A-level Chemistry/OCR (Salters)/Kinetics
< A-level Chemistry < OCR (Salters)Rate equations
![\mbox{rate} = k[A]^m[B]^n \,\!](../I/m/61c7ba86d11aad21afd891b4f1e8b17f.png)
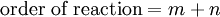
Arrhenius equation
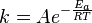
Arrhenius plot
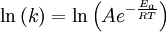
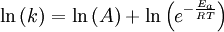
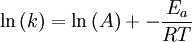
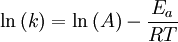
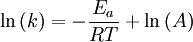
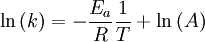
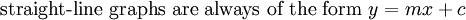
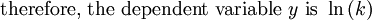
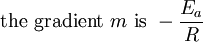
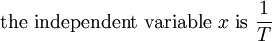
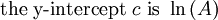
This article is issued from Wikibooks. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.