Adventist Youth Honors Answer Book/Nature/Orchids
< Adventist Youth Honors Answer Book < Nature| Orchids | ||
|---|---|---|
| Nature General Conference |
Skill Level 1 |  |
| Year of Introduction: 1964 | ||
1. Define the characteristics of an orchid.
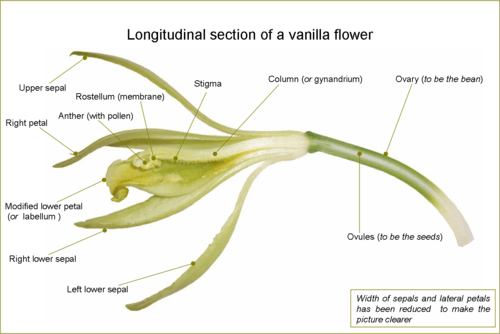
Orchids are monocot plants characterised by the presence of three sepals , two petals and the third petal modified as a lip.
2. What are the two main groupings of orchids? Name and show examples of each from a live plant or picture.
There are five identified groupings of orchids. (Also see Taxonomy of the Orchid family)
- Apostasioideae: 2 group(s) in this sub-family and 16 species, south-western Asia
- Cypripedioideae: 5 group(s) in this sub-family and 130 species, mostly from the temperate regions of the world, some in tropical America
- Vanilloideae: 15 group(s) in this sub-family and 180 species, humid tropical and subtropical regions, eastern North America
- Epidendroideae: more than 500 group(s) in this sub-family and more or less 20 000 species, cosmopolitan
- Orchidoideae: 208 group(s) in this sub-family and 3,630 species, cosmopolitan
The last two, Epidendroideae and Orchidoideae are the largest subfamilies (main groupings).
 Neuwiedia griffithii (in the subfamily Apostasioideae)
Neuwiedia griffithii (in the subfamily Apostasioideae) Pink Lady's Slipper (in the subfamily Cypripedioidea)
Pink Lady's Slipper (in the subfamily Cypripedioidea) Vanilla fragrans (in the subfamily Vanilloideae)
Vanilla fragrans (in the subfamily Vanilloideae) Vanda Miss Joaquim (in the subfamily Epidendroideae)
Vanda Miss Joaquim (in the subfamily Epidendroideae) Neotinea tridentata (in the subfamily Orchidoideae)
Neotinea tridentata (in the subfamily Orchidoideae)
3. What are the differences between epiphytic, parasitic, and saprophytic orchids?
Epiphytic
An epiphytic is an organism that grows upon or attached to a living plant.

 Epiphytes on a tree
Epiphytes on a tree Epiphyte assemblage of orchids and bromeliads
Epiphyte assemblage of orchids and bromeliads
Parasitic
Parasitic is symbiosis or "living together", a phenomenon in which two organisms which are unrelated co-exist over a long period of time, usually the lifetime of one of the individuals. A parasitic relationship does not benefit the host and can, in fact, be detrimental to it.
Saprophytic
A saprotroph (or saprobe) is an organism that obtains its nutrients from non-living organic matter, usually dead and decaying plant or animal matter, by absorbing soluble organic compounds. They cannot make food for themselves.
4. Discuss the distribution of orchids, making particular reference to the occurrence of these in your area.
Distribution
Orchids are cosmopolitan, occurring in almost every habitat. The great majority are to be found in the tropics, mostly Asia, South America and Central America. They are found above the Arctic Circle, in southern Patagonia and even on Macquarie Island, close to Antarctica.
The following list gives a rough overview of their distribution:
- tropical America: 300 to 350 genera
- tropical Asia: 250 to 300 genera
- tropical Africa: 125 to 150 genera
- Oceania: 50 to 70 genera
- Europe and temperate Asia: 40 to 60 genera
- North America: 20 to 30 genera
5. Name the main cultivated genera of orchids. Identify three from plants or picture. What is cultivar?
Most cultivated orchids are tropical or subtropical, but quite a few which grow in colder climates can be found on the market.
Temperate species available at nurseries include:
- Ophrys apifera (bee orchid),
- Gymnadenia conopsea (fragrant orchid),
- Anacamptis pyramidalis (pyramidal orchid) and
- Dactylorhiza fuchsii (common spotted orchid).
The main cultivated genera of orchids is Epidendroideae.
 Tulip Orchid
Tulip Orchid Crimson Cattleya
Crimson Cattleya Boat orchids
Boat orchids Laelia anceps
Laelia anceps Dendrobium lindleyi
Dendrobium lindleyi Moon orchid
Moon orchid Paphiopedilum bellatulum
Paphiopedilum bellatulum Florida orchid
Florida orchid- Blue orchid
 Epidendrum radicans
Epidendrum radicans Brassia arcuigera
Brassia arcuigera Bulbophyllum echinolabium
Bulbophyllum echinolabium Catasetum saccatum
Catasetum saccatum Sophronitis tenebrosa
Sophronitis tenebrosa Miltonia Aquarius
Miltonia Aquarius.jpg) Phaius rosellus
Phaius rosellus
6. Discuss the main essentials to observe in the cultivation of orchids. Grow at least one orchid for at least six months.
- Light - is important in all living things.
- Temperature - mature plants need a 15-20 degree F temperature difference between day and night.
- Water - seedlings need more moisture, mature plants must dry out between watering.
- Humidity - they live in tropical regions
- Fertilizer - remember that these are usually parasitic plants.
- Potting - plant in material that allows good aeration and drainage.
The Wikipedia article Hippeastrum has detailed instructions for growing this orchid throughout the year. Another common houseplant orchid is the Cymbidium.
Another option is to grow your orchids using hydroponics, which satisfies a requirement of the Voyager curriculum. Again Wikipedia has an article called "Hydroponics for orchid cultivation" which is filled with important details.
Have a fun time growing your orchid(s).
7. What are the main uses of orchids? What orchid is used commercially?
Main Uses of Orchids
- The underground tubers of terrestrial orchids (mainly Orchis mascula) are ground to a powder and used for cooking, such as in the hot beverage salep or the so-called "fox-testicle ice cream" salepi dondurma.
- The scent of orchids is frequently analysed by perfumists (using Gas-liquid chromatography) to identify potential fragrance chemicals.
- The other important use of orchids is their cultivation for the enjoyment of the flowers.
What orchid is used commercially?
- Vanilla is a flavoring derived from orchids in the genus Vanilla native to Mexico. The name came from the Spanish word vainilla, meaning little pod.
8. Know the laws in your area (if any) that protect wild orchids.
Navasota Ladies'-Tresses
The Navasota Ladies'-Tresses (Spiranthes parksii) is on the Federal endangered species list
Reason for Concern: Navasota ladies-tresses is endemic to the Oak Woodlands and Prairies region of east-central Texas. Once thought to be extremely rare, it is now known to be locally common in parts of its range. However, many of the sites are near an active coal stripmining operation. Other sites are within the area of Bryan-College Station and are threatened by the rapid development of this metroplex.
Pink Lady's Slipper
Cypripedium acaule, or Pink Lady's Slipper, is endangered in Nova Scotia, Canada, and in the U.S. States of Georgia, Tennessee, Illinois, and New York. Because of a fungus association needed for growth, and the high acid this plant needs, C. acaule is very difficult to grow in the average garden and is unlikely to survive any attempts at transplantation. It should not be removed or disturbed if found in nature.
Showy Lady's Slipper
Cypripedium reginae, or Showy Lady's Slipper is endangered (or extirpated) in the U.S. States of Arkansas, Connecticut, Illinois, Iowa, Kentucky, Maine, Maryland, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, New Jersey, New York, Ohio, Pennsylvania, and Tennessee.