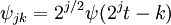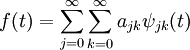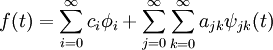Engineering Analysis/Wavelets
< Engineering AnalysisWavelets are orthogonal basis functions that only exist for certain windows in time. This is in contrast to sinusoidal waves, which exist for all times t. A wavelet, because it is dependant on time, can be used as a basis function. A wavelet basis set gives rise to wavelet decomposition, which is a 2-variable decomposition of a 1-variable function. Wavelet analysis allows us to decompose a function in terms of time and frequency, while fourier decomposition only allows us to decompose a function in terms of frequency.
Mother Wavelet
If we have a basic wavelet function ψ(t), we can write a 2-dimensional function known as the mother wavelet function as such:
Wavelet Series
If we have our mother wavelet function, we can write out a fourier-style series as a double-sum of all the wavelets:
Scaling Function
Sometimes, we can add in an additional function, known as a scaling function:
The idea is that the scaling function is larger than the wavelet functions, and occupies more time. In this case, the scaling function will show long-term changes in the signal, and the wavelet functions will show short-term changes in the signal.