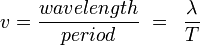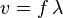A-level Physics/Wave properties/Reflection and Refraction
< A-level Physics < Wave propertiesDefinitions and units
- Frequency (f) — the number of complete oscillations of a particle each second.
- Frequency is measured in hertz (Hz). 1 Hz = 1 complete cycle per second.
- Period (T) — the time taken for one complete oscillation.
- Period is usually measured in seconds, especially when used in equations.
- Amplitude (A) — the maximum displacement of a particle from its equilibrium position.
- Wavelength (λ) — the shortest distance between two parts of the same wave that are oscillating in phase with each other.
Relationship between f and T
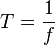
and hence,
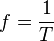
Wave speed
The speed of a wave (v) is just the distance the wave has travelled over the time. If we take the time to be one period, then the distance will be one wavelength. Hence the speed of the wave is given by:
Using the fact that,
we can re-arrange the above equation to give
Laws of reflection
Angle of Incidence = Angle of Reflection
The incident ray, reflected ray and the normal to the surface at the point of incidence are all in the same plane.
Refractive index
When light passes from one material to another the refractive index is the ratio of the speeds of light in the two materials.
Refractive Index = Speed in Air / Speed in Medium
Snell's Law
Snell's law is the simple formula used to calculate the refraction of light when travelling between two media of differing refractive index.
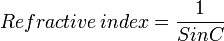
| ||||||||||||||
This article is issued from Wikibooks. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.