3x3 kernels.
There are 2 Sobel kernels, one for computing horizontal changes and other for computing vertical changes. Notice that a large horizontal change may indicate a vertical border, and a large vertical change may indicate a horizontal border. The x-coordinate is here defined as increasing in the "right"-direction, and the y-coordinate is defined as increasing in the "down"-direction.
The Sobel kernel for computing horizontal changes is:
The Sobel kernel for computing vertical changes is:
Note that :
- sum of weights of kernels are zero
- One kernel is simply the other rotated by 90 degrees [15]
- 3 weights in each kernal are zero
Pixel kernel
Pixel kernel A containing central pixel with its 3x3 neghbourhood :
Other notations for pixel kernel :
where : [16]
unsigned char ul, // upper left
unsigned char um, // upper middle
unsigned char ur, // upper right
unsigned char ml, // middle left
unsigned char mm, // middle = central pixel
unsigned char mr, // middle right
unsigned char ll, // lower left
unsigned char lm, // lower middle
unsigned char lr, // lower right
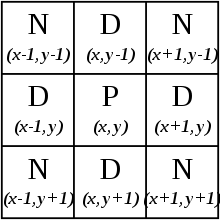
In array notation it is :[17]
In geographic notation usede in cellular aotomats it is central pixel of Moore neighbourhood.
So central ( tested ) pixel is :
Sobel filters
Compute sobel filters ( where here denotes the 2-dimensional convolution operation not matrix multiplication ). It is a sum of products of pixel and its weghts :
Because 3 weights in each kernal are zero so there are only 6 products. [18]
short Gh = ur + 2*mr + lr - ul - 2*ml - ll;
short Gv = ul + 2*um + ur - ll - 2*lm - lr;
Result
Result is computed (magnitude of gradient):
It is a color of tested pixel .
One can also approximate result by sum of 2 magnitudes :
which is much faster to compute.[19]
Algorithm
- choose pixel and its 3x3 neighberhood A
- compute sobel filter for horizontal Gh and vertical lines Gv
- compute sobel filter G
- compute color of pixel
Programming
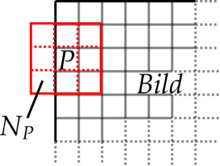
Lets take array of 8-bit colors ( image) called data. To find borders in this image simply do :
for(iY=1;iY<iYmax-1;++iY){
for(iX=1;iX<iXmax-1;++iX){
Gv= - data[iY-1][iX-1] - 2*data[iY-1][iX] - data[iY-1][iX+1] + data[iY+1][iX-1] + 2*data[iY+1][iX] + data[iY+1][iX+1];
Gh= - data[iY+1][iX-1] + data[iY-1][iX+1] - 2*data[iY][iX-1] + 2*data[iY][iX+1] - data[iY-1][iX-1] + data[iY+1][iX+1];
G = sqrt(Gh*Gh + Gv*Gv);
if (G==0) {edge[iY][iX]=255;} /* background */
else {edge[iY][iX]=0;} /* boundary */
}
}
Note that here points on borders of array ( iY= 0 , iY = iYmax , iX=0, iX=iXmax) are skipped
Result is saved to another array called edge ( with the same size).
One can save edge array to file showing only borders, or merge 2 arrays :
for(iY=1;iY<iYmax-1;++iY){
for(iX=1;iX<iXmax-1;++iX){ if (edge[iY][iX]==0) data[iY][iX]=0;}}
to have new image with marked borders.
Above example is for 8-bit or indexed color. For higher bit colors "the formula is applied to all three color channels separately" ( from RoboRealm doc).
Other implementations :
- ImagMagic discussion : using a sobel operator - edge detection
- Sobel in c from GIMP code
- Cpp code by Aaron Brooks - Brent Bolton - Jason O'Kane
- rosettacode : Image convolution
- C and opencl by royger
- C++ by Glenn Fiedler
- Convolution and Deconvolution
- Sobel Edge Detector by R. Fisher, S. Perkins, A. Walker and E. Wolfart with examples in Java
- Qt and GDI+ versions of the Sobel edge detection algorithm by Ken Earle
- Qt and OpenCV
Problems

Edge position :
In ImageMagic as "you can see, the edge is added only to areas with a color gradient that is more than 50% white! I don't know if this is a bug or intentional, but it means that the edge in the above is located almost completely in the white parts of the original mask image. This fact can be extremely important when making use of the results of the "-edge" operator." [20]
The result is :
- doubling edges ; "if you are edge detecting an image containing an black outline, the "-edge" operator will 'twin' the black lines, producing a weird result."[21]
- lines are not meeting in good points
See also new operators from 6 version of Image Magic : EdgeIn and EdgeOut from Morphology [22]
Edge thickening
convert $tmp0 -convolve "1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1" -threshold 0 $outfile
Filling contour
Quality of image
Interval arithemthic
Antialiasing

- TechInfo -AntiAliasing by Michael Condron
- Fract ( Lisp code) by Yannick Gingras
- Spatial anti aliasing at wikipedia [32]
- fractalforums discussion : Antialiasing fractals - how best to do it? [33]
Supersampling
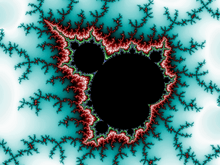
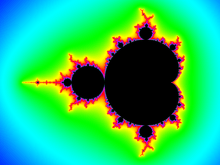
Other names :
- antigrain geometry
- Supersampling ( downsampling) [34][35]
- downsizing
- downscaling[36]
- subpixel accuracy
Examples :
- Cpp code by User Geek3
// subpixels finished -> make arithmetic mean
char pixel[3];
for (int c = 0; c < 3; c++)
pixel[c] = (int)(255.0 * sum[c] / (subpix * subpix) + 0.5);
fwrite(pixel, 1, 3, image_file);
//pixel finished
- command line version of Aptus ( python and c code ) by Ned Batchelder [37] ( see aptuscmd.py ) is using a high-quality downsampling filter thru PIL function resize [38]
- Java code by Josef Jelinek [39]: supersampling with grid algorithm, computes 4 new points (corners), resulting color is an avarage of each color component :
//Created by Josef Jelinek
// http://java.rubikscube.info/
Color c0 = color(dx, dy); // color of central point
// computation of 4 new points for antialiasing
if (antialias) { // computes 4 new points (corners)
Color c1 = color(dx - 0.25 * r, dy - 0.25 * r);
Color c2 = color(dx + 0.25 * r, dy - 0.25 * r);
Color c3 = color(dx + 0.25 * r, dy + 0.25 * r);
Color c4 = color(dx - 0.25 * r, dy + 0.25 * r);
// resulting color; each component of color is an avarage of 5 values ( central point and 4 corners )
int red = (c0.getRed() + c1.getRed() + c2.getRed() + c3.getRed() + c4.getRed()) / 5;
int green = (c0.getGreen() + c1.getGreen() + c2.getGreen() + c3.getGreen() + c4.getGreen()) / 5;
int blue = (c0.getBlue() + c1.getBlue() + c2.getBlue() + c3.getBlue() + c4.getBlue()) / 5;
color = new Color(red, green, blue);
}
- one can make big image ( like 10 000 x 10 000 ) and convert/resize it ( downsize ). For example using ImageMagic :
convert big.ppm -resize 2000x2000 m.png
Plane
Description is here
Optimization
Optimisation is described here
References
- ↑ IPOL Journal · Image Processing On Line
- ↑ ImageMagick image processing libraries
- ↑ GEGL (Generic Graphics Library)
- ↑ http://openil.sourceforge.net/
- ↑ http://freeimage.sourceforge.net/
- ↑ GD Graphics Library
- ↑ graphics magick
- ↑ OpenCv
- ↑ OpenImageIO
- ↑ w:Direct Rendering Infrastructure (DRI)
- ↑ wikipedia : Field line
- ↑ Curve sketching in wikipedia
- ↑ mathwords : simple_closed_curve
- ↑ matrixlab - line-detection
- ↑ Sobel Edge Detector by R. Fisher, S. Perkins, A. Walker and E. Wolfart.
- ↑ NVIDIA Forums , CUDA GPU Computing discussion by kr1_karin
- ↑ Sobel Edge by RoboRealm
- ↑ forum nvidia : Sobel Filter Don't understand a little thing in the SDK example
- ↑ Sobel Edge Detector by R. Fisher, S. Perkins, A. Walker and E. Wolfart.
- ↑ Image Magic doc
- ↑ Edge operator from Imagew Magic dosc
- ↑ imagemagick doc : morphology / edgein
- ↑ dilation at HIPR2 by Robert Fisher, Simon Perkins, Ashley Walker, Erik Wolfart
- ↑ imagemagick doc : morphology, dilate
- ↑ Fred's ImageMagick Scripts
- ↑ Images of Julia sets that you can trust Luiz Henrique de Figueiredo
- ↑ ON THE NUMERICAL CONSTRUCTION OF HYPERBOLIC STRUCTURES FOR COMPLEX DYNAMICAL SYSTEMS by Jennifer Suzanne Lynch Hruska
- ↑ "Images of Julia sets that you can trust" by Luiz Henrique de Figueiredo and Joao Batista Oliveira
- ↑ adaptive algorithms for generating guaranteed images of Julia sets by Luiz Henrique de Figueiredo
- ↑ Drawing Fractals With Interval Arithmetic - Part 1 by Dr Rupert Rawnsley
- ↑ Drawing Fractals With Interval Arithmetic - Part 2 by Dr Rupert Rawnsley
- ↑ Spatial anti aliasing at wikipedia
- ↑ fractalforums discussion : Antialiasing fractals - how best to do it?
- ↑ Supersampling at wikipedia
- ↑ ImageMagick v6 Examples -- Resampling Filters
- ↑ What is the best image downscaling algorithm (quality-wise)?
- ↑ Aptus ( python and c code ) by Ned Batchelder
- ↑ Pil function resize
- ↑ Java code by Josef Jelinek