Engineering Tables/Fourier Transform Properties
< Engineering Tables| Signal | Fourier transform unitary, angular frequency | Fourier transform unitary, ordinary frequency | Remarks | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
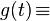 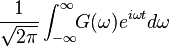 |
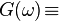 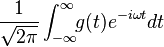 |
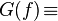 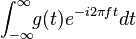 |
||
| 1 |  |
 |
 |
Linearity |
| 2 | 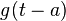 |
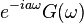 |
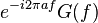 |
Shift in time domain |
| 3 | 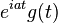 |
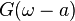 |
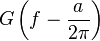 |
Shift in frequency domain, dual of 2 |
| 4 | 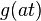 |
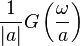 |
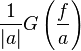 |
If  is large, then is large, then 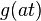 is concentrated around 0 and is concentrated around 0 and 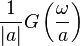 spreads out and flattens spreads out and flattens |
| 5 | 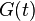 |
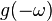 |
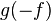 |
Duality property of the Fourier transform. Results from swapping "dummy" variables of  and and 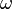 . . |
| 6 | 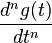 |
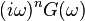 |
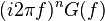 |
Generalized derivative property of the Fourier transform |
| 7 | 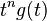 |
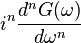 |
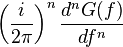 |
This is the dual to 6 |
| 8 | 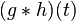 |
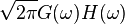 |
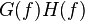 |
 denotes the convolution of denotes the convolution of 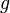 and and 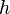 — this rule is the convolution theorem — this rule is the convolution theorem |
| 9 | 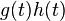 |
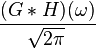 |
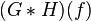 |
This is the dual of 8 |
| 10 | For a purely real even function 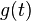 |
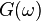 is a purely real even function is a purely real even function |
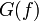 is a purely real even function is a purely real even function | |
| 11 | For a purely real odd function 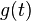 |
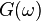 is a purely imaginary odd function is a purely imaginary odd function |
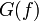 is a purely imaginary odd function is a purely imaginary odd function |
This article is issued from Wikibooks. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.