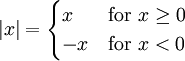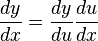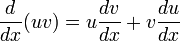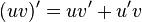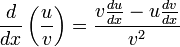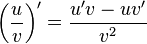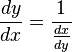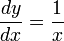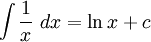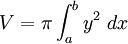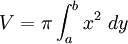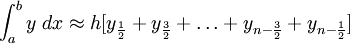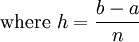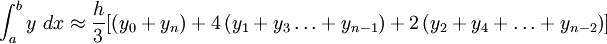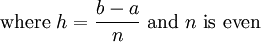A-level Mathematics/AQA/MPC3
< A-level Mathematics < AQAFunctions
Domain and range of a function
In general:
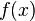 is called the image of
is called the image of 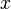 .
.- The set of permitted
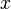 values is called the domain of the function
values is called the domain of the function - The set of all images is called the range of the function
Modulus function
The modulus of 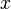 , written
, written 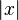 , is defined as
, is defined as
Differentiation
Chain rule
The chain rule states that:
If 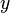 is a function of
is a function of 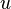 , and
, and 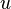 is a function of
is a function of 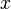 ,
,
Product rule
The product rule states that:
If  , where
, where 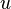 and
and 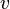 are both functions of
are both functions of 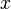 , then
, then
An alternative way of writing the product rule is:
Quotient rule
The quotient rule states that:
If 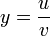 , where
, where 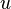 and
and 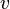 are functions of
are functions of 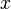 , then
, then
An alternative way of writing the quotient rule is:
x as a function of y
In general,
Trigonometric functions
The functions cosec θ, sec θ and cot θ
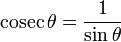
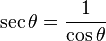
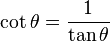
Standard trigonometric identities
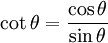
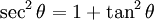
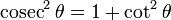
Differentiation of sin x, cos x and tan x
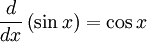
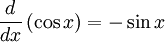
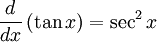
Integration of sin(kx) and cos(kx)
In general,
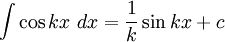
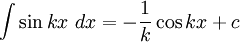
Exponentials and logarithms
Differentiating exponentials and logarithms
In general,
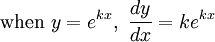
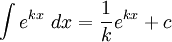
Natural logarithms
If 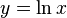 , then
, then
It follows from this result that
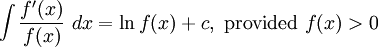
Integration
Integration by parts
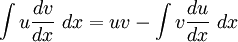
Standard integrals
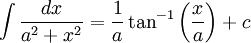
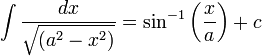
Volumes of revolution
The volume of the solid formed when the area under the curve 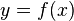 , between
, between  and
and  , is rotated through 360° about the
, is rotated through 360° about the 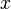 -axis is given by:
-axis is given by:
The volume of the solid formed when the area under the curve 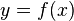 , between
, between  and
and  , is rotated through 360° about the
, is rotated through 360° about the 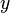 -axis is given by:
-axis is given by:
Numerical methods
Iterative methods
An iterative method is a process that is repeated to produce a sequence of approximations to the required solution.
Numerical integration
Mid ordinate rule
Simpson's rule