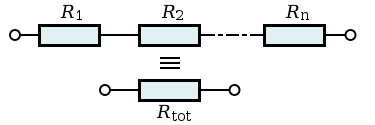
Circuit Theory/Series Resistance
< Circuit TheorySeries Resistance
Two or more resistor can be connected in series to increase the total resistance . The Total Resistance is equal to the sum of all the resistor's resistance . The total resistance In Series connected circuit Current and voltage will be reduced
Series Impedance
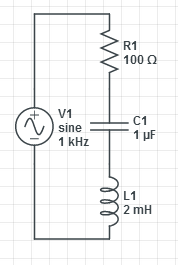
A branch is defined as any group of resistors, capacitors and inductors that can be circled with only two wires crossing the circle boundary.
A branch connects two, non-trivial nodes or junctions.
Within a branch the components are said to be "in series."
Consider a branch containing a Resistor, Capacitor and Inductor.
Say the driving function or source is
There is just one current, .
Symbolic Derivation
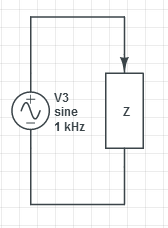
The terminal equations are:
- or
- or
There are no junction equations and the loop equation is:
Solving the terminal equations for voltage, substituting and then dividing by yields:
In terms of impedance, if:
Then:
In general, impedances add in series like resistors do in the time domain:

Numeric Example
In rectangular form:
In polar form (remember impedance is not a phasor, it is a concept in the phasor or complex frequency domain):
Notes
- Calculations like this are only necessary when trying to find out what is going on in one little part of the circuit ... and Kirchhoff would take too long. This was true in the past, but given the modern capabilities of matLab and mupad, the importance of the series concept may diminish.
- It appears that the exponential term decreases the overall magnitude and increases the reactance ... increases in the inductive direction with the exponential term.
- The V/I ratio sets up/prepares for the transfer function discussion later.