Astrodynamics/The Earth
< AstrodynamicsThe Earth is an object of special importance, not because it has any special characteristics, but because it is our starting point. All satellites that we lauch start on the surface of earth, and all our observations are made from the surface of earth. The only exception to the second rule is that some observations are made from satellites that have been previously launched from earth. Most of the practical applications of astrodynamics are centered around the earth (orbiting satellites, ballistic missiles, etc.), and so we will focus much of our attention on it.
Size and Shape
While it is typically thought that the earth is a sphere, it is not. The radius of the earth is over 21 kilometers longer at the equator than it is at the poles. This is known as the equatorial bulge of the earth, and can affect some of our more precise calculations. We will discuss the effects of this bulge later when we have developed more theory.
Orbit and Rotation
One earth rotation on its axis, such that the sun is at the same place in the sky, is known as a solar day. A solar day is 24 hours by definition.
The period of the Earth's rotation is known as a solar year. A solar year is equal to 365.25 solar days.
The Earth's orbital plane is not parallel with the Earth's equator. This tilt in the orbital plane causes the seasons.
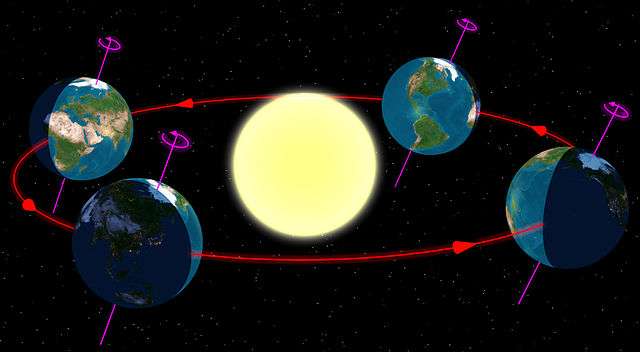
Equinoxes
When the sun appears directly over the equator, and the day is the same length as the night, it is called the equinox. The equinox between the months of March and April is known as the vernal equinox. The autumnal equinox is the transition between the months of September and October.
Equatorial Plane
The equator around the center of the earth is a circle, if we cut the earth in half. If we extend this circle out to infinity, we have the equatorial plane. Anything on the equatorial plane appears directly overhead to a person standing on the equator.
Canonical Units
The distance between the earth and the sun can be difficult to measure, and the units involved can make calculations difficult. However, we can define a new unit, the astronomical unit (AU) that is the average distance between the earth and the sun. 1 AU = 149 597 870.691 km.