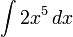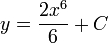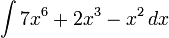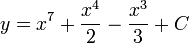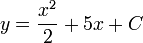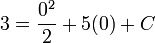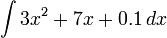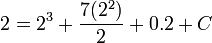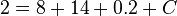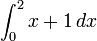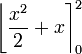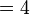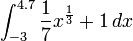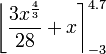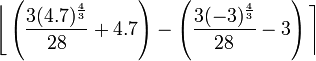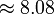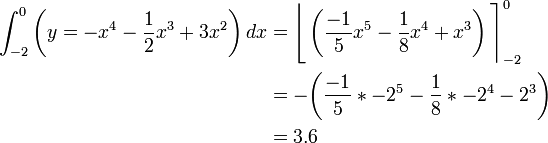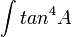A-level Mathematics/OCR/C2/Integration/Solutions
< A-level Mathematics < OCR < C2 < IntegrationWorked Solutions
1a)
- Using our rule: That
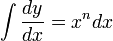 is equal to
is equal to 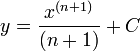
- We get:
b)
- Again using our rule, we would get:
2a)
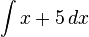 given that the point
given that the point 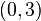 lies on the curve.
lies on the curve.
- Using our rule, the intergral becomes
- Now we can sub in our points
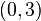 , So that:
, So that:
- Therefore C = 3
b)
- Evaulating this we get:
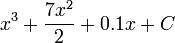
- Given (2,2), subing these points in:
3a)
- Evaluating this we get:
- Substituting in values we get:
b)
- Evaluating this we get:
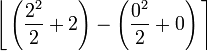
4)
- The question is simply to evaluate this definite integral:
5 )
This article is issued from Wikibooks. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.