A-level Chemistry/OCR (Salters)/Equilibrium constants
< A-level Chemistry < OCR (Salters)Mathematical definition of an equilibrium constant
For a reversible reaction,
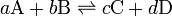
the equilibrium constant K is defined as
![K = \frac{ [\mbox{C}]^c [\mbox{D}]^d }{ [\mbox{A}]^a [\mbox{B}]^b }](../I/m/67c395e7d24a6c7f6b7700f8ab6074f1.png)
where [X] denotes the concentration of chemical species X.
For example, for the Haber process reaction,
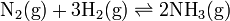
the equilibrium constant can be calculated by
![K = \frac{ [\mbox{NH}_3 (\mbox{g})]^2 }{ [\mbox{N}_2(\mbox{g})] [\mbox{H}_2(\mbox{g})]^3 }](../I/m/d5630d3fd8a293f04f6eef9928418d4e.png)
This article is issued from Wikibooks. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.