Digital Signal Processing/Transforms
< Digital Signal ProcessingThis page lists some of the transforms from the book, explains their uses, and lists some transform pairs of common functions.
Continuous-Time Fourier Transform (CTFT)
[CTFT]
CTFT Table
| Time Domain | Frequency Domain | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ||||||||||||
| 2 | ||||||||||||
| 3 | ||||||||||||
| 4 | ||||||||||||
| 5 | ||||||||||||
| 6 | ||||||||||||
| 7 | ||||||||||||
| 8 | ||||||||||||
| 9 | ||||||||||||
| 10 | ||||||||||||
| 11 | ||||||||||||
| 12 | ||||||||||||
| 13 | ||||||||||||
| 14 | ||||||||||||
| 15 | ||||||||||||
| 16 | ||||||||||||
| Notes: |
| |||||||||||
Discrete-Time Fourier Transform (DTFT)
DTFT Table
The information in the table below may be inaccurate - The DTFT transfers into the periodic frequency domain. The signals shown in the table are not periodic, and hence they are obviously wrong. The table seems to list ordinary Fourier transforms for angular frequency, which coincidentally also uses the greek letter ω, although with a different meaning.
| Time domain where |
Frequency domain where |
Remarks |
|---|---|---|
| Here represents the delta function which is 1 if and zero otherwise. | ||
| for some | ||
| For any real number . Here is a periodic Dirac delta function. That is and informally if | ||
| | ||
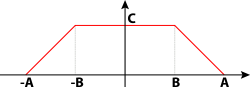 |
|
DTFT Properties
| Property | Time domain |
Frequency domain |
Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Linearity | |||
| Shift in time | integer k | ||
| Shift in frequency | real number a | ||
| Time reversal | |||
| Time conjugation | |||
| Time reversal & conjugation | |||
| Derivative in frequency | |||
| Integral in frequency | |||
| Convolve in time | |||
| Multiply in time | |||
| Correlation |
Where:
- is the convolution between two signals
- is the complex conjugate of the function x[n]
- represents the correlation between x[n] and y[n].
Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT)
DFT Table
| Time-Domain x[n] | Frequency Domain X[k] | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| DFT Definition | ||
| Shift theorem | ||
| Real DFT | ||
Z-Transform
Z-Transform Table
Here:
- for , for
- for , otherwise
| Signal, | Z-transform, | ROC | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | |||
| 2 | |||
| 3 | |||
| 4 | |||
| 5 | |||
| 6 | |||
| 7 | |||
| 8 | |||
| 9 | |||
| 10 | |||
| 11 | |||
| 12 | |||
| 13 | |||
| 14 | |||
| 15 | |||
| 16 | |||
| 17 | |||
| 18 | |||
| 19 | |||
| 20 |
Bilinear Transform
This article is issued from Wikibooks. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.