Algorithm Implementation/Mathematics/Pythagorean theorem
< Algorithm Implementation < Mathematics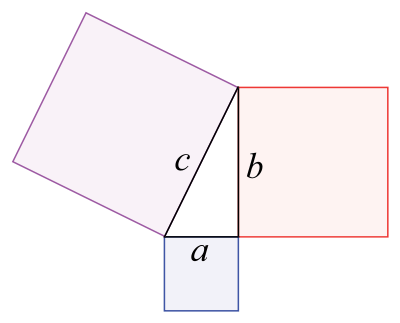
The Pythagorean theorem: The sum of the areas of the two squares on the legs (a and b) equals the area of the square on the hypotenuse (c).
In mathematics, the Pythagorean theorem or Pythagoras' theorem is a relation in Euclidean geometry among the three sides of a right triangle (right-angled triangle). In terms of areas, it states:
In any right triangle, the area of the square whose side is the hypotenuse (the side opposite the right angle) is equal to the sum of the areas of the squares whose sides are the two legs (the two sides that meet at a right angle).
The theorem can be written as an equation relating the lengths of the sides a, b and c, often called the Pythagorean equation:[1]
where c represents the length of the hypotenuse, and a and b represent the lengths of the other two sides.
Scheme
(define (hypotenuse a b) (sqrt (+ (expt a 2) (expt b 2))))
;; Equivalent, but does not check the number of arguments
(define (hypotenuse . xs) (sqrt (fold (lambda (x acc) (+ (expt x 2) acc)) 0 xs)))
Visual Basic
Function Hypotenuse(sideA as Double, sideB as Double) as Double
Hypotenuse = sqr(sideA^2 + sideB^2)
End Function
Java
public static double hypotenuse(double sideA, double sideB) {
double hypotenuse = Math.sqrt((sideA*sideA) + (sideB*sideB));
return hypotenuse;
}
Python
def hypotenuse(a,b):
return ( a**2 + b**2 )**.5
Haskell
pythag a b = sqrt $ a^2 + b^2
References
- ↑ Judith D. Sally, Paul Sally (2007). "Chapter 3: Pythagorean triples". Roots to research: a vertical development of mathematical problems. American Mathematical Society Bookstore. p. 63. ISBN 0821844032. http://books.google.com/books?id=nHxBw-WlECUC&pg=PA63.
This article is issued from Wikibooks. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.