Widened mediastinum
Background
- Diagnosed on plain radiography of the chest
- Mediastinal width >8cm is abnormal
- Potential causes include:
- AP projection (Mediastinal structures further away from imaging plate)
- Thoracic aortic aneurysm
- Aortic dissection/rupture
- Mediastinal mass
Anatomy
- Mediastinum is divided into superior and inferior compartments, the latter further subdivided into anterior, middle and posterior compartments.[1]
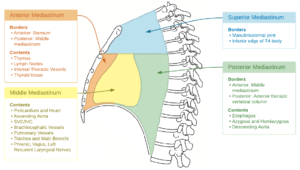
Anatomy and contents of the mediastinum[2]
Mediastinal Masses
- Anterior
- Retrosternal goiter
- Thymoma
- Germ-cell tumor
- Lymphadenopathy (lymphoma)
- Middle
- Aortic arch aneurysm
- Dilated pulmonary artery
- Tracheal lesion
- Posterior
- Esophageal lesions
- Hiatal hernia
- Descending aortic aneurysm
- Paraspinal abscess
Imaging
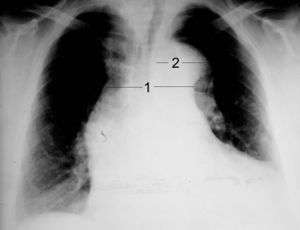
CXR showing widened mediastinum and porminent aortic knob in nontraumatic thoracic aortic dissection
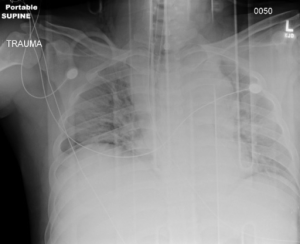
Blunt thoracic aortic injury on CXR showing widened mediastinum
See Also
External Links
References
- Whitten CR, Khan S, Munneke GJ, Grubnic S. A diagnostic approach to mediastinal abnormalities. Radiographics. 2007;27(3):657–671. doi:10.1148/rg.273065136.
- Faiz, O., & Moffat, D. (2002). Anatomy at a glance. Malden, MA: Blackwell Science.
This article is issued from
Wikem.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.