Calculus/Functions
< CalculusWhat functions are and how are they described
Note: This is an attempt at a rewrite of "Classical understanding of functions". If others approve, consider deleting that section.
Whenever one quantity uniquely determines the value of another quantity, we have a function.
{ ---- comments ------
ie X uniquely determines Y but Y is not uniquely determined by X
Let set X consists of x's and set Y consists of y's
two x's can have same y ie one y can be determined by two x's
but one x cannot have two y's
---- end of comments ------
}
You can think of a function as a kind of machine. You feed the machine raw materials, and the machine changes the raw materials into a finished product.
|
A function in everyday life Think about dropping a ball from a bridge. At each moment in time, the ball is a height above the ground. The height of the ball is a function of time. It was the job of physicists to come up with a formula for this function. This type of function is called real-valued since the "finished product" is a number (or, more specifically, a real number). |
|
A function in everyday life (Preview of Multivariable Calculus) Think about a wind storm. At different places, the wind can be blowing in different directions with different intensities. The direction and intensity of the wind can be thought of as a function of position. This is a function of two real variables (a location is described by two values - an and a ) which results in a vector (which is something that can be used to hold a direction and an intensity). These functions are studied in multivariable calculus (which is usually studied after a one year college level calculus course). This a vector-valued function of two real variables. |
We will be looking at real-valued functions until studying multivariable calculus. Think of a real-valued function as an input-output machine; you give the function an input, and it gives you an output which is a number (more specifically, a real number). For example, the squaring function takes the input 4 and gives the output value 16. The same squaring function takes the input -1 and gives the output value 1.
There are many ways which people describe functions. In the examples above, a verbal descriptions is given (the height of the ball above the earth as a function of time). Here is a list of ways to describe functions. The top three listed approaches to describing functions are the most popular and you could skip the rest if you like.
- A function is given a name (such as ) and a formula for the function is also given. For example, describes a function. We refer to the input as the argument of the function (or the independent variable), and to the output as the value of the function at the given argument.
- A function is described using an equation and two variables. One variable is for the input of the function and one is for the output of the function. The variable for the input is called the independent variable. The variable for the output is called the dependent variable. For example, describes a function. The dependent variable appears by itself on the left hand side of equal sign.
- A verbal description of the function.
When a function is given a name (like in number 1 above), the name of the function is usually a single letter of the alphabet (such as or ). Some functions whose names are multiple letters (like the sine function .
|
Plugging a value into a function If we write , then we know that
How would we know the value of the function at 3? We would have the following three thoughts: and we would write . The value of at 3 is 11. Note that means the value of the dependent variable when takes on the value of 3. So we see that the number 11 is the output of the function when we give the number 3 as the input. People often summarize the work above by writing "the value of at three is eleven", or simply " of three equals eleven". |
Classical understanding of functions
To provide the classical understanding of functions, think of a function as a kind of machine. You feed the machine raw materials, and the machine changes the raw materials into a finished product based on a specific set of instructions. The kinds of functions we consider here, for the most part, take in a real number, change it in a formulaic way, and give out a real number (possibly the same as the one it took in). Think of this as an input-output machine; you give the function an input, and it gives you an output. For example, the squaring function takes the input 4 and gives the output value 16. The same squaring function takes the input and gives the output value 1.
A function is usually written as , , or something similar - although it doesn't have to be. A function is always defined as "of a variable" which tells us what to replace in the formula for the function.
For example, tells us:
- The function is a function of .
- To evaluate the function at a certain number, replace the with that number.
- Replacing with that number in the right side of the function will produce the function's output for that certain input.
- In English, the definition of is interpreted, "Given a number, will return two more than the triple of that number."
Thus, if we want to know the value (or output) of the function at 3:
- We evaluate the function at .
- The value of at 3 is 11.
See? It's easy!
Note that means the value of the dependent variable when takes on the value of 3. So we see that the number 11 is the output of the function when we give the number 3 as the input. We refer to the input as the argument of the function (or the independent variable), and to the output as the value of the function at the given argument (or the dependent variable). A good way to think of it is the dependent variable 'depends' on the value of the independent variable . This is read as "the value of at three is eleven", or simply " of three equals eleven".
Notation
Functions are used so much that there is a special notation for them. The notation is somewhat ambiguous, so familiarity with it is important in order to understand the intention of an equation or formula.
Though there are no strict rules for naming a function, it is standard practice to use the letters , , and to denote functions, and the variable to denote an independent variable. is used for both dependent and independent variables.
When discussing or working with a function , it's important to know not only the function, but also its independent variable . Thus, when referring to a function , you usually do not write , but instead . The function is now referred to as " of ". The name of the function is adjacent to the independent variable (in parentheses). This is useful for indicating the value of the function at a particular value of the independent variable. For instance, if
- ,
and if we want to use the value of for equal to , then we would substitute 2 for on both sides of the definition above and write
This notation is more informative than leaving off the independent variable and writing simply '' , but can be ambiguous since the parentheses can be misinterpreted as multiplication.
Modern understanding of functions
The formal definition of a function states that a function is actually a rule that associates elements of one set called the domain of the function, with the elements of another set called the range of the function. For each value we select from the domain of the function, there exists exactly one corresponding element in the range of the function. The definition of the function tells us which element in the range corresponds to the element we picked from the domain. Classically, the element picked from the domain is pictured as something that is fed into the function and the corresponding element in the range is pictured as the output. Since we "pick" the element in the domain whose corresponding element in the range we want to find, we have control over what element we pick and hence this element is also known as the "independent variable". The element mapped in the range is beyond our control and is "mapped to" by the function. This element is hence also known as the "dependent variable", for it depends on which independent variable we pick. Since the elementary idea of functions is better understood from the classical viewpoint, we shall use it hereafter. However, it is still important to remember the correct definition of functions at all times.
To make it simple, for the function , all of the possible values constitute the domain, and all of the values ( on the x-y plane) constitute the range.
Remarks
The following arise as a direct consequence of the definition of functions:
- By definition, for each "input" a function returns only one "output", corresponding to that input. While the same output may correspond to more than one input, one input cannot correspond to more than one output. This is expressed graphically as the vertical line test: a line drawn parallel to the axis of the dependent variable (normally vertical) will intersect the graph of a function only once. However, a line drawn parallel to the axis of the independent variable (normally horizontal) may intersect the graph of a function as many times as it likes. Equivalently, this has an algebraic (or formula-based) interpretation. We can always say if , then , but if we only know that then we can't be sure that .
- Each function has a set of values, the function's domain, which it can accept as input. Perhaps this set is all positive real numbers; perhaps it is the set {pork, mutton, beef}. This set must be implicitly/explicitly defined in the definition of the function. You cannot feed the function an element that isn't in the domain, as the function is not defined for that input element.
- Each function has a set of values, the function's range, which it can output. This may be the set of real numbers. It may be the set of positive integers or even the set {0,1}. This set, too, must be implicitly/explicitly defined in the definition of the function.
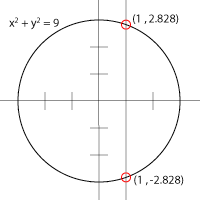
The vertical line test
The vertical line test, mentioned in the preceding paragraph, is a systematic test to find out if an equation involving and can serve as a function (with the independent variable and the dependent variable). Simply graph the equation and draw a vertical line through each point of the -axis. If any vertical line ever touches the graph at more than one point, then the equation is not a function; if the line always touches at most one point of the graph, then the equation is a function.
(There are a lot of useful curves, like circles, that aren't functions (see picture). Some people call these graphs with multiple intercepts, like our circle, "multi-valued functions"; they would refer to our "functions" as "single-valued functions".)
Important functions
| Constant function |
It disregards the input and always outputs the constant , and is a polynomial of the zeroth degree where . Its graph is a horizontal line. | |
| Linear function |
Takes an input, multiplies by and adds . It is a polynomial of the first degree. Its graph is a line (slanted, except ). | |
| Identity function |
Takes an input and outputs it unchanged. A polynomial of the first degree, . Special case of a linear function. | |
| Quadratic function |
A polynomial of the second degree. Its graph is a parabola, unless . (Don't worry if you don't know what this is.) | |
| Polynomial function |
The number is called the degree. | |
| Signum function |
Example functions
Some more simple examples of functions have been listed below.
|
|
|
It is possible to replace the independent variable with any mathematical expression, not just a number. For instance, if the independent variable is itself a function of another variable, then it could be replaced with that function. This is called composition, and is discussed later.
Manipulating functions
Addition, Subtraction, Multiplication and Division of functions
For two real-valued functions, we can add the functions, multiply the functions, raised to a power, etc.
|
Example: Adding, subtracting, multiplying and dividing functions which do not have a name If we add the functions and , we obtain . If we subtract from , we obtain . We can also write this as . If we multiply the function and the function , we obtain . We can also write this as . If we divide the function by the function , we obtain . |
If a math problem wants you to add two functions and , there are two ways that the problem will likely be worded:
- If you are told that , that , that and asked about , then you are being asked to add two functions. Your answer would be .
- If you are told that , that and you are asked about , then you are being asked to add two functions. The addition of and is called . Your answer would be .
Similar statements can be made for subtraction, multiplication and division.
|
Example: Adding, subtracting, multiplying and dividing functions which do have a name Let and: . Let's add, subtract, multiply and divide.
|
Composition of functions
We begin with a fun (and not too complicated) application of composition of functions before we talk about what composition of functions is.
|
Example: Dropping a ball If we drop a ball from a bridge which is 20 meters above the ground, then the height of our ball above the earth is a function of time. The physicists tell us that if we measure time in seconds and distance in meters, then the formula for height in terms of time is . Suppose we are tracking the ball with a camera and always want the ball to be in the center of our picture. Suppose we have The angle will depend upon the height of the ball above the ground and the height above the ground depends upon time. So the angle will depend upon time. This can be written as . We replace with what it is equal to. This is the essence of composition. |
Composition of functions is another way to combine functions which is different from addition, subtraction, multiplication or division.
The value of a function depends upon the value of another variable ; however, that variable could be equal to another function , so its value depends on the value of a third variable. If this is the case, then the first variable is a function of the third variable; this function () is called the composition of the other two functions ( and ).
|
Example: Composing two functions Let and: . The composition of with is read as either "f composed with g" or "f of g of x." Let Then
Sometimes a math problem asks you compute when they want you to compute , Here, is the composition of and and we write . Note that composition is not commutative:
|
Composition of functions is very common, mainly because functions themselves are common. For instance, squaring and sine are both functions:
Thus, the expression is a composition of functions:
(Note that this is not the same as .) Since the function sine equals if ,
- .
Since the function square equals if ,
- .
Transformations
Transformations are a type of function manipulation that are very common. They consist of multiplying, dividing, adding or subtracting constants to either the input or the output. Multiplying by a constant is called dilation and adding a constant is called translation. Here are a few examples:
- Dilation
- Translation
- Dilation
- Translation
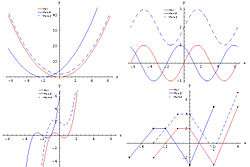
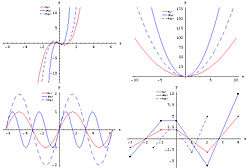
Translations and dilations can be either horizontal or vertical. Examples of both vertical and horizontal translations can be seen at right. The red graphs represent functions in their 'original' state, the solid blue graphs have been translated (shifted) horizontally, and the dashed graphs have been translated vertically.
Dilations are demonstrated in a similar fashion. The function
has had its input doubled. One way to think about this is that now any change in the input will be doubled. If I add one to , I add two to the input of , so it will now change twice as quickly. Thus, this is a horizontal dilation by because the distance to the -axis has been halved. A vertical dilation, such as
is slightly more straightforward. In this case, you double the output of the function. The output represents the distance from the -axis, so in effect, you have made the graph of the function 'taller'. Here are a few basic examples where is any positive constant:
| Original graph | Rotation about origin | ||
| Horizontal translation by units left | Horizontal translation by units right | ||
| Horizontal dilation by a factor of | Vertical dilation by a factor of | ||
| Vertical translation by units down | Vertical translation by units up | ||
| Reflection about -axis | Reflection about -axis |
Domain and Range
Domain
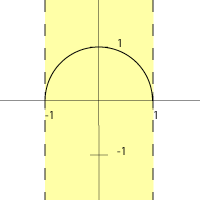
The domain of a function is the set of all points over which it is defined. More simply, it represents the set of x-values which the function can accept as input. For instance, if
then is only defined for values of between and , because the square root function is not defined (in real numbers) for negative values. Thus, the domain, in interval notation, is . In other words,
- .
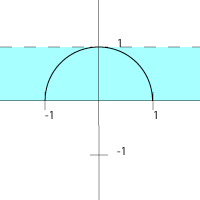
Range
The range of a function is the set of all values which it attains (i.e. the y-values). For instance, if:
then can only equal values in the interval from to . Thus, the range of is .
One-to-one Functions
A function is one-to-one (or less commonly injective) if, for every value of , there is only one value of that corresponds to that value of . For instance, the function is not one-to-one, because both and result in . However, the function is one-to-one, because, for every possible value of , there is exactly one corresponding value of . Other examples of one-to-one functions are , where . Note that if you have a one-to-one function and translate or dilate it, it remains one-to-one. (Of course you can't multiply or by a zero factor).
Horizontal Line Test
If you know what the graph of a function looks like, it is easy to determine whether or not the function is one-to-one. If every horizontal line intersects the graph in at most one point, then the function is one-to-one. This is known as the Horizontal Line Test.
Algebraic 1-1 Test
You can also show one-to-oneness algebraically by assuming that two inputs give the same output and then showing that the two inputs must have been equal. For example,
Is a 1:1 function?
Therefore by the algebraic 1:1 test, the function is 1:1.
You can show that a function is not one-to-one by finding two distinct inputs that give the same output. For example, is not one-to-one because but .
Inverse functions
We call the inverse function of if, for all :
A function has an inverse function if and only if is one-to-one. For example, the inverse of is . The function has no inverse.
Notation
The inverse function of is denoted as . Thus, is defined as the function that follows this rule
To determine when given a function , substitute for and substitute for . Then solve for , provided that it is also a function.
Example: Given , find .
Substitute for and substitute for . Then solve for :
To check your work, confirm that :
If isn't one-to-one, then, as we said before, it doesn't have an inverse. Then this method will fail.
Example: Given , find .
Substitute for and substitute for . Then solve for :
Since there are two possibilities for , it's not a function. Thus doesn't have an inverse. Of course, we could also have found this out from the graph by applying the Horizontal Line Test. It's useful, though, to have lots of ways to solve a problem, since in a specific case some of them might be very difficult while others might be easy. For example, we might only know an algebraic expression for but not a graph.