Engineering Analysis/Probability Functions
< Engineering AnalysisProbability Density Function
The probability density function, or pdf of a random variable is the function defined by:
Remember here that X is the random variable, and x is a related variable (but is not random). The subscript X on 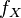 denotes that this is the pdf for the X variable.
denotes that this is the pdf for the X variable.
pdf's follow a few simple rules:
- The pdf is always non-negative.
- The area under the pdf curve is 1.
Cumulative Distribution Function
The cumulative distribution function, (CDF), is also known as the Probability Distribution Function, (PDF). to reduce confusion with the pdf of a random variable, we will use the acronym CDF to denote this function. The CDF of a random variable is the function defined by:
The CDF and the pdf of a random variable are related:
The CDF is the function corresponding to the probability that a given value x is less than the value of the random variable X. The CDF is a non-decreasing function, and is always non-negative.
Example: X between two bounds
To determine whether our random variable X lies between two bounds, [a, b], we can take the CDF functions:
![f_X(x) = P[X = x]](../I/m/244e7122e663a97f4ade740298ab9047.png)
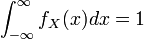
![F_X(x) = P[X \le x]](../I/m/322919e9e2a3a1fee1db1db579bb8fa2.png)
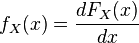
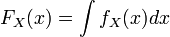
![P[a \le X \le b] = F_X(b) - F_X(a)](../I/m/2bea8ac227ff6dff0746b6899a897c96.png)